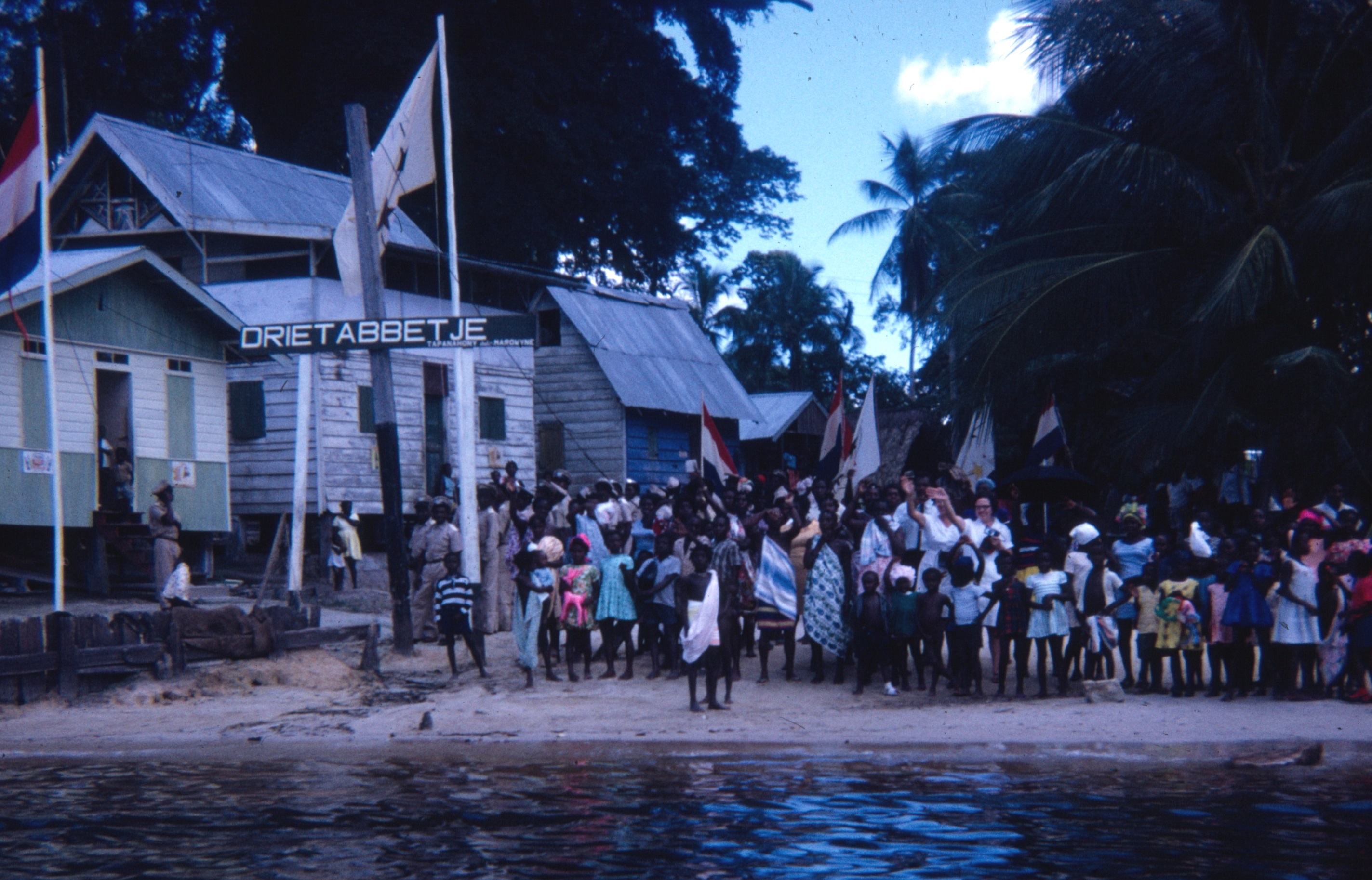|
Surinamese Language
Sranan Tongo (also Sranantongo "Surinamese tongue," Sranan, Surinaams, Surinamese, Surinamese Creole) is an English-based creole language that is spoken as a ''lingua franca'' by approximately 550,000 people in Suriname. Developed originally among slaves from West Africa and English colonists, its use as a ''lingua franca'' expanded after the Dutch took over the colony in 1667, and 85% of the vocabulary comes from English and Dutch. It also became the common language among the indigenous peoples and the indentured laborers imported by the Dutch; these groups included speakers of Javanese, Sarnami Hindustani, Saramaccan, and varieties of Chinese. Origins The Sranan Tongo words for "to know" and "small children" are and (respectively derived from Portuguese and ). The Portuguese were the first European explorers of the West African coast. A trading pidgin language developed between them and Africans, and later explorers, including the English, also used this creole. Based ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suriname
Suriname (; srn, Sranankondre or ), officially the Republic of Suriname ( nl, Republiek Suriname , srn, Ripolik fu Sranan), is a country on the northeastern Atlantic coast of South America. It is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the north, French Guiana to the east, Guyana to the west, and Brazil to the south. At just under , it is the smallest sovereign state in South America. It has a population of approximately , dominated by descendants from the slaves and labourers brought in from Africa and Asia by the Dutch Empire and Republic. Most of the people live by the country's (north) coast, in and around its capital and largest city, Paramaribo. It is also one of the least densely populated countries on Earth. Situated slightly north of the equator, Suriname is a tropical country dominated by rainforests. Its extensive tree cover is vital to the country's efforts to mitigate climate change and maintain carbon negativity. A developing country with a relatively high ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer-mediated Communication
Computer-mediated communication (CMC) is defined as any human communication that occurs through the use of two or more electronic devices. While the term has traditionally referred to those communications that occur via computer-mediated formats (e.g., instant messaging, email, chat rooms, online forums, social network services), it has also been applied to other forms of text-based interaction such as text messaging. Research on CMC focuses largely on the social effects of different computer-supported communication technologies. Many recent studies involve Internet-based social networking supported by social software. Forms Computer-mediated communication can be broken down into two forms: synchronous and asynchronous. Synchronous computer-mediated communication refers to communication that occurs in real-time. All parties are engaged in the communication simultaneously; however, they are not necessarily all in the same location. Examples of synchronous communicatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Celestine Raalte
Celestine Raalte (12 November 1948) is a writer and performance artist from Suriname living in the Netherlands. She was born in the Commewijne District. During the 1970s, she was a member of the Surinamese women's group Sranan S'ma Abi Wan Oso. Her work first appeared in the 1981 anthology ''Tide tamara, Dichten voor het volk''. Raalte moved to Utrecht in 1986. In 1989, she published her first collection of poems ''Akwenda / Streven''. That was followed by ''Ma Awitya'' in 1997. Both works also appeared in Dutch. Celestine Raalte has published both in Dutch as Sranan Tongo Sranan Tongo (also Sranantongo "Surinamese tongue," Sranan, Surinaams, Surinamese, Surinamese Creole) is an English-based creole language that is spoken as a ''lingua franca'' by approximately 550,000 people in Suriname. Developed originally amo .... Her work has also appeared in various magazines and in the 1995 anthology ''Spiegel van de Surinaamse poëzie''. Raalte also wrote a play ''Witte de Witlaan 25 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
André Pakosie
André R.M. Pakosie (born 25 May 1955) is a Surinamese historian, poet, Ndyuka activist and ''Edebukuman'' (head of experts) of the Afaka script. Pakosie comes from a family of herbal doctors and is himself a phytotherapist in the Surinamese Maroon tradition. He founded the Sabanapeti health center and the Maroon Institute Sabanapeti Foundation. In the 1980s he had to leave Suriname because of the Suriname Guerrilla War and settled in the Netherlands. He has received honors from the Queen of the Netherlands and the President of Suriname. He was the founder of "Maroon Day", celebrating the Maroon struggle for freedom. In his teens he rejected Christianity as he felt it hostile to pre-Christian traditions. In addition to being a herbalist and activist he is also a poet and historian. He is noted for his writing concerning the Maroon peoples. André Pakosie has written more than 30 books as of 1972, in the following languages: Dutch, Sranan Tongo and the Ndyuka or Okanisi lang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eugène Drenthe
Eugène Constantijn Donders Drenthe (12 December 1925 in Laarwijk, Surinam – 30 March 2009 in Rotterdam, Netherlands) was a prominent Surinamese poet and playwright. Biography Drenthe was born in Laarwijk, Surinam, as an illegitimate child of Louise Drenthe and the local police officer who was also the parish clerk. Drenthe used to talk about it as if it was normal. This down-to-earth attitude also characterized his plays which showed the normal life of the Creoles in Suriname. The plays were successful, ''Geheim in het gezin'' was performed 57 times in Suriname. Drenthe produced 25 plays in all, which include ''Rudy'' (1959), ''Kedjaman'' (1969) and ''Djomp abra'' (1977). From 1968 onwards, the plays of Drenthe were being performed outside of Suriname. First to Curaçao, Aruba, and Puerto Rico, and later to the Netherlands. Drenthe was one of the founding members and first president of NAKS. NAKS was founded in 1948 as a social and cultural organization which promotes Afro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Anthem
A national anthem is a patriotic musical composition symbolizing and evoking eulogies of the history and traditions of a country or nation. The majority of national anthems are marches or hymns in style. American, Central Asian, and European nations tend towards more ornate and operatic pieces, while those in the Middle East, Oceania, Africa, and the Caribbean use a more simplistic fanfare. Some countries that are devolved into multiple constituent states have their own official musical compositions for them (such as with the United Kingdom, Russia, and the former Soviet Union); their constituencies' songs are sometimes referred to as national anthems even though they are not sovereign states. History In the early modern period, some European monarchies adopted royal anthems. Some of these anthems have survived into current use. " God Save the King/Queen", first performed in 1619, remains the royal anthem of the United Kingdom and the Commonwealth realms. , adopte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
God Zij Met Ons Suriname
"" () or "" ("Rise, countrymen" in Sranan Tongo) is the national anthem of Suriname. It has two verses: the first in Dutch and the second in Sranan Tongo. History The original version of the anthem was written by Cornelis Atses Hoekstra in 1893 and based on a 1876 melody by Johannes Corstianus de Puy. It was written to replace the old anthem " Wien Neêrlands Bloed". The anthem did not have an official status. In 1959, the Government of Suriname appointed Surinamese writer Henri Frans de Ziel to add a stanza about the unity of the country to Hoekstra's anthem. De Ziel was concerned about the negative nuance in the original and started to transform the anthem into a positive message. He combined this with a poem he wrote in Sranan Tongo on the death of Ronald Elwin Kappel. His anthem was unanimously approved by the Government of Suriname on 7 December 1959. De Ziel originally used a melody by Surinamese composer Johannes Helstone Johannes Helstone, born ''Nicodemus Johannes H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henri Frans De Ziel
Henri Frans de Ziel (15 January 1916 – 3 February 1975), working under the pen name of Trefossa, was a neoromantic writer in Dutch and Sranan Tongo from Suriname. He is best known for the Sranan Tongo stanzas of Suriname's National Anthem. Biography He was an educator and lived in the Netherlands from 1953 to 1956. Upon his return to Suriname he was part of the editorial staff of the magazines ''Tongoni'' (1958-1959) and ''Soela'' (1962-1964). He also served briefly as the director-librarian of Suriname's Cultural Centre (Cultureel Centrum Suriname (CCS)). He subsequently returned to the Netherlands to work on the publication of Johannes King's memoirs. Trefossa wrote primarily about the beauty of his native country, Suriname, especially as a source of peace to the restless mind. He influenced many writers in Suriname, including Corly Verlooghen, Eugène Rellum, Johanna Schouten-Elsenhout and Michaël Slory, but the depth and subtlety of his verse remain almost unique. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moravian Church
, image = AgnusDeiWindow.jpg , imagewidth = 250px , caption = Church emblem featuring the Agnus Dei.Stained glass at the Rights Chapel of Trinity Moravian Church, Winston-Salem, North Carolina, United States , main_classification = Proto-Protestant , orientation = Hussite ( Bohemian) with Pietist Lutheran influences , founder = followers of Jan Hus and Petr Chelčický , founded_date = 1457 , founded_place = Bohemia , congregations = 1,000+ , number_of_followers = 1,112,120 (2016) , website = The Moravian Church ( cs, Moravská církev), or the Moravian Brethren, formally the (Latin: "Unity of the Brethren"), is one of the oldest Protestant denominations in Christianity, dating back to the Bohemian Reformation of the 15th century and the Unity of the Brethren ( cs, Jednota bratrská, links=no) founded in the Kingdom of Bohemia, sixty years before Luther's Reformation. The church's heritage can be traced to 1457 in Bohemian Crown territory, including its c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drietabbetje
Diitabiki (Sranan Tongo: ''Dritabiki'', Dutch: ''Drietabbetje'') is a Ndyuka village in the Sipaliwini District of Suriname. Diitabiki is the residence of the gaanman of the Ndyuka people, since 1950, and the location of the oracle. Name Both the Ndyuka and Sranan Tongo name for the village translates to "three islands," with the word ''tabiki'' meaning "island" in both languages. While ''drie'' indeed also translates as "three" in the Dutch language, the word ''tabbetje'' is a homophonic translation of the Ndyuka word. History The Ndyuka people are of African descent, and were shipped as slaves to Suriname in the 17-18th century to work on Dutch-owned colonial plantations. The escaped slaves moved into the rainforest, and banded together. There were frequent clashes between the colonists and the Ndyuka, however in 1760, a peace treaty was signed granting the Ndyuka autonomy. From 1761 onwards, the Ndyuka gradually moved southwards in order to protected themselves from th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johannes King
Johannes King (born: Adiri circa 1830 - 24 October 1898), was the first Maroon missionary, and the first important writer in Sranan Tongo. King belonged to the Matawai tribe, and performed his missionary activities for the Moravian Church. Biography Adiri was born as a son of granman (paramount chief) Kodjo of the Matawai, near the plantations of Haarlem and Maho in Suriname. Adiri was born and raised in a completely illiterate society. In 1852, Adiri moved to Maripaston. During this period, he fell ill, and the illness lasted many years. In 1855, Adiri started to receive visions: a strange god pointed at an alien religion, told him to go to the city, and be baptized. Adiri went to Paramaribo, where he met van Calker, who was the preacher at the Moravian Church. He didn't stay long, and returned to his village soon after. Adiri returned in 1860, and had taught himself to read by then. He had used an A.B.C. (alphabet) book, and '' Singiboekoe'', a book with psalms from the Moravian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brigham Young University
Brigham Young University (BYU, sometimes referred to colloquially as The Y) is a private research university in Provo, Utah. It was founded in 1875 by religious leader Brigham Young and is sponsored by the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (LDS Church). BYU offers a variety of academic programs including those in the liberal arts, engineering, agriculture, management, physical and mathematical sciences, nursing, and law. It has 186 undergraduate majors, 64 master's programs, and 26 doctoral programs. It is broadly organized into 11 colleges or schools at its main Provo campus, with some colleges and divisions defining their own admission standards. The university also administers two satellite campuses, one in Jerusalem and one in Salt Lake City, while its parent organization the Church Educational System (CES) sponsors sister schools in Hawaii and Idaho. The university is accredited by the Northwest Commission on Colleges and Universities. Almost all BYU student ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |