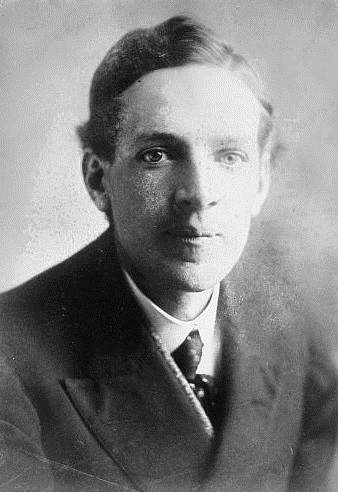|
Sygnały
''Sygnały'' Magazyn (''Signals'' Magazine) was a Polish cultural and social magazine published 1933–1939 in Lwów (Lemberg, today Lviv, Ukraine). It was a leading periodical of the leftist Polish intelligentsia. The journal started as a 12-page monthly and was subsequently published once every two weeks, with editions of up to 32 pages. Sygnały was published in the tabloid format, similar to the ''New York Times'' at about 56x40 cm (22x16 inches). Editors Its editor-in-chief was Karol Kuryluk, and the editorial committee included Tadeusz Banaś, Stanisława Blumenfeld, Halina Górska, Tadeusz Hollender, Anna Kowalska, Andrzej Kurczkowski and Marian Prominski. Polish contributors Among the literary contributors from Poland figured Erwin Axer, Maria Dąbrowska, Jan Kasprowicz, Stanisław Jerzy Lec, Bruno Schulz, Leopold Staff, Julian Tuwim, Debora Vogel and Józef Wittlin. International contributors International literary contributors included Henri Barbusse, A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karol Kuryluk
Karol Kuryluk (27 October 1910 – 9 December 1967) was a Polish journalist, editor, activist, politician and diplomat. In 2002, he was honored by Yad Vashem for saving Jews in the Holocaust. Biography Kuryluk was born on 27 October 1910 in Zbaraż (Zbarazh), a small town in Galicia, the eastern province of the Austro-Hungarian Empire (after World War I part of Poland, today in Ukraine), and died in Budapest. He was the eldest son of Franciszek Kuryluk, a mason, and Łucja, née Pańczyszak. He had four brothers (two of them died in early childhood) and five sisters. In 1930, after finishing high school in his native town, Kuryluk received a small scholarship to study Polish language at the University of Lviv in the former capital of the Austro-Hungarian province of Galicia and a multicultural metropolis (Poles, Jews, Ukrainians, Armenians, Belarusians, Germans and Tatars). He was multilingual (Polish, Ukrainian, Russian and German), and during his studies he supported himsel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halina Górska
Halina Górska (14 May 1898 in Warsaw – 4 June 1942 in Lwów) was a Polish writer and a communist activist. Biography Halina Endelman was the daughter of Zygmund and Czeslawa Endelman. She married Marian Gorski. They had one child born in 1924. She also had a granddaughter, who was born, long after she died Beginning in 1924 Górska became associated with the Lwów literary scene. Her first publication, in 1925, was "Mam mieszkanie" (''I have an apartment''), in the ''Kurier Lwowski''. In 1930 she published the fairy tale "O księciu Gotfrydzie, Rycerzu Gwiazdy Wigilijnej" (''About Prince Gotfried, Knight of the Christmas Star''). For many years she worked for the Lwów radio station, as a host of a special program for young adults. On her initiative, in 1931, the "Związek Błękitnych" (Blue Organization) was created, whose purpose was philanthropic activity. In 1933, together with Tadeusz Hollender and Karol Kuryluk she started the social-cultural monthly "Sygnały" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tadeusz Hollender
Tadeusz Hollender (30 May 1910 – 31 May 1943) was a Polish poet, translator and humorist. During World War II, he wrote satirical articles and poems in underground press, for that he was arrested by the German Gestapo and executed in May in the infamous prison, Pawiak. In 1929-1933 he studied law and Polish philology at the Jan Kazimierz University in Lviv (studies did not finish). In 1929 he made his debut as a poet. Since 1933 he worked in the editorial staff of "Yesterday – Today – Tomorrow". Co-founder, and later editor of "Signals"; he also wrote to "Pins". In 1937, he moved to Warsaw. In 1938 he traveled in Palestine, Greece, Turkey and Romania, sending reports to national magazines. In 1939, again in Lviv, where he became famous for his refusal to sign the servile declaration of Polish writers, welcoming the "reunification" of Ukraine. In 1941, after the occupation of Lviv by the Germans, he returned to Warsaw. He participated in the underground literary life, publishe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henri Barbusse
Henri Barbusse (; 17 May 1873 – 30 August 1935) was a French novelist and a member of the French Communist Party. He was a lifelong friend of Albert Einstein. Life The son of a French father and an English mother, Barbusse was born in Asnières-sur-Seine, France in 1873.Time Magazine, Monday, 9 September 1935 Although he grew up in a small town, he left for Paris in 1889, at age 16. In 1914, at age 41, he enlisted in the French Army and served on the western front during World War I. Invalided out of the army three times, Barbusse would serve in the war for 17 months, until November 1915, when he was permanently moved into a clerical position due to pulmonary damage, exhaustion, and dysentery. On 8 June 1915, he is awarded the Croix de guerre with citation. He was reformed on 1 June 1917. Barbusse first came to fame with the publication of his novel ''Le Feu'' (translated by William Fitzwater Wray as '' Under Fire'') in 1916, which was based on his experiences during Wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
André Malraux
Georges André Malraux ( , ; 3 November 1901 – 23 November 1976) was a French novelist, art theorist, and minister of cultural affairs. Malraux's novel ''La Condition Humaine'' (Man's Fate) (1933) won the Prix Goncourt. He was appointed by President Charles de Gaulle as information minister (1945–46) and subsequently as France's first cultural affairs minister during de Gaulle's presidency (1959–1969). Early years Malraux was born in Paris in 1901, the son of Fernand-Georges Malraux (1875–1930) and Berthe Félicie Lamy (1877–1932). His parents separated in 1905 and eventually divorced. There are suggestions that Malraux's paternal grandfather committed suicide in 1909."Biographie détaillée" , André Malraux Website, accessed 3 September 2010 Malraux was raised by his mother, maternal aun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Von Ossietzky
Carl von Ossietzky (; 3 October 1889 – 4 May 1938) was a German journalist and pacifist. He was the recipient of the 1935 Nobel Peace Prize for his work in exposing the clandestine German re-armament. As editor-in-chief of the magazine ''Die Weltbühne'', Ossietzky published a series of exposés in the late 1920s, detailing Germany's violation of the Treaty of Versailles by rebuilding an air force (the predecessor of the Luftwaffe) and training pilots in the Soviet Union. He was convicted of treason and espionage in 1931 and sentenced to eighteen months in prison but was granted amnesty in December 1932. Ossietzky continued to be a vocal critic against German militarism after the Nazis' rise to power. Following the 1933 Reichstag fire, Ossietzky was again arrested and sent to the Esterwegen concentration camp near Oldenburg. In 1936, he was awarded the 1935 Nobel Peace Prize but was forbidden from travelling to Norway and accepting the prize. After enduring years of mistre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bertrand Russell
Bertrand Arthur William Russell, 3rd Earl Russell, (18 May 1872 – 2 February 1970) was a British mathematician, philosopher, logician, and public intellectual. He had a considerable influence on mathematics, logic, set theory, linguistics, artificial intelligence, cognitive science, computer science and various areas of analytic philosophy, especially philosophy of mathematics, philosophy of language, epistemology, and metaphysics.Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy"Bertrand Russell" 1 May 2003. He was one of the early 20th century's most prominent logicians, and a founder of analytic philosophy, along with his predecessor Gottlob Frege, his friend and colleague G. E. Moore and his student and protégé Ludwig Wittgenstein. Russell with Moore led the British "revolt against idealism". Together with his former teacher A. N. Whitehead, Russell wrote ''Principia Mathematica'', a milestone in the development of classical logic, and a major attempt to reduce the whole ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upton Sinclair
Upton Beall Sinclair Jr. (September 20, 1878 – November 25, 1968) was an American writer, muckraker, political activist and the 1934 Democratic Party nominee for governor of California who wrote nearly 100 books and other works in several genres. Sinclair's work was well known and popular in the first half of the 20th century, and he won the Pulitzer Prize for Fiction in 1943. In 1906, Sinclair acquired particular fame for his classic muck-raking novel, ''The Jungle'', which exposed labor and sanitary conditions in the U.S. meatpacking industry, causing a public uproar that contributed in part to the passage a few months later of the 1906 Pure Food and Drug Act and the Meat Inspection Act. In 1919, he published ''The Brass Check'', a muck-raking exposé of American journalism that publicized the issue of yellow journalism and the limitations of the "free press" in the United States. Four years after publication of ''The Brass Check'', the first code of ethics for journ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Valéry
Ambroise Paul Toussaint Jules Valéry (; 30 October 1871 – 20 July 1945) was a French poet, essayist, and philosopher. In addition to his poetry and fiction (drama and dialogues), his interests included aphorisms on art, history, letters, music, and current events. Valéry was nominated for the Nobel Prize in Literature in 12 different years. Biography Valéry was born to a Corsican father and Genoese-Istrian mother in Sète, a town on the Mediterranean coast of the Hérault, but he was raised in Montpellier, a larger urban center close by. After a traditional Roman Catholic education, he studied law at university and then resided in Paris for most of the remainder of his life, where he was, for a while, part of the circle of Stéphane Mallarmé. In 1900, he married Jeannine Gobillard, a friend of Stéphane Mallarmé's family, who was also a niece of the painter Berthe Morisot. The wedding was a double ceremony in which the bride's cousin, Berthe Morisot's daughter, Ju ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Archipenko
Alexander Porfyrovych Archipenko (also referred to as Olexandr, Oleksandr, or Aleksandr; uk, Олександр Порфирович Архипенко, Romanized: Olexandr Porfyrovych Arkhypenko; February 25, 1964) was a Ukrainian and American avant-garde artist, sculptor, and graphic artist. He was one of the first to apply the principles of Cubism to architecture, analyzing human figure into geometrical forms. Biography Alexander Archipenko was born in Kyiv (Russian Empire, now Ukraine) in 1887, to Porfiry Antonowych Archipenko and Poroskowia Vassylivna Machowa Archipenko; he was the younger brother of Eugene Archipenko. From 1902 to 1905 he attended the Kyiv Art School (KKHU). In 1906 he continued his education in the arts at Serhiy Svetoslavsky (Kyiv), and later that year had an exhibition there with Alexander Bogomazov. He then moved to Moscow where he had a chance to exhibit his work in some group shows. Archipenko moved to Paris in 1908 and quickly enrolled in the É ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |