|
Swa Saw Ke
Mingyi Swa Saw Ke ( my, မင်းကြီး စွာစော်ကဲ, ; also spelled စွာစောကဲ, Minkyiswasawke or Swasawke; 1330–1400) was king of Ava from 1367 to 1400. He reestablished central authority in Upper Myanmar (Burma) for the first time since the fall of the Pagan Empire in the 1280s. He essentially founded the Ava Kingdom that would dominate Upper Burma for the next two centuries. When he was elected by the ministers to succeed King Thado Minbya, Swa took over a small kingdom barely three years old, and one that still faced several external and internal threats. In the north, he successfully fought off the Maw raids into Upper Burma, a longstanding problem since the waning days of Sagaing and Pinya kingdoms. He maintained friendly relations with Lan Na in the east, and Arakan in the west, placing his nominees on the Arakense throne between 1373 and 1385. In the south, he brought semi-independent kingdoms of Toungoo (Taungoo) and Prome ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Burmese Monarchs
This is a list of the monarchs of Burma (Myanmar), covering the monarchs of all the major kingdoms that existed in the present day Burma (Myanmar). Although Burmese chronicles, Burmese chronicle tradition maintains that various monarchies of Burma (Mon people, Mon, Bamar people, Burman, Rakhine people, Arakanese), began in the 9th century Common Era, BCE, historically verified data date back only to 1044 CE at the accession of Anawrahta of Pagan dynasty, Pagan. The farther away the data are from 1044, the less verifiable they are. For example, the founding of the city of Pagan (Bagan) in the 9th century is verifiable–although the accuracy of the actual date, given in the Chronicles as 849, remains in question–but the founding of early Pagan dynasty, given as the 2nd century, is not.Harvey 1925: 364 For early kingdoms, see List of early and legendary monarchs of Burma. The reign dates follow the latest available dates as discussed in each section. Early kingdoms * See List of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
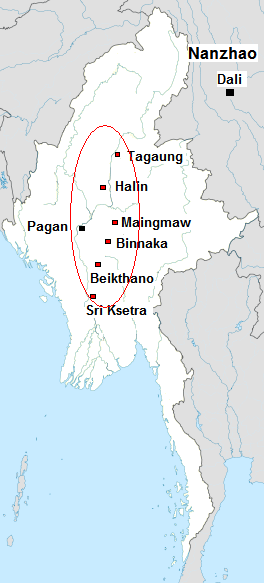
Burmese Calendar
The Burmese calendar ( my, မြန်မာသက္ကရာဇ်, , or , ; Burmese Era (BE) or Myanmar Era (ME)) is a lunisolar calendar in which the months are based on lunar months and years are based on sidereal years. The calendar is largely based on an older version of the Hindu calendar, though unlike the Indian systems, it employs a version of the Metonic cycle. The calendar therefore has to reconcile the sidereal years of the Hindu calendar with the Metonic cycle's near tropical years by adding intercalary months and days at ''irregular'' intervals. The calendar has been used continuously in various Burmese states since its purported launch in 640 CE in the Sri Ksetra Kingdom, also called the ''Pyu era''. It was also used as the official calendar in other mainland Southeast Asian kingdoms of Arakan, Lan Na, Xishuangbanna, Lan Xang, Siam, and Cambodia down to the late 19th century. Today, the calendar is used in Myanmar as one of the two official calendars alo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toungoo
Taungoo (, ''Tauñngu myoú''; ; also spelled Toungoo) is a district-level city in the Bago Region of Myanmar, 220 km from Yangon, towards the north-eastern end of the division, with mountain ranges to the east and west. The main industry is in forestry products, with teak and other hardwoods extracted from the mountains. The city is known for its areca palms, to the extent that a Burmese proverb for unexpected good fortune is equated to a " betel lover winning a trip to Taungoo". The city is famous in Burmese history for the Toungoo dynasty which ruled the country for over 200 years between the 16th and 18th centuries. Taungoo was the capital of Burma in 1510–1539 and 1551–1552. Kaytumadi new city (new city of Taungoo) is the central command of the southern command division region of Armed Forces (''Tatmadaw''). Hanthawaddy United Football Club is based in Taungoo. Names The classical Pali name of Taungoo is Ketumadi (ကေတုမဒီ;), which translates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Launggyet Kingdom
Launggyet ( my, လောင်းကြက်မြို့ ) is a former capital of the Launggyet Dynasty of Arakan from 1237/1251 to 1430. It is also last capital of Laymro Kingdom. The former capital site is located a few miles northwest of Mrauk U, Rakhine State, Myanmar. The Arakanese chronicle ''Rakhine Razawin Thit ''Rakhine Razawin Thit'' ( my, ရခိုင် ရာဇဝင်သစ်, , Arakanese pronunciation: ) is a Burmese chronicle covering the history of Arakan from time immemorial to the First Anglo-Burmese War (1824–1826). The author was ...'' gives the foundation date as 22 April 1251.(Sandamala Linkara Vol. 1 1997: 171): The city was founded on Saturday, 2nd waxing of Nayon 613 ME (Saturday, 22 April 1251.) Some Arakanese chronicles give the foundation date as 1237 CE.Harvey 1925: 371 History Launggret City was founded in 1237 by King Alawmaphyu after relocating from Nareinjara Toungoo and ended in 1430. References Bibliography * * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lan Na
The Lan Na Kingdom ( nod, , , "Kingdom of a Million Rice Fields"; th, อาณาจักรล้านนา, , ), also known as Lannathai, and most commonly called Lanna or Lanna Kingdom, was an Indianized state centered in present-day Northern Thailand from the 13th to 18th centuries. The cultural development of the Northern Thai people had begun long before as successive kingdoms preceded Lan Na. As a continuation of the kingdom of Ngoenyang, Lan Na emerged strong enough in the 15th century to rival the Ayutthaya Kingdom, with whom wars were fought. However, the Lan Na Kingdom was weakened and became a tributary state of the Taungoo Dynasty in 1558. Lan Na was ruled by successive vassal kings, though some enjoyed autonomy. The Burmese rule gradually withdrew but then resumed as the new Konbaung Dynasty expanded its influence. In 1775, Lan Na chiefs left the Burmese control to join Siam, leading to the Burmese–Siamese War (1775–76). Following the retreat of the Bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sagaing Kingdom
The Sagaing Kingdom ( my, စစ်ကိုင်း နေပြည်တော်, ) was a small kingdom ruled by a junior branch of the Myinsaing dynasty from 1315 to 1365. Originally the northern province of Sagaing of the Pinya Kingdom, it became de facto independent after Prince Saw Yun successfully fought for autonomy from his father King Thihathu in 1315–17. Sagaing formally seceded from Pinya in 1325 after Thihathu's death. The northern petty state stayed independent for the next four decades mainly due to Pinya's internal divisions. Sagaing itself was full of palace intrigues, and the court led by Nanda Pakyan came to control a string of weak monarchs from the mid-1330s to the 1350s. In the 1350s, Princess Soe Min successfully repaired Sagaing's long-strained relationship with Pinya in order to defend against the northern Shan state of Maw. Sagaing bore the brunt of repeated Maw invasions of Upper Myanmar (Burma) (1356–64). Maw forces broke through in 1364, sack ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mong Mao
Mong may refer to: People *A proposed original name for the Hmong people, based on the main group, the Mong community * Bob Mong (), American journalist and academic administrator *Henry Mong (), American surgeon and Presbyterian missionary *Mong Monichariya (), Cambodian judge *Mong Thongdee (born ), Thai origami artist *William Mong (1927–2010), Hong Kong businessman *William V. Mong (1875–1940), American film actor, screenwriter and director *MC Mong, stage name of South Korean hip hop artist Shin Dong-hyun (born 1979) Places *Mong, Punjab, a town and Union Council in Pakistan *Mong, Azad Kashmir, a town in Kashmir, Pakistan *Mong Circle, a hereditary chiefdom in Bangladesh Other uses * Mong or Hmong language * Mong, the ISO 15924 code for Mongolian script The classical or traditional Mongolian script, also known as the , was the first writing system created specifically for the Mongolian language, and was the most widespread until the introduction of Cyrillic in 194 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pagan Empire
The Kingdom of Pagan ( my, ပုဂံခေတ်, , ; also known as the Pagan Dynasty and the Pagan Empire; also the Bagan Dynasty or Bagan Empire) was the first Burmese kingdom to unify the regions that would later constitute modern-day Myanmar. Pagan's 250-year rule over the Irrawaddy valley and its periphery laid the foundation for the ascent of Burmese language and culture, the spread of Bamar ethnicity in Upper Myanmar, and the growth of Theravada Buddhism in Myanmar and in mainland Southeast Asia.Lieberman 2003: 88–123 The kingdom grew out of a small 9th-century settlement at Pagan (present-day Bagan) by the Mranma/Burmans, who had recently entered the Irrawaddy valley from the Kingdom of Nanzhao. Over the next two hundred years, the small principality gradually grew to absorb its surrounding regions until the 1050s and 1060s when King Anawrahta founded the Pagan Empire, for the first time unifying under one polity the Irrawaddy valley and its periphery. By ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upper Myanmar
Upper Myanmar ( my, အထက်မြန်မာပြည်, also called Upper Burma) is a geographic region of Myanmar, traditionally encompassing Mandalay and its periphery (modern Mandalay, Sagaing, Magway Regions), or more broadly speaking, Kachin and Shan States. In the Burmese language, people originating from Upper Myanmar are typically called ''a-nya tha'' (), whereas those from Lower Myanmar are called ''auk tha'' (). The term "upper Burma" was first used by the British to refer to the central and northern area of what is now modern day Myanmar. After the Second Anglo-Burmese War of 1852, Lower Myanmar was annexed by the British Empire, while Upper Myanmar remained independent under the Burmese Empire until the Third Anglo-Burmese War of 1885. Upper Myanmar was also known as encompassing "Burma proper" and the Kingdom of Ava. Historically, Upper Myanmar was predominantly Bamar (whereas Lower Myanmar was historically Mon-speaking until the early 19th century), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burmese Royal Titles
Burmese royal titles are the royal styles that were in use by the Burmese monarchy until the disintegration of the last Burmese monarchy, the Konbaung dynasty, in 1885. These titles were exclusively used by those of royal lineage (; ; ), or more formally, Maha Zi Maha Thwei (). Titles and rank in the Konbaung dynasty King Kings in Burma assumed a distinctive regnal name and title, usually a combination of Pali and Sanskrit, upon ascending to the throne. The King was known by a variety of titles, including the following: *''Hpondawgyi (Hlathaw) Hpaya'' ( ) *''Ashin Hpaya'' ( ) *''Shwe Nan Shin Hpaya'' () *''Ekarit Min Myat'' () *''Shin Bayin'' () *''Athet U San Paing Than Ashin'' (, lit. "Lord of the life, head, and hair of all beings") *''Shwe Nan Shwe Pyatthat Thahkin'' (, lit. "Master Lord of the Golden Palace and Golden Spired Roofs") - used in the Taungoo and Konbaung dynasties *''Hkamedaw'' ( , lit. "royal father") - by his children (the princes and princesses) *''Dagadaw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theravada Buddhism
''Theravāda'' () ( si, ථේරවාදය, my, ထေရဝါဒ, th, เถรวาท, km, ថេរវាទ, lo, ເຖຣະວາດ, pi, , ) is the most commonly accepted name of Buddhism's oldest existing school. The school's adherents, termed Theravādins, have preserved their version of Gautama Buddha's teaching or ''Dharma (Buddhism), Buddha Dhamma'' in the Pāli Canon for over two millennia. The Pāli Canon is the most complete Buddhist canon surviving in a Indo-Aryan languages, classical Indian language, Pali, Pāli, which serves as the school's sacred language and ''lingua franca''.Crosby, Kate (2013), ''Theravada Buddhism: Continuity, Diversity, and Identity'', p. 2. In contrast to ''Mahāyāna'' and ''Vajrayāna'', Theravāda tends to be conservative in matters of doctrine (''pariyatti'') and monastic discipline (''vinaya''). One element of this conservatism is the fact that Theravāda rejects the authenticity of the Mahayana sutras (which appeared c. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ava Kingdom
The Kingdom of Ava ( my, အင်းဝခေတ်, ) was the dominant kingdom that ruled upper Burma (Myanmar) from 1364 to 1555. Founded in 1365, the kingdom was the successor state to the petty kingdoms of Myinsaing, Pinya and Sagaing that had ruled central Burma since the collapse of the Pagan Empire in the late 13th century. Like the small kingdoms that preceded it, Ava may have been led by Bamarised Shan kings who claimed descent from the kings of Pagan.Htin Aung 1967: 84–103Phayre 1883: 63–75 Scholars debate that the Shan ethnicity of Avan kings comes from mistranslation, particularly from a record of the Avan kings' ancestors ruling a Shan village in central Burma prior to their rise or prominence.Aung-Thwin 2010: 881–901 History The kingdom was founded by Thado Minbya in 1364Coedès 1968: 227 following the collapse of the Sagaing and Pinya Kingdoms due to raids by the Shan States to the north. In its first years of existence, Ava, which viewed itself as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |