|
Synonym (taxonomy)
The Botanical and Zoological Codes of nomenclature treat the concept of synonymy differently. * In botanical nomenclature, a synonym is a scientific name that applies to a taxon that (now) goes by a different scientific name. For example, Linnaeus was the first to give a scientific name (under the currently used system of scientific nomenclature) to the Norway spruce, which he called ''Pinus abies''. This name is no longer in use, so it is now a synonym of the current scientific name, '' Picea abies''. * In zoology, moving a species from one genus to another results in a different binomen, but the name is considered an alternative combination rather than a synonym. The concept of synonymy in zoology is reserved for two names at the same rank that refers to a taxon at that rank – for example, the name ''Papilio prorsa'' Linnaeus, 1758 is a junior synonym of ''Papilio levana'' Linnaeus, 1758, being names for different seasonal forms of the species now referred to as ''Araschnia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nomenclature
Nomenclature (, ) is a system of names or terms, or the rules for forming these terms in a particular field of arts or sciences. The principles of naming vary from the relatively informal naming conventions, conventions of everyday speech to the internationally agreed principles, rules and recommendations that govern the formation and use of the specialist terms used in scientific and any other disciplines. Naming "things" is a part of general human communication using words and language: it is an aspect of everyday Taxonomy (general), taxonomy as people distinguish the objects of their experience, together with their similarities and differences, which observers Identification (information), identify, name and wikt:classification, classify. The use of names, as the many different kinds of nouns embedded in different languages, connects nomenclature to theoretical linguistics, while the way humans mentally structure the world in relation to semantics, word meanings and Experience ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bubo (genus)
The American (North and South America) horned owls and the Old World eagle-owls make up the genus ''Bubo'', at least as traditionally described. The genus name ''Bubo'' is Latin for the Eurasian eagle-owl. This genus contains 19 species that are found in many parts of the world. Some of the largest living Strigiformes are in ''Bubo''. Traditionally, only owls with ear-tufts were included in this genus, but that is no longer the case. Taxonomy The genus ''Bubo'' was introduced in 1805 by the French zoologist André Duméril for the horned owls. The type species is the Eurasian eagle-owl. The word ''bubo'' is Latin for the Eurasian eagle owl and was used as the specific epithet for the species by Carl Linnaeus in 1758. A molecular phylogenetic study published in 2019 found that species in the genera ''Scotopelia'' and ''Ketupa'' were embedded within the clade containing members of the genus ''Bubo''. Thus, the genus ''Bubo'' as currently defined is paraphyletic. Systematics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacques Philippe Raymond Draparnaud
Jacques Philippe Raymond Draparnaud (3 June 1772, Montpellier – 2 February 1804) was a French naturalist, malacologist and botanist. Draparnaud is considered the father of malacology in France. He was professor of medicine and pathology at the Faculté de Médecine de Montpellier. Draparnaud understood the breadth of the fauna he studied, as can be seen in a quote from him, in ''Histoire Naturelle des Mollusques'', published in 1805:Au reste, quoique j'aie décrit pour la France seule un bien plus grand nombre d'espèces que Muller et Schroeter n'ent ont fait connoître pour l'Europe entière, et trois fois autant que Geoffroy et Poiret n'en ont observé dans les environs de Paris, je suis convaincu qu'il reste encore en ce genre bien des découvertes à faire. Translation: As for the remainder, even though I have described for France a greater number of species than Müller and Schroeter made known for the whole of Europe, and three times as many as Geoffroy and Poiret obs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petasina Edentula
''Petasina edentula'' is a species of air-breathing land snail, a terrestrial pulmonate gastropod mollusk in the family Hygromiidae Hygromiidae is a taxonomic family of small to medium-sized air-breathing land snails, terrestrial pulmonate gastropod mollusks in the superfamily Helicoidea. Helicellidae Ihering, 1909 Anatomy Some snails in genera within this family create ..., the hairy snails and their allies. References Petasina Gastropods described in 1805 {{Hygromiidae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nomen Oblitum
In zoological nomenclature, a ''nomen oblitum'' (plural: ''nomina oblita''; Latin for "forgotten name") is a disused scientific name which has been declared to be obsolete (figuratively 'forgotten') in favour of another 'protected' name. In its present meaning, the ''nomen oblitum'' came into being with the fourth, 1999, edition of the ''International Code of Zoological Nomenclature''. After 1 January 2000, a scientific name may be formally declared to be a ''nomen oblitum'' when it has been shown not to have been used as a valid name within the scientific community since 1899, and when it is either a senior synonym (there is also a more recent name which applies to the same taxon, and which is in common use) or a homonym (it is spelled the same as another name, which is in common use), and when the preferred junior synonym or homonym has been shown to be in wide use in 50 or more publications in the past few decades. Once a name has formally been declared to be a ''nomen oblitum'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nomen Oblitum
In zoological nomenclature, a ''nomen oblitum'' (plural: ''nomina oblita''; Latin for "forgotten name") is a disused scientific name which has been declared to be obsolete (figuratively 'forgotten') in favour of another 'protected' name. In its present meaning, the ''nomen oblitum'' came into being with the fourth, 1999, edition of the ''International Code of Zoological Nomenclature''. After 1 January 2000, a scientific name may be formally declared to be a ''nomen oblitum'' when it has been shown not to have been used as a valid name within the scientific community since 1899, and when it is either a senior synonym (there is also a more recent name which applies to the same taxon, and which is in common use) or a homonym (it is spelled the same as another name, which is in common use), and when the preferred junior synonym or homonym has been shown to be in wide use in 50 or more publications in the past few decades. Once a name has formally been declared to be a ''nomen oblitum'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
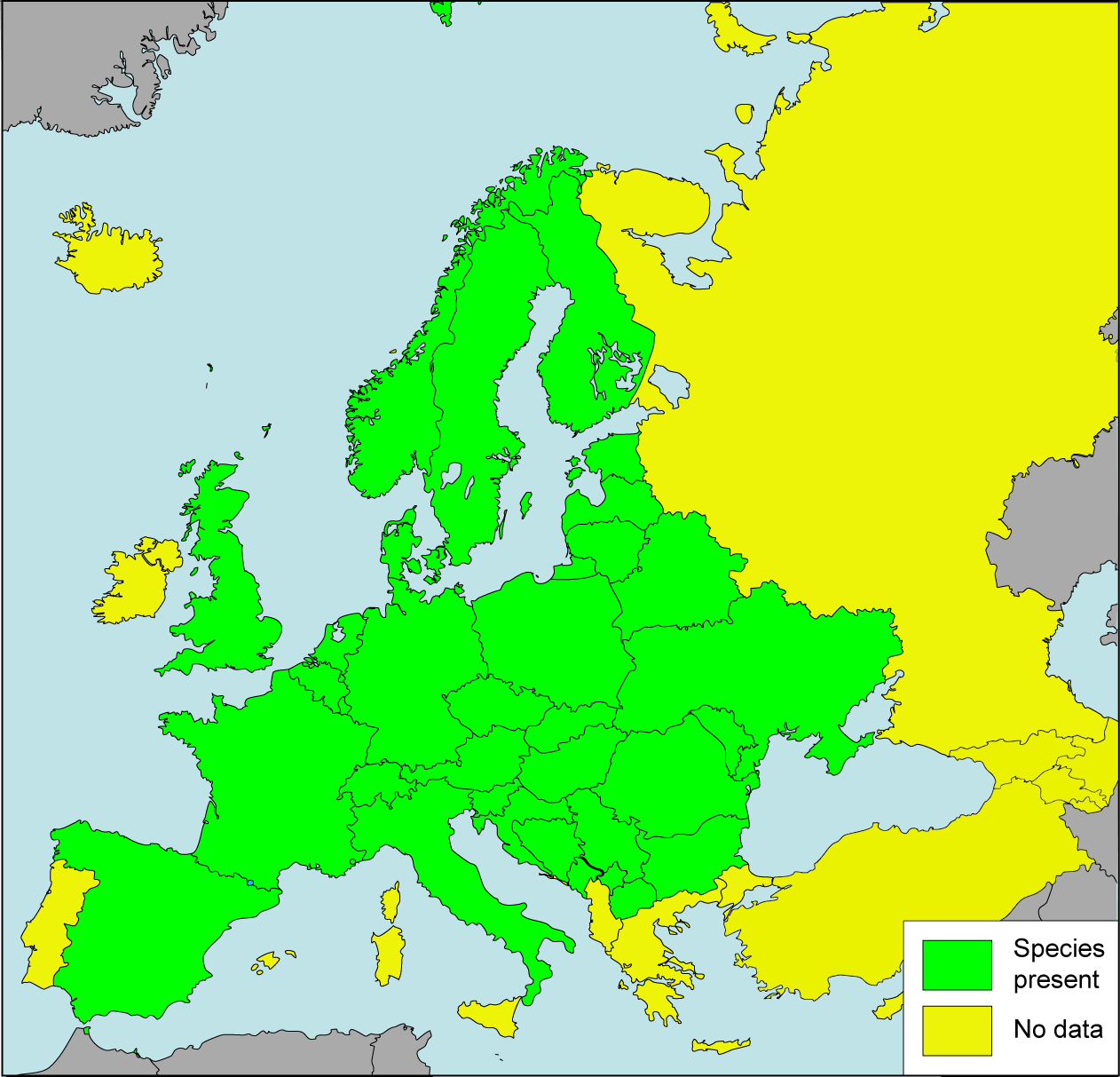
Helix Pomatia
''Helix pomatia'', common names the Roman snail, Burgundy snail, or escargot, is a species of large, edible, air-breathing land snail, a pulmonate gastropod terrestrial mollusc in the family Helicidae.MolluscaBase eds. (2021). MolluscaBase. Helix pomatia Linnaeus, 1758. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at: http://marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=1050286 on 2021-02-19 It is one of Europe's biggest species of land snail. Distribution Distribution of ''H. pomatia'' includes: Southeastern and Central Europe: * Germany – listed as a specially protected species in annex 1 of the Bundesartenschutzverordnung. * Austria * Czech Republic – least concern species (LC): Its conservation status in 2004–2006 is favourable (FV) in the report for the European Commission in accordance with the Habitats Directive. * Poland * Slovakia * Hungary * Romania * In southwestern Bulgaria up to an altitude more than 1600 m. * Northern and central Balkans * Slove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Ord
George Ord, Jr. (March 4, 1781 – January 24, 1866) was an American zoologist who specialized in North American ornithology and mammalogy. Based in part on specimens collected by Lewis and Clark in the North American interior, Ord's article "Zoology of North America''"'' (1815), which was published in the second American edition of William Guthrie's ''Geographical, Historical, and Commercial Grammar'' (Johnson and Warner), has been recognized as the "first systematic zoology of America by an American". Ord (1815) published the first scientific descriptions of Pronghorn antelope (''Antilocapra americana''), Grizzly bear (''Ursus arctos horribilis'')'','' Meadow vole (''Microtus pennsylvanicus''), Bushy-tailed woodrat (''Neotoma cinerea''), Eastern gray squirrel (''Sciurus carolinensis pennsylvanicus''), Columbian ground squirrel (''Urocitellus columbianus''), Black-tailed prairie-dog (''Cynomys ludovicianus''), Bonaparte's gull (''Chroicocephalus philadelphia''), Ring-billed Gull ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
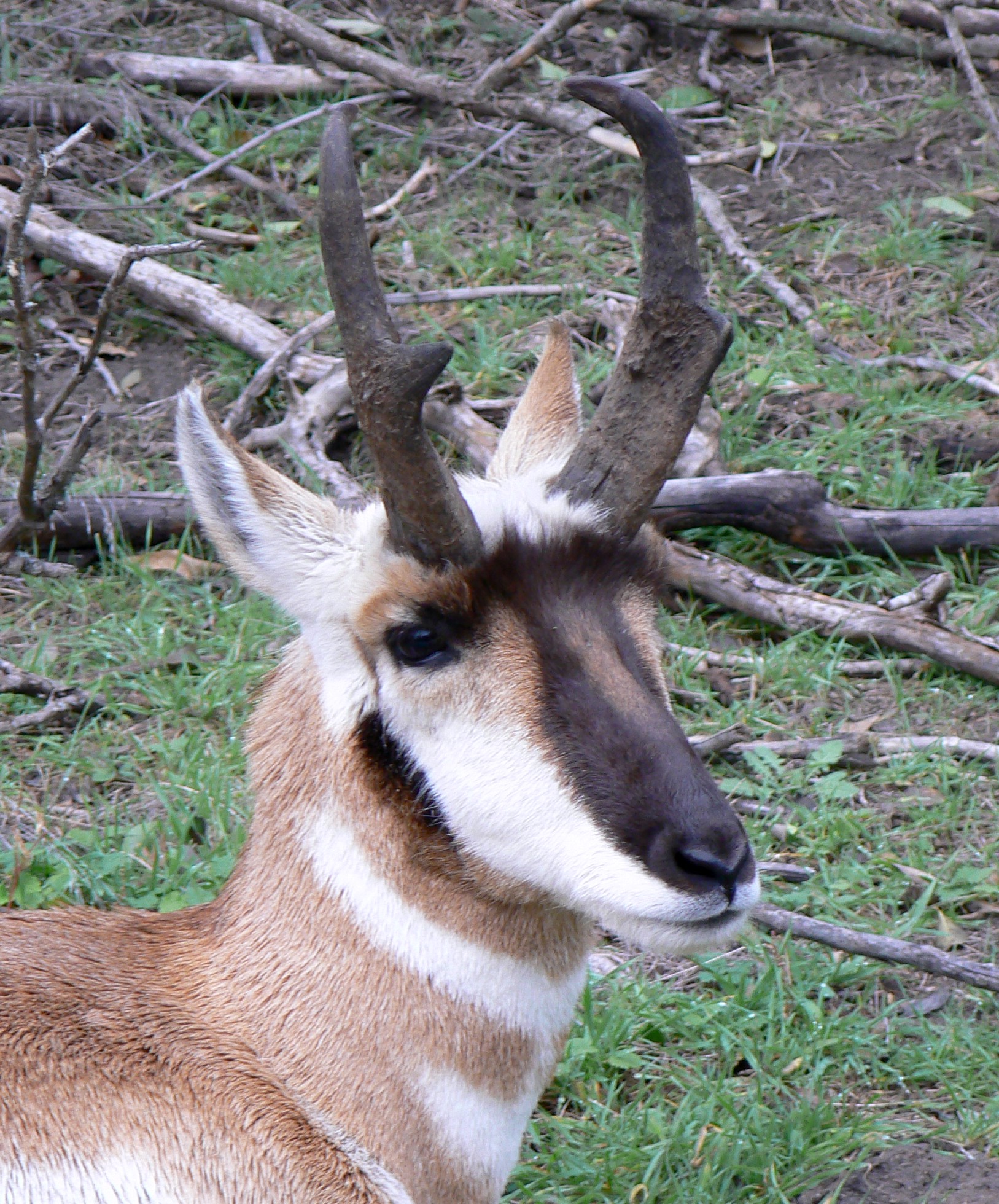
Pronghorn
The pronghorn (, ) (''Antilocapra americana'') is a species of artiodactyl (even-toed, hoofed) mammal indigenous to interior western and central North America. Though not an antelope, it is known colloquially in North America as the American antelope, prong buck, pronghorn antelope and prairie antelope, because it closely resembles the antelopes of the Old World and fills a similar ecological niche due to parallel evolution. It is the only surviving member of the family Antilocapridae. During the Pleistocene epoch, about 11 other antilocaprid species existed in North America.Smithsonian Institution. North American MammalsPronghorn ''Antilocapra americana''/ref> Three other genera (''Capromeryx'', '' Stockoceros'' and ''Tetrameryx'') existed when humans entered North America but are now extinct. As a member of the superfamily Giraffoidea, the pronghorn's closest living relatives are the giraffe and okapi. See Fig. S10 in Supplementary Information. The Giraffoidea are in tu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Edward Gray
John Edward Gray, FRS (12 February 1800 – 7 March 1875) was a British zoologist. He was the elder brother of zoologist George Robert Gray and son of the pharmacologist and botanist Samuel Frederick Gray (1766–1828). The same is used for a zoological name. Gray was keeper of zoology at the British Museum in London from 1840 until Christmas 1874, before the natural history holdings were split off to the Natural History Museum. He published several catalogues of the museum collections that included comprehensive discussions of animal groups and descriptions of new species. He improved the zoological collections to make them amongst the best in the world. Biography Gray was born in Walsall, but his family soon moved to London, where Gray studied medicine. He assisted his father in writing ''The Natural Arrangement of British Plants'' (1821). After being blackballed by the Linnean Society of London, Gray shifted his interest from botany to zoology. He began his zoologica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type Species
In zoological nomenclature, a type species (''species typica'') is the species name with which the name of a genus or subgenus is considered to be permanently taxonomically associated, i.e., the species that contains the biological type specimen(s). Article 67.1 A similar concept is used for suprageneric groups and called a type genus. In botanical nomenclature, these terms have no formal standing under the code of nomenclature, but are sometimes borrowed from zoological nomenclature. In botany, the type of a genus name is a specimen (or, rarely, an illustration) which is also the type of a species name. The species name that has that type can also be referred to as the type of the genus name. Names of genus and family ranks, the various subdivisions of those ranks, and some higher-rank names based on genus names, have such types. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type (biology)
In biology, a type is a particular specimen (or in some cases a group of specimens) of an organism to which the scientific name of that organism is formally attached. In other words, a type is an example that serves to anchor or centralizes the defining features of that particular taxon. In older usage (pre-1900 in botany), a type was a taxon rather than a specimen. A taxon is a scientifically named grouping of organisms with other like organisms, a set that includes some organisms and excludes others, based on a detailed published description (for example a species description) and on the provision of type material, which is usually available to scientists for examination in a major museum research collection, or similar institution. Type specimen According to a precise set of rules laid down in the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN) and the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants (ICN), the scientific name of every taxon is almost al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)


_(2).jpg)
.jpg)