|
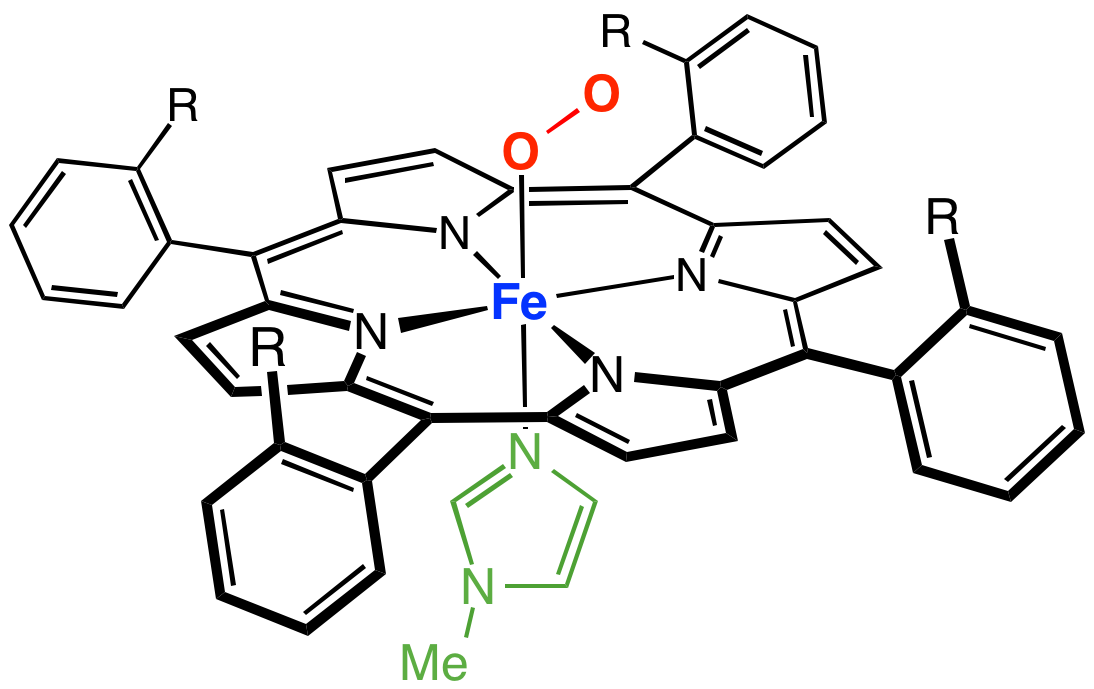
Synzyme
Synzymes are substances with catalytic capabilities. The name synzyme is derived from synthetic enzyme. Current synzymes consist mainly of organic molecules tailored in such a way that they catalyse certain kinds of reactions. Like enzymes, they bind a transition state of a substrate in an active site, and like enzymes they generally obey Michaelis-Menten kinetics. Derivatised proteins: If u(NH3)5sup>3+ is attached to certain histidine residues in a myoglobin protein, myoglobin is no longer a passive oxygen carrier, but gains enzymatic activity of an oxidase. Ascorbic acid is oxidised with molecular oxygen. Antibodies can act as enzymes, then named abzymes, if they are selected against transition state analogues. Abzymes have a low KM, meaning that they readily bind a target molecule, but have low Vmax values, indicating a slow reaction rate. Synzymes from organic molecules: Cyclodextrins are cap structures with a hydrophilic exterior but a hydrophobic interior. If pyridoxal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artificial Enzyme
An artificial enzyme is a synthetic organic molecule or ion that recreates one or more functions of an enzyme. It seeks to deliver catalysis at rates and selectivity observed in naturally occurring enzymes. History Enzyme catalysis of chemical reactions occur with high selectivity and rate. The substrate is activated in a small part of the enzyme's macromolecule called the active site. There, the binding of a substrate close to functional groups in the enzyme causes catalysis by so-called proximity effects. It is possible to create similar catalysts from small molecules by combining substrate-binding with catalytic functional groups. Classically, artificial enzymes bind substrates using receptors such as cyclodextrin, crown ethers, and calixarene. Artificial enzymes based on amino acids or peptides have expanded the field of artificial enzymes or enzyme mimics. For instance, scaffolded histidine residues mimic certain metalloproteins and enzymes such as hemocyanin, tyrosinase, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts are catalytic RNA molecules, called ribozymes. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures. Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the reaction ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histidine
Histidine (symbol His or H) is an essential amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated –NH3+ form under biological conditions), a carboxylic acid group (which is in the deprotonated –COO− form under biological conditions), and an imidazole side chain (which is partially protonated), classifying it as a positively charged amino acid at physiological pH. Initially thought essential only for infants, it has now been shown in longer-term studies to be essential for adults also. It is encoded by the codons CAU and CAC. Histidine was first isolated by Albrecht Kossel and Sven Gustaf Hedin in 1896. It is also a precursor to histamine, a vital inflammatory agent in immune responses. The acyl radical is histidyl. Properties of the imidazole side chain The conjugate acid (protonated form) of the imidazole side chain in histidine has a p''K''a of approximately 6.0. Thus, below a pH of 6, the imidazole ring ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myoglobin
Myoglobin (symbol Mb or MB) is an iron- and oxygen-binding protein found in the cardiac and skeletal muscle tissue of vertebrates in general and in almost all mammals. Myoglobin is distantly related to hemoglobin. Compared to hemoglobin, myoglobin has a higher affinity for oxygen and does not have cooperative binding with oxygen like hemoglobin does. In humans, myoglobin is only found in the bloodstream after muscle injury. (Google books link is the 2008 edition) High concentrations of myoglobin in muscle cells allow organisms to hold their breath for a longer period of time. Diving mammals such as whales and seals have muscles with particularly high abundance of myoglobin. Myoglobin is found in Type I muscle, Type II A, and Type II B; although many texts consider myoglobin not to be found in smooth muscle, this has proved erroneous: there is also myoglobin in smooth muscle cells. Myoglobin was the first protein to have its three-dimensional structure revealed by X-ray crystal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxidase
In biochemistry, an oxidase is an enzyme that catalyzes oxidation-reduction reactions, especially one involving dioxygen (O2) as the electron acceptor. In reactions involving donation of a hydrogen atom, oxygen is reduced to water (H2O) or hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). Some oxidation reactions, such as those involving monoamine oxidase or xanthine oxidase, typically do not involve free molecular oxygen. The oxidases are a subclass of the oxidoreductases. Examples An important example is cytochrome c oxidase, the key enzyme that allows the body to employ oxygen in the generation of energy and the final component of the electron transfer chain. Other examples are: * Glucose oxidase * Monoamine oxidase * Cytochrome P450 oxidase * NADPH oxidase * Xanthine oxidase * L-gulonolactone oxidase * Laccase * Lysyl oxidase * Polyphenol oxidase * Sulfhydryl oxidase. This enzyme oxidises thiol groups. Oxidase test In microbiology, the oxidase test is used as a phenotypic characteristic for t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ascorbic Acid
Vitamin C (also known as ascorbic acid and ascorbate) is a water-soluble vitamin found in citrus and other fruits and vegetables, also sold as a dietary supplement and as a topical 'serum' ingredient to treat melasma (dark pigment spots) and wrinkles on the face. It is used to prevent and treat scurvy. Vitamin C is an essential nutrient involved in the repair of tissue, the formation of collagen, and the enzymatic production of certain neurotransmitters. It is required for the functioning of several enzymes and is important for immune system function. It also functions as an antioxidant. Most animals are able to synthesize their own vitamin C. However, apes (including humans) and monkeys (but not all primates), most bats, some rodents, and certain other animals must acquire it from dietary sources. There is some evidence that regular use of supplements may reduce the duration of the common cold, but it does not appear to prevent infection. It is unclear whether supp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antibodies
An antibody (Ab), also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig), is a large, Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as pathogenic bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique molecule of the pathogen, called an antigen. Each tip of the "Y" of an antibody contains a paratope (analogous to a lock) that is specific for one particular epitope (analogous to a key) on an antigen, allowing these two structures to bind together with precision. Using this binding mechanism, an antibody can ''tag'' a microbe or an infected cell for attack by other parts of the immune system, or can neutralize it directly (for example, by blocking a part of a virus that is essential for its invasion). To allow the immune system to recognize millions of different antigens, the antigen-binding sites at both tips of the antibody come in an equally wide variety. In contrast, the remainder of the antibody is relatively constant. It only occurs in a few vari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abzyme
An abzyme (from antibody and enzyme), also called catmab (from catalytic monoclonal antibody), and most often called catalytic antibody or sometimes catab, is a monoclonal antibody with catalytic activity. Abzymes are usually raised in lab animals immunized against synthetic haptens, but some natural abzymes can be found in normal humans (anti-vasoactive intestinal peptide autoantibodies) and in patients with autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus, where they can bind to and hydrolyze DNA. To date abzymes display only weak, modest catalytic activity and have not proved to be of any practical use.Barrera, G. J., Portillo, R., Mijares, A., Rocafull, M. A., del Castillo, J. R., & Thomas, L. E. (2009). Immunoglobulin A with protease activity secreted in human milk activates PAR-2 receptors, of intestinal epithelial cells HT-29, and promotes beta-defensin-2 expression. Immunology letters, 123(1), 52-59. They are, however, subjects of considerable academic interest. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclodextrins
Cyclodextrins are a family of cyclic oligosaccharides, consisting of a macrocyclic ring of glucose subunits joined by α-1,4 glycosidic bonds. Cyclodextrins are produced from starch by enzymatic conversion. They are used in food, pharmaceutical, drug delivery, and chemical industries, as well as agriculture and environmental engineering. Cyclodextrins are composed of 5 or more α-D-glucopyranoside units linked 1->4, as in amylose (a fragment of starch). Typical cyclodextrins contain a number of glucose monomers ranging from six to eight units in a ring, creating a cone shape: * α (alpha)-cyclodextrin: 6 glucose subunits * β (beta)-cyclodextrin: 7 glucose subunits * γ (gamma)-cyclodextrin: 8 glucose subunits The largest well-characterized cyclodextrin contains 32 1,4-anhydroglucopyranoside units. Poorly-characterized mixtures, containing at least 150-membered cyclic oligosaccharides are also known. Applications Drug delivery Cyclodextrins are ingredients in more than 30 d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyridoxal
Pyridoxal is one form of vitamin B6. Some medically relevant bacteria, such as those in the genera ''Granulicatella'' and ''Abiotrophia'', require pyridoxal for growth. This nutritional requirement can lead to the culture phenomenon of satellite growth. In ''in vitro'' culture, these pyridoxal-dependent bacteria may only grow in areas surrounding colonies of bacteria from other genera ("satellitism") that are capable of producing pyridoxal. Pyridoxal is involved in what is believed to be the most ancient reaction of aerobic metabolism on Earth, about 2.9 billion years ago, a forerunner of the Great Oxidation Event."Protein Domain Structure Uncovers the Origin of Aerobic Metabolism and the Rise of Planetary Oxygen", Gustavo Caetano-Anolles et al., published in Structure; paper available from University of Illinois News Bureau, 2012. See also * Pyridoxal phosphate Pyridoxal phosphate (PLP, pyridoxal 5'-phosphate, P5P), the active form of vitamin B6, is a coenzyme in a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transaminase
Transaminases or aminotransferases are enzymes that catalyze a transamination reaction between an amino acid and an α-keto acid. They are important in the synthesis of amino acids, which form proteins. Function and mechanism An amino acid contains an amine (NH2) group. A keto acid contains a keto (=O) group. In transamination, the NH2 group on one molecule is exchanged with the =O group on the other molecule. The amino acid becomes a keto acid, and the keto acid becomes an amino acid. Most transaminases are protein enzymes. However, some transamination activities of the ribosome have been found to be catalyzed by ribozymes (RNA enzymes). Examples being the hammerhead ribozyme, the VS ribozyme and the hairpin ribozyme. Transaminases require the coenzyme pyridoxal phosphate, which is converted into pyridoxamine in the first half-reaction, when an amino acid is converted into a keto acid. Enzyme-bound pyridoxamine in turn reacts with pyruvate, oxaloacetate, or alpha-ketoglut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |