|
Symbolist Movement In Romania
The Symbolist movement in Romania, active during the late 19th and early 20th centuries, marked the development of Culture of Romania, Romanian culture in both Literature of Romania, literature and Art of Romania, visual arts. Bringing the assimilation of France's Symbolism (arts), Symbolism, Decadent movement, Decadence and Parnassianism, it promoted a distinctly urban culture, characterized by cosmopolitanism, Francophilia and endorsement of Westernization, and was generally opposed to either rural themes or Patriotism, patriotic displays in art. Like its Western European counterparts, the movement stood for idealism, Sentimentalism (literature), sentimentalism or exoticism, alongside a noted interest in spirituality and Western esotericism, esotericism, covering on its own the ground between local Romanticism and the emerging modernism of the ''fin de siècle''. Despite such unifying traits, Romanian Symbolism was an Eclecticism, eclectic, factionalized and often self-contradicto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romania
Romania is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern and Southeast Europe. It borders Ukraine to the north and east, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Bulgaria to the south, Moldova to the east, and the Black Sea to the southeast. It has a mainly continental climate, and an area of with a population of 19 million people. Romania is the List of European countries by area, twelfth-largest country in Europe and the List of European Union member states by population, sixth-most populous member state of the European Union. Europe's second-longest river, the Danube, empties into the Danube Delta in the southeast of the country. The Carpathian Mountains cross Romania from the north to the southwest and include Moldoveanu Peak, at an altitude of . Bucharest is the country's Bucharest metropolitan area, largest urban area and Economy of Romania, financial centre. Other major urban centers, urban areas include Cluj-Napoca, Timiș ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
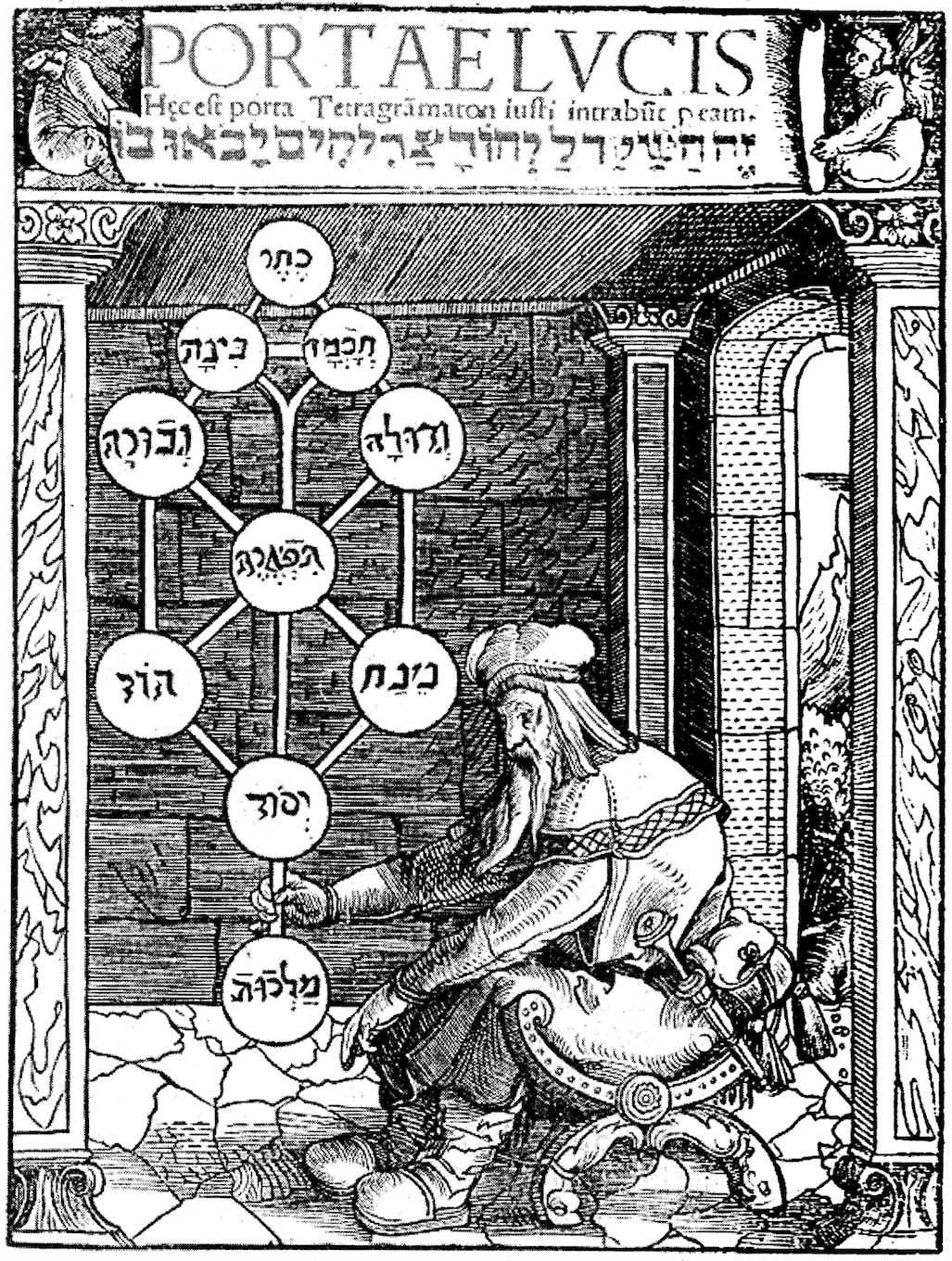
Western Esotericism
Western esotericism, also known as the Western mystery tradition, is a wide range of loosely related ideas and movements that developed within Western society. These ideas and currents are united since they are largely distinct both from orthodox Judeo-Christian, Judeo-Christian religion and Age of Enlightenment rationalism. It has influenced, or contributed to, various forms of Western philosophy, mysticism, Western religions, religion, science, pseudoscience, Western art history, art, Western literature, literature, and Western culture#Music, music. The idea of grouping a wide range of Western traditions and philosophies together under the term ''esotericism'' developed in 17th-century Europe. Various academics have debated numerous definitions of Western esotericism. One view adopts a definition from certain esotericist schools of thought themselves, treating "esotericism" as a perennial philosophy, perennial hidden inner tradition. A second perspective sees esotericism as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neo-romanticism
The term neo-romanticism is used to cover a variety of movements in philosophy, literature, music, painting, and architecture, as well as social movements, that exist after and incorporate elements from the era of Romanticism. It has been used with reference to late-19th-century composers such as Richard Wagner particularly by Carl Dahlhaus who describes his music as "a late flowering of romanticism in a positivist age". He regards it as synonymous with "the age of Wagner", from about 1850 until 1890—the start of the era of modernism, whose leading early representatives were Richard Strauss and Gustav Mahler . It has been applied to writers, painters, and composers who rejected, abandoned, or opposed realism, naturalism, or avant-garde modernism at various points in time from about 1840 down to the present. Late 19th century and early 20th century Neo-romanticism as well as Romanticism is considered in opposition to naturalism—indeed, so far as music is concerned, natur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Art For Art's Sake
Art for art's sake—the usual English rendering of (), a French slogan from the latter half of the 19th century—is a phrase that expresses the philosophy that 'true' art is utterly independent of all social values and utilitarian functions, be they didactic, moral, or political. Such works are sometimes described as '' autotelic'' (from Greek: ''autoteles'', 'complete in itself'), a concept also applied to "inner-directed" or "self-motivated" persons. The phrase is sometimes used commercially. A Latin version of this phrase, (), is used as a motto by Metro-Goldwyn-Mayer film studio, appearing in the film scroll around the roaring head of Leo the Lion in its logo. History The phrase "'" had been used by Parisian intellectuals since the beginning of the 19th century, but it was Théophile Gautier (1811–1872) who first fully articulated its current metaphysical meaning in the prefaces of his 1832 poetry volume ''Albertus'' and 1835 novel ''Mademoiselle de Maupin''. The p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poporanism
Poporanism is a Romanian version of nationalism and populism. The word is derived from ''popor'', meaning "people" in Romanian language, Romanian. Founded by Constantin Stere in the early 1890s, Poporanism is distinguished by its opposition to Marxism, promotion of Suffrage, voting rights for all and its intent to reform the Parliament of Romania, Parliament and the farming system. Regarding Romania's agrarian situation, Poporanists wished to form Cooperative, co-operative farms for the peasants and to remove them from Aristocracy (class), aristocratic control. Unlike Junimea, Junimism, another popular political philosophy, Poporanism focused mainly on expanding the power of the peasants. In a very nationalist manner, it was also a champion of the Romanian language and of maintaining the Romanian spirit. Several famous Romanians, including Ion Agârbiceanu, supported it. Narodism and Constantin Dobrogeanu-Gherea Constantin Dobrogeanu-Gherea, a Romanian political activist, first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Left-wing
Left-wing politics describes the range of Ideology#Political ideologies, political ideologies that support and seek to achieve social equality and egalitarianism, often in opposition to social hierarchy either as a whole or of certain social hierarchies. Left-wing politics typically involve a concern for those in society whom its adherents perceive as disadvantaged relative to others as well as a belief that there are unjustified inequalities that need to be reduced or abolished, through radical means that change the nature of the society they are implemented in. According to emeritus professor of economics Barry Clark, supporters of left-wing politics "claim that human development flourishes when individuals engage in cooperative, mutually respectful relations that can thrive only when excessive differences in status, power, and wealth are eliminated." Within the left–right political spectrum, ''Left'' and ''right-wing politics, Right'' were coined during the French Revolu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sămănătorul
''Sămănătorul'' or ''Semănătorul'' (, Romanian language, Romanian for "The Sower") was a Literary magazine, literary and Political journalism, political magazine published in Romania between 1901 and 1910. Founded by poets Alexandru Vlahuță and George Coșbuc, it is primarily remembered as a tribune for early 20th century traditionalism, Neo-romanticism, neoromanticism and ethnic nationalism. The magazine's ideology, commonly known as ''Sămănătorism'' or ''Semănătorism'', was articulated after 1905, when historian and literary theorist Nicolae Iorga became editor in chief. While its populism, critique of capitalism and emphasis on peasant society separated it from other Conservatism, conservative groups, ''Sămănătorul'' shared views with its main conservative predecessor, the ''Junimea'' society, particularly in expressing reserve toward Westernization. In parallel, its right-wing agenda made it stand in contrast to the Poporanism, Poporanists, a Romanian populist fac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Junimea
''Junimea'' was a Romanian literary society founded in Iași in 1863, through the initiative of several foreign-educated personalities led by Titu Maiorescu, Petre P. Carp, Vasile Pogor, Theodor Rosetti and Iacob Negruzzi. The foremost personality and mentor of the society was Maiorescu, who, through the means of scientific papers and essays, helped establish the basis of the modern Romanian culture. Junimea was the most influential intellectual and political association from Romania in the 19th century. Beginnings In 1863, four years after the unification of Moldavia and Wallachia (''see: United Principalities''), and after the moving of the capital to Bucharest, five enthusiastic young people who had just returned from their studies abroad created in Iaşi a society which wanted to stimulate the cultural life in the city. They chose the name "''Junimea''", a slightly antiquated Romanian word for "Youth". It is notable that four of the founders were part of the Romanian elite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conservatism
Conservatism is a Philosophy of culture, cultural, Social philosophy, social, and political philosophy and ideology that seeks to promote and preserve traditional institutions, Convention (norm), customs, and Value (ethics and social sciences), values. The central tenets of conservatism may vary in relation to the culture and civilization in which it appears. In Western culture, depending on the particular nation, conservatives seek to promote and preserve a range of institutions, such as the nuclear family, organized religion, the military, the nation-state, property rights, rule of law, aristocracy, and monarchy. Conservatives tend to favor institutions and practices that enhance social order and historical continuity. The 18th-century Anglo-Irish statesman Edmund Burke, who opposed the French Revolution but supported the American Revolution, is credited as one of the forefathers of conservative thought in the 1790s along with Savoyard statesman Joseph de Maistre. The first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
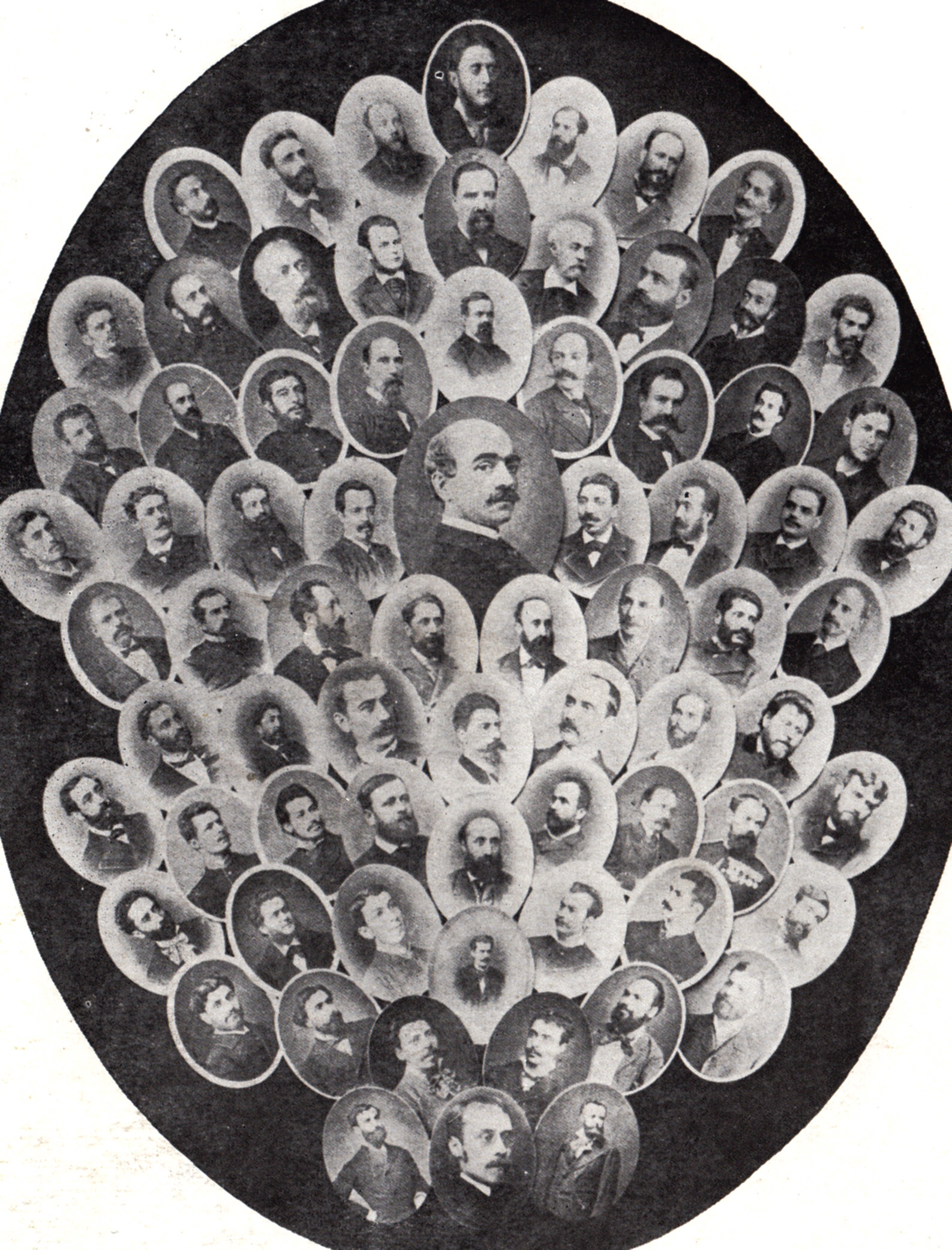
Alexandru Macedonski
Alexandru Macedonski (; also rendered as Al. A. Macedonski, Macedonschi or Macedonsky; 14 March 1854 – 24 November 1920) was a Romanian poet, novelist, dramatist and literary critic, known especially for having promoted French Symbolism (arts), Symbolism in his native country, and for leading the Symbolist movement in Romania, Romanian Symbolist movement during its early decades. A forerunner of local modernist literature, he is the first local author to have used free verse, and claimed by some to have been the first in modern European literature. Within the framework of Literature of Romania, Romanian literature, Macedonski is seen by critics as second only to List of national poets, national poet Mihai Eminescu; as leader of a Cosmopolitanism, cosmopolitan and Aestheticism, aestheticist trend formed around his ''Literatorul'' journal, he was diametrically opposed to the inward-looking traditionalism of Eminescu and his school. Debuting as a Neo-romanticism, Neoromantic in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eclecticism
Eclecticism is a conceptual approach that does not hold rigidly to a single paradigm or set of assumptions, but instead draws upon multiple theories, styles, or ideas to gain complementary insights into a subject, or applies different theories in particular cases. However, this is often without conventions or rules dictating how or which theories were combined. Eclecticism in ethics, philosophy, politics, and religion is often compared to syncretism, but the two concepts differ in their approach to combining elements from different traditions. While syncretism in religion involves the merging or assimilation of several distinct traditions into a new, unified system, eclecticism adopts elements from various systems without necessarily integrating them into a single cohesive framework. This distinction allows for a broader, more inclusive approach in eclecticism, where the selection is based on individual merit or preference rather than an attempt to create a new unified tradition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |