|
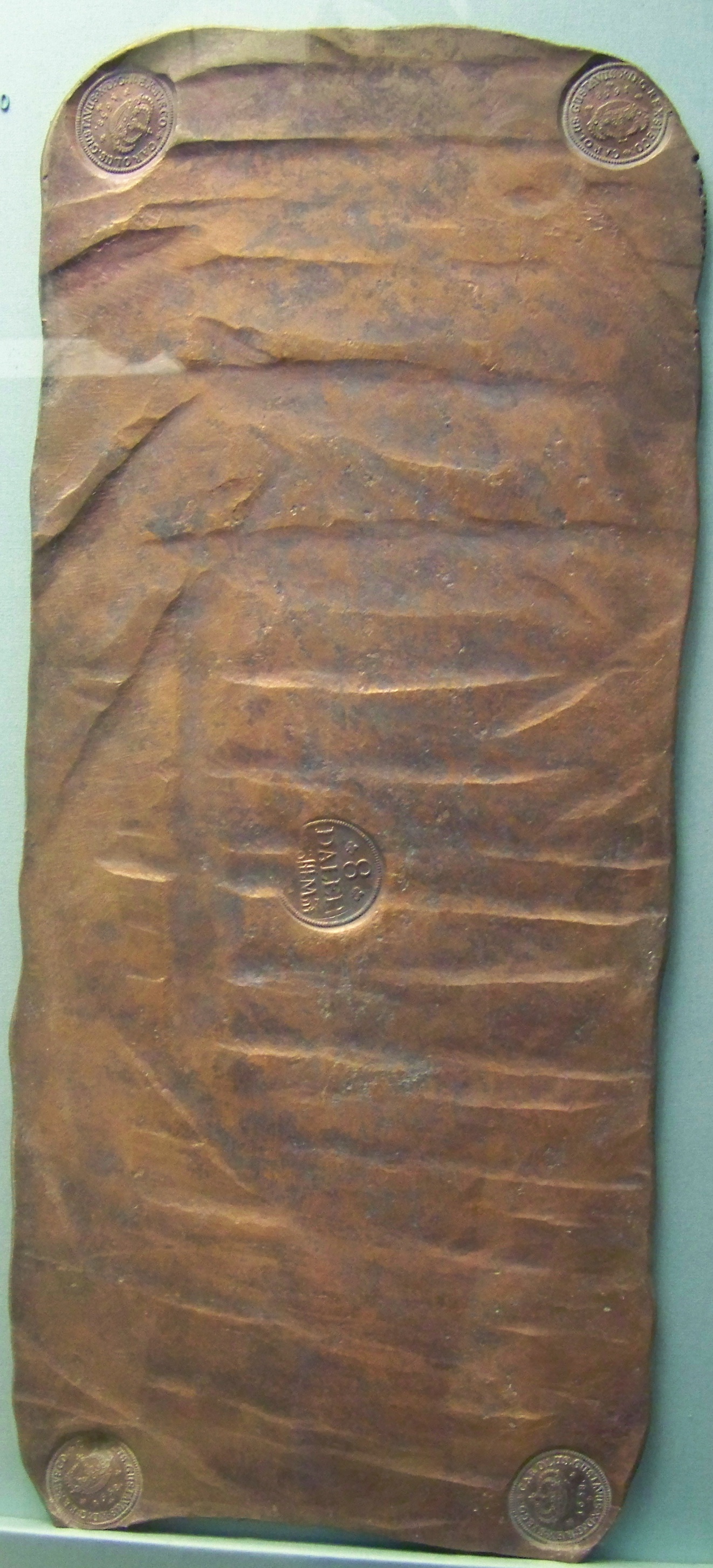
Swedish Penning
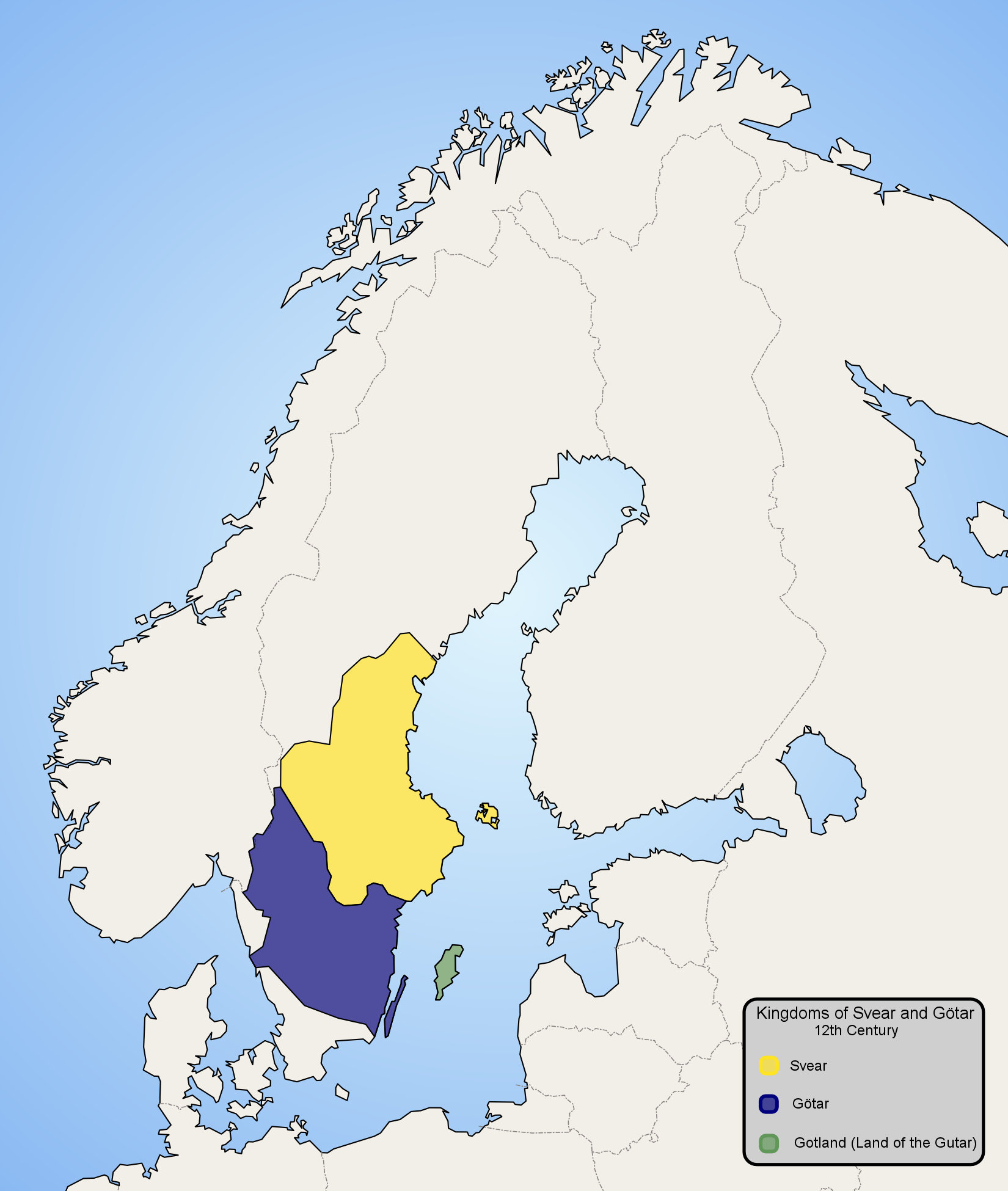
The penning or penny was the Swedish variant of the Norwegian penning that was minted from about 1150 until 1548, and which remained as a unit of account in Sweden until 1777. Originally, penning was first minted in Norway by the kings of Norway, Norwegian king Olaf Tryggvason from the year 995, and was later adapted in both Sweden and Denmark as a coin system. The penning was minted in imitation of the Penny, pennies, pfennig and Denier (coin), deniers issued elsewhere in Europe. However, although based on these coins, the accounting system was distinct, with different systems operating in different regions. All used the ''öre'' (derived from the Latin ''aureus'') which was worth 1/8 of a Mark (money), mark or 3 örtugar. However, in Svealand, one öre was worth 24 penningar, but in Götaland it was worth 48 penningar and 36 in roughly the Diocese of Linköping and on Gotland. Around 1300, by royal command, the Svealand standard became the national standard, except on Gotland. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norwegian Penning
The penning was the dominant currency of the Norwegian coin system in the period 995–1387. Minted in Norway by the kings of Norway from Olaf Tryggvason (995-1000) and up to Olaf Haakonsson (1380-1387), it remained as a unit of account in the kingdom until 1513. It was introduced the year 995 in the image of the Anglo-Saxon coinage, and was the first and oldest currency of Norway. The coin system was later adapted in both Sweden and Denmark. The name lives on in the North Germanic languages in the contracted form of the plural, ''penger/pengar'', which means money. In the old Norwegian weight system it entered into units as ertog, øre and mark. Penning amended standard on several occasions through the Middle Ages. Both coin image, inscriptions, size, weight, and the silver content could vary considerably. The penning was minted in imitation of the pennies, pfennig and deniers issued elsewhere in Europe. However, although based on these coins, the accounting system wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
örtug
Örtug or ortig (Finnish: ''äyrityinen'', ''aurto'' or ''aurtua'') was a Middle Ages, medieval currency unit in Sweden. It was originally minted as a silver coin in 1370 during the reign of king Albert, King of Sweden, Albert of Sweden. The coin weighed about 1.3 grams and consisted of 81% silver. As time passed, the örtug was debasement, debased: during the reign of Eric of Pomerania, the örtug contained 0.88 grams of silver; under Christian I of Denmark, Christian I, 0.7 grams; and in 1534 only 0.54 grams of silver. During the reign of Gustav I of Sweden, Gustav Vasa (1523–1560), the monetary system of Sweden was reformed: an örtug was now subdivided into 12 pennings, not 8 as before, while still valued as one third of an öre. Örtug coins were struck during the years 1523–1534; 1535–1540 in Stockholm; 1528–1531 in Västerås and 1589–1589 in Stockholm and Uppsala. Production ceased after another monetary reform in 1776. The örtug is also used as the official n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Currencies Of Europe
There are 27 currencies currently used in the 50 countries of Europe. All '' de facto'' present currencies in Europe, and an incomplete list of the preceding currency, are listed here. In Europe, the most commonly used currency is the euro (used by 26 countries); any country entering the European Union (EU) is expected to join the eurozone when they meet the five convergence criteria. Denmark is the only EU member state which has been granted an exemption from using the euro. Czechia, Hungary, Poland, Romania and Sweden have not adopted the Euro either, although unlike Denmark, they have not formally opted out; instead, they fail to meet the ERM II (Exchange Rate Mechanism) which results in the non-use of the Euro. For countries which hope to join the eurozone, there are five guidelines that need to be followed, grouped in the Maastricht criteria. The United Kingdom's currency, sterling, is rated fourth on Investopedia's list of the top 8 most tradable currencies, and that it i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Denier
The denier (; , , ; . d.) or penny was a medieval coin which takes its name from the Frankish empire, Frankish coin first issued in the late seventh century; in English it is sometimes referred to as a silver penny. Its appearance represents the end of gold coinage, which, at the start of Frankish rule, had either been Roman (Byzantine) or "pseudo-imperial" (minted by the Franks in imitation of Byzantine coinage). Silver would be the basis for Frankish coinage from then on. The ''denier'' was minted in France, Cyprus and parts of the Italian peninsula for the whole of the Middle Ages, in states such as the Patriarchate of Aquileia (state), patriarchate of Aquileia, the Kingdom of Sicily, the Republic of Genoa, the Republic of Siena, Kingdom of Cyprus, and the crusader state Kingdom of Jerusalem, among others. History Coin Around 755, amid the Carolingian Renaissance, Carolingian Reforms, Pepin the Short introduced a new French currency, currency system which was eventually a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penny
A penny is a coin (: pennies) or a unit of currency (: pence) in various countries. Borrowed from the Carolingian denarius (hence its former abbreviation d.), it is usually the smallest denomination within a currency system. At present, it is the formal name of the British penny ( p) and the '' de facto'' name of the American one-cent coin (abbr. ¢). ''Penny'' is also the informal name of the cent unit of account in Canada, although the production of one-cent coins was ended in 2012. The name ''penny'' is also used in reference to various historical currencies, also derived from the Carolingian system, such as the French denier and the German pfennig. It may also be informally used to refer to any similar smallest-denomination coin, such as the euro cent or Chinese fen. The Carolingian penny was originally a 0.940-fine silver coin, weighing pound. It was adopted by Offa of Mercia and other English kings and remained the principal currency in Europe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swedish Language
Swedish ( ) is a North Germanic languages, North Germanic language from the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family, spoken predominantly in Sweden and parts of Finland. It has at least 10 million native speakers, making it the Germanic_languages#Statistics, fourth most spoken Germanic language, and the first among its type in the Nordic countries overall. Swedish, like the other North Germanic languages, Nordic languages, is a descendant of Old Norse, the common language of the Germanic peoples living in Scandinavia during the Viking Age. It is largely mutually intelligible with Norwegian language, Norwegian and Danish language, Danish, although the degree of mutual intelligibility is dependent on the dialect and accent of the speaker. Standard Swedish, spoken by most Swedes, is the national language that evolved from the Central Swedish dialects in the 19th century, and was well established by the beginning of the 20th century. While distinct regional Variety ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norwegian Language
Norwegian ( ) is a North Germanic language from the Indo-European language family spoken mainly in Norway, where it is an official language. Along with Swedish and Danish, Norwegian forms a dialect continuum of more or less mutually intelligible local and regional varieties; some Norwegian and Swedish dialects, in particular, are very close. These Scandinavian languages, together with Faroese and Icelandic as well as some extinct languages, constitute the North Germanic languages. Faroese and Icelandic are not mutually intelligible with Norwegian in their spoken form because continental Scandinavian has diverged from them. While the two Germanic languages with the greatest numbers of speakers, English and German, have close similarities with Norwegian, neither is mutually intelligible with it. Norwegian is a descendant of Old Norse, the common language of the Germanic peoples living in Scandinavia during the Viking Age. Today there are two official forms of ''written'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swedish Riksdaler
The Svenska riksdaler () was the name of a Swedish coin first minted in 1604. Between 1777 and 1873, it was the currency of Sweden. The daler, like the dollar,''National Geographic''. June 2002. p. 1. ''Ask Us''. was named after the German Thaler. The similarly named Reichsthaler, rijksdaalder, and rigsdaler were used in Germany and Austria-Hungary, the Netherlands, and Denmark-Norway, respectively. ''Riksdaler'' is still used as a colloquial term for krona, Sweden's modern-day currency. History Penning accounting system The ''daler'' was introduced in 1534. It was initially intended for international use and was divided into 4 marks and then a mark is further subdivided into 8 öre and then an öre is further subdivided into 24 pennings. In 1604, the name was changed to ''riksdaler'' ("daler of the realm", cf. Reichsthaler). In 1609, the riksdaler rose to a value of 6 mark when the other Swedish coins were debased but the riksdaler remained constant. From 1624, dale ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gotland
Gotland (; ; ''Gutland'' in Gutnish), also historically spelled Gottland or Gothland (), is Sweden's largest island. It is also a Provinces of Sweden, province/Counties of Sweden, county (Swedish län), Municipalities of Sweden, municipality, and List of dioceses, deaneries and parishes of the Church of Sweden, diocese. The province includes the islands of Fårö and Gotska Sandön to the north, as well as the Karlsö Islands (Lilla Karlsö, Lilla and Stora Karlsö, Stora) to the west. The population is 61,023 (2024) of which about 23,600 live in Visby, the main town. Outside Visby, there are minor settlements and a mainly rural population. The island of Gotland and the other areas of the province of Gotland make up less than one percent of Sweden's total land area. The county formed by the archipelago is the second smallest by area and is the least populated in Sweden. In spite of the small size due to its narrow width, the driving distance between the furthermost points of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diocese Of Linköping
The Diocese of Linköping () is a diocese within the Church of Sweden administering the Östergötland County, the north eastern part of Jönköping County and the northern part of Kalmar County. It comprises nine deaneries subdivided into 176 parishes with a total of 443,000 members. The diocese's largest parish is Motala. The Diocese of Linköping has a rank directly below the Archdiocese of Uppsala of the Church of Sweden. The current bishop is Marika Markovits. The diocesan territory comprises Östergötland County and parts of Jönköping and Kalmar County. It has 212 parishes with a total of 443,000 members. Pre-Reformation history The diocese originally included Småland, Östergötland, the Islands of Gotland and Öland. The district of Värend in Småland was taken from Linköping and formed into the Diocese of Växjö about 1160. From 990 to 1100 the Diocese of Skara embraced the whole country of the Goths ( Gauthiod); it was then divided between those of Skar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Götaland
Götaland (; also '' Gothia'', ''Gothland'', ''Gothenland'' or ''Gautland'') is one of three lands of Sweden and comprises ten provinces. Geographically it is located in the south of Sweden, bounded to the north by Svealand, with the deep woods of Tiveden, Tylöskog and Kolmården marking the border. Götaland once consisted of petty kingdoms, and their inhabitants were called ''Gautar'' in Old Norse. However, the term mainly referred to the population of modern Västergötland. It is agreed that these were the same as the ''Geats'', the people of the hero Beowulf in England's national epic, ''Beowulf''. The modern state of Sweden started forming when some provinces of Götaland gradually became more and more politically intertwined with those of Svealand. This process can be traced back to at least the 10th century, and would continue for several hundred years. Other parts of modern Götaland were at that time either Danish or Norwegian. The province of Småland, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Svealand
Svealand (), or Swealand, is the historical core region of Sweden. It is located in south-central Sweden and is one of the three historical lands of Sweden, bounded to the north by Norrland and to the south by Götaland. Deep forests, Tiveden, Tylöskog, and Kolmården, separated Svealand from Götaland. Historically, its inhabitants were called , from which is derived the English 'Swedes'. Svealand consists of the capital region Mälardalen in the east, Roslagen in the north-east, the former mining district Bergslagen in the center, and Dalarna and Värmland in the west. It includes an extensive archipelago of thousands of small islands in Södermanland and Uppland and has lakeshores on the four largest lakes in the country. In the interior, there are several ski resorts in the southern parts of the Scandinavian Mountains. Two large rivers run through Svealand. Klarälven originates in Norway and enters lake Vänern through Värmland, whereas Dalälven runs from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |