|
Surprise Locomotive
The ''Surprise'' was a nineteenth-century British railway locomotive. It became notorious after its boiler exploded and killed several crew members during unsuccessful trials in the early days of the Lickey Incline. William Church, the ''Surprise'''s inventor, is mainly remembered for his typesetting machine, but also experimented with locomotives. His 0-2-2 well tank locomotive, exemplified by the ''Surprise,'' featured horizontal outside cylinders at the rear. Dr Church had invented an expanding mandrel for fixing boiler tubes, and it was the first tank engine to have a multitube boiler. It used piston valves and eccentric motion. The ''Surprise'' (named ''Victoria'' at the time) began trial runs as a ballast locomotive on the London and Birmingham Railway in January 1838, then transferred to the Grand Junction Railway. Notwithstanding its having reportedly achieved a speed of , it was never particularly successful. On 10 November 1840, when the Birmingham and Gloucester ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland. The United Kingdom includes the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland, and many smaller islands within the British Isles. Northern Ireland shares a land border with the Republic of Ireland; otherwise, the United Kingdom is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, the North Sea, the English Channel, the Celtic Sea and the Irish Sea. The total area of the United Kingdom is , with an estimated 2020 population of more than 67 million people. The United Kingdom has evolved from a series of annexations, unions and separations of constituent countries over several hundred years. The Treaty of Union between the Kingdom of England (which included Wales, annexed in 1542) and the Kingdom of Scotland in 170 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bromsgrove Scaife Rutherford 1840 Refurbished
Bromsgrove is a town in Worcestershire, England, about northeast of Worcester and southwest of Birmingham city centre. It had a population of 29,237 in 2001 (39,644 in the wider Bromsgrove/Catshill urban area). Bromsgrove is the main town in the larger Bromsgrove District. In the Middle Ages it was a small market town; primarily producing cloth through the early modern period. In the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries it became a major centre for nail making. History Anglo-Saxon Bromsgrove is first documented in the early 9th century as Bremesgraf. An ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' entry for 909 AD mentions a ''Bremesburh''; possibly also referring to Bromsgrove. The Domesday Book of 1086 references ''Bremesgrave''. The name means ''Bremi’s grove''. The grove element may refer to the supply of wood to Droitwich for the salt pans. During the Anglo-Saxon period the Bromsgrove area had a woodland economy; including hunting, maintenance of haies and pig farming. At the time of Ed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Individual Locomotives Of Great Britain
An individual is that which exists as a distinct entity. Individuality (or self-hood) is the state or quality of being an individual; particularly (in the case of humans) of being a person unique from other people and possessing one's own needs or goals, rights and responsibilities. The concept of an individual features in diverse fields, including biology, law, and philosophy. Etymology From the 15th century and earlier (and also today within the fields of statistics and metaphysics) ''individual'' meant " indivisible", typically describing any numerically singular thing, but sometimes meaning "a person". From the 17th century on, ''individual'' has indicated separateness, as in individualism. Law Although individuality and individualism are commonly considered to mature with age/time and experience/wealth, a sane adult human being is usually considered by the state as an "individual person" in law, even if the person denies individual culpability ("I followed instruct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Steam Locomotives
Articles about steam locomotive A steam locomotive is a locomotive that provides the force to move itself and other vehicles by means of the expansion of steam. It is fuelled by burning combustible material (usually coal, oil or, rarely, wood) to heat water in the locomot ...s (and locomotive types/classes) built before 1840. Of these, see info-box immediately below for the most well-known individual steam locomotives built before 1830 (listed by year). {{early-steam-locos Steam locomotives 1 Rolling stock innovations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swansea Vale Railway
The Swansea Vale Railway (SVR) was a railway line connecting the port of Swansea in South Wales to industries and coalfields along the River Tawe on the northern margin of Swansea, by taking over a tramroad in 1846. It was extended to Brynamman in 1868. Passengers were carried from 1860, and a loop line through Morriston was built. The company was profitable but it was always short of capital, and it looked for a larger company to buy it out. The Midland Railway did so in 1874 when it leased the network, and it absorbed it in 1876. The Midland Railway used the line to get access to Swansea, which it had long sought. After 1923 the Midland's successor transferred the through traffic to another route. Road omnibus services abstracted much of the local passenger business, and only anthracite traffic kept the line going. When that industry declined the railway mineral traffic followed, and from 1965 closures set in. Parts of the network continued for a time, but by 1983 the entire li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
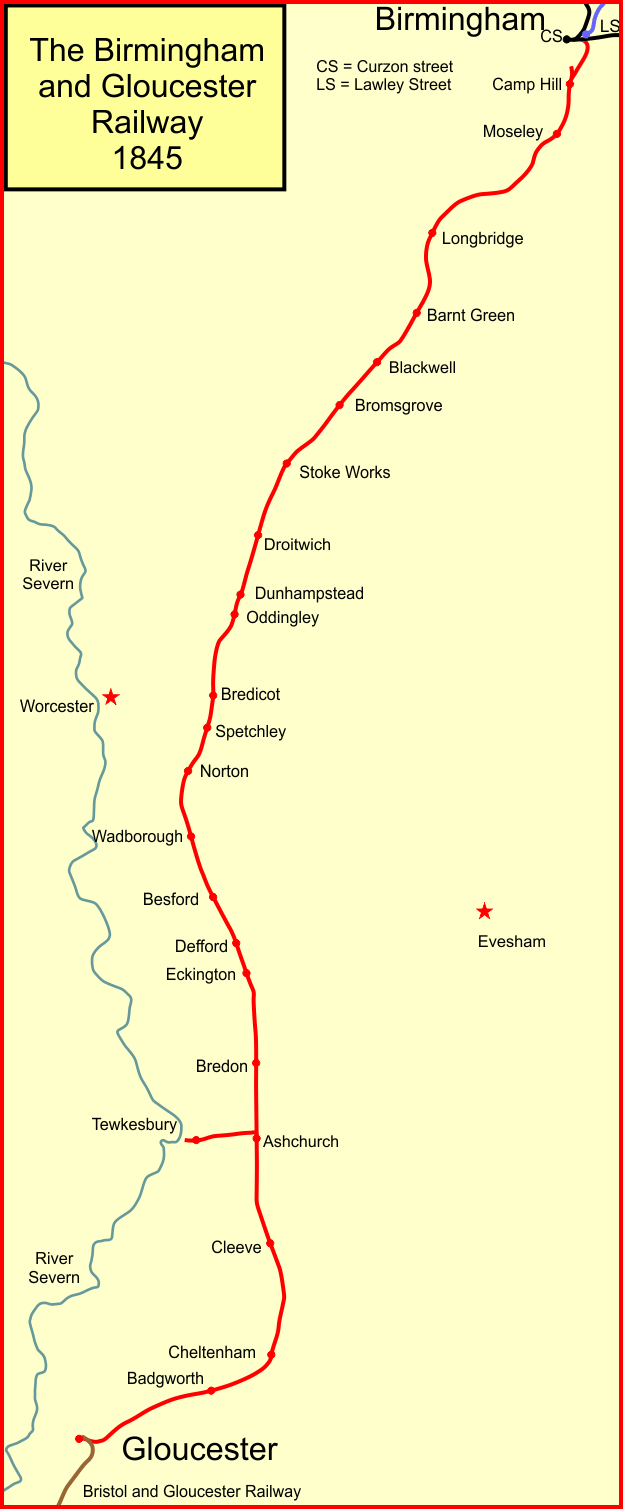
Camp Hill Railway Station
Camp Hill railway station was a railway station in Camp Hill, Birmingham. History It was opened by the Birmingham and Gloucester Railway (B&GR) in 1840 and was its first terminus. Subsequently, the line extended to join the London and Birmingham Railway to the latter's Curzon Street terminus. From 1854, New Street opened but because of the necessity for a reversal many trains from the Midland Railway line from Derby continued to use Camp Hill until New Street was extended in the 1880s. From 1867 to 1904, it was known as Camp Hill and Balsall Heath. The station had a goods yard, which is now the site of a retail estate. It formed part of the Camp Hill Line, closed to passenger traffic on 27 January 1941. Incidents On 26 June 1845, a B&GR passenger train from Gloucester, hauled by one of the company's Philadelphia, United States-built engines, ran into a slow-moving "heavy, powerful" goods engine which was crossing the line from a siding, via a diamond crossing A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norris Locomotive Works
The Norris Locomotive Works was a steam locomotive manufacturing company based in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, that produced nearly one thousand railroad engines between 1832 and 1866. It was the dominant American locomotive producer during most of that period, as well as the first major exporter of American locomotives, selling its popular 4-2-0 engines to railways in Europe and building the first locomotive used in South America. History Origin The company was started in 1832 as the American Steam Carriage Company by William Norris (1802-1867) and Major Stephen H. Long (1784-1864), a military topographical engineer and explorer. The two men had experimented with steam engine building for years and, as early as 1829, designed a locomotive to burn anthracite coal. Norris and Long also built an engine called the ''Black Hawk'', which performed with partial success on the Boston and Providence Railroad and the Philadelphia and Columbia Railroad in the early 1830s. Major Long la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
St John The Baptist Church, Bromsgrove
The Church of St John the Baptist, Bromsgrove is a Grade I listed parish church in the Church of England in Bromsgrove. History The church belonged to a particularly large Parish during the early Norman period. Henry III arranged for the church and lands to be granted to Worcester Priory in order to support the remembrance of his father King John I, who is buried there. The Priory then ran the manor and collected rents and other income until the dissolution, at which point the lands transferred to the new Dean and Chapter. In February 1643, Charles I ordered that Bromsgrove's vicar John Hall be removed from his post as a rebel. Disputes about the vicarage continued through the Interregnum and Protectorate. John Hall was vicar again until 1652. His successor John Spilsbury, previously a fellow of Magdalen College, was unpopular with some of Bromsgrove's churchgoers, who attempted unsuccessfully to eject him. Spilsbury was removed after the Restoration of the Monarchy in 1660, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bromsgrove Railway Station
Bromsgrove railway station serves the town of Bromsgrove in Worcestershire, England. It is located at the foot of the two-mile Lickey Incline which ascends at a gradient of 1-in-37.7 towards Barnt Green on the line between Birmingham and Worcester. Bromsgrove is managed by West Midlands Railway. The current station opened on 12 July 2016, replacing an older station located slightly to the north. History The station opened as part of the Birmingham and Gloucester Railway (later part of the Midland Railway) on 24 June 1840.Jowett's Railway Centres Volume 1, Alan Jowett (PSL, 1993) On 10 November of that year, an experimental steam locomotive named 'Surprise' burst its boiler at the station, killing the driver, Thomas Scaife, and fireman, Joseph Rutherford (some authorities say the incident happened on the Lickey Incline but this is due to an erroneous early report in the ''Worcestershire Chronicle'' which was later corrected.). They are buried in Bromsgrove churchyard. In June 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birmingham And Gloucester Railway
The Birmingham and Gloucester Railway (B&GR) was the first name of the railway linking the cities in its name and of the company which pioneered and developed it; the line opened in stages in 1840, using a terminus at Camp Hill in Birmingham. It linked with the Bristol and Gloucester Railway in Gloucester, but at first that company's line was broad gauge, and Gloucester was a point of the necessary but inconvenient transhipment of goods and passengers onto gauge that became the national standard. Nearly all of the original main line remains active as a "trunk" route, also known as an arterial route or line. Its main line incorporated the Lickey Incline of track climbing a 1-in-37 (2.7%) gradient, northbound (and descending in the other). The climb was a challenge or impediment for many of the heaviest loads and weaker engines during the era of steam traction. Having attracted its own patronage, capital and accomplished fully functional transformation and employment of land, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Junction Railway
The Grand Junction Railway (GJR) was an early railway company in the United Kingdom, which existed between 1833 and 1846 when it was amalgamated with other railways to form the London and North Western Railway. The line built by the company was the first trunk railway to be completed in England, and arguably the world's first long-distance railway with steam traction. The lines which comprised the GJR now form the central section of the West Coast Main Line. History The Grand Junction Railway Company was established in the second half of 1832 by the consolidation of two rival companies: the Birmingham and Liverpool Railway Company and the Liverpool and Birmingham Railway Company. Authorised by Parliament on 6 May 1833 and designed by George Stephenson and Joseph Locke, the Grand Junction Railway opened for business on 4 July 1837, running for from Birmingham through Wolverhampton (via Perry Barr and Bescot), Stafford, Crewe, and Warrington, then via the existing Warrington ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Locomotive
A locomotive or engine is a rail transport vehicle that provides the Power (physics), motive power for a train. If a locomotive is capable of carrying a payload, it is usually rather referred to as a multiple unit, Motor coach (rail), motor coach, railcar or power car; the use of these self-propelled vehicles is increasingly common for passenger trains, but rare for freight (see CargoSprinter). Traditionally, locomotives pulled trains from the front. However, Push-pull train, push-pull operation has become common, where the train may have a locomotive (or locomotives) at the front, at the rear, or at each end. Most recently railroads have begun adopting DPU or distributed power. The front may have one or two locomotives followed by a mid-train locomotive that is controlled remotely from the lead unit. __TOC__ Etymology The word ''locomotive'' originates from the Latin language, Latin 'from a place', Ablative case, ablative of 'place', and the Medieval Latin 'causing mot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)