|
Suraqah Al-Bariqi
Suraqah al-Bariqi ( ar, سراقة بن مرداس البارقي; died 698) was a companion of Muhammad and was a member of the Tribe Bariq. He was an Arab from Bareq in Arabian Peninsula, which was then part of the Umayyad caliphate. He is considered one of the greatest poets. Much of his poetry revolves around the philosophy of life. Some consider his poems to be a great representation of his life story. He started writing poetry when he was young. He is well known for his sharp intelligence and wittiness. Among the topics he discussed were courage, the philosophy of life, and the description of battles. His great talent brought him very close to many leaders of his time. He praised those leaders and kings. His powerful and honest poetic style earned great popularity in his time. He was a contemporary of the great trio, Akhtal, Farazdaq, and Jarir, whose names stand out so pre-eminently in the list of the Umayyad bards that all contemporary poets are thrown into the shade. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bareq
Bareq ( ar, بارق; also transliterated as '), is one of the governorates of Asir in the north-west of the region, north of Abha. It occupies a distinct location midway between Tihama and Asir, above sea level. With an estimated population of 75,351, it is well off economically; the city has grown rapidly and has many government services and public utilities available. It is one of Asir's winter resorts because of its natural environment and mild winter weather. Bareq has valleys. History Bareq was founded in 220 AD. (citation?) Bareq is part of the territory which is historically known as the "Yemen", which dates back to the second millennium BC and was inhabited by an immigrant tribe from Marib in Yemen called Bariq belonging to the ancient tribe of Al-Azd that has many clans linked to it. Known before the advent of Islam as ''Diyār Bāriq'', it was traversed by the ancient trade route from Yemen to Mecca and the Levant, known as the winter and summer journeys. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saba'a
The Sabaeans or Sabeans (Sabaean:, ; ar, ٱلسَّبَئِيُّوْن, ''as-Sabaʾiyyūn''; he, סְבָאִים, Səḇāʾīm) were an ancient group of South Arabians. They spoke the Sabaean language, one of the Old South Arabian languages.Stuart Munro-Hay, ''Aksum: An African Civilization of Late Antiquity'', 1991. They founded the kingdom of Sabaʾ ( ar, سَبَأ, links=no) in modern-day Yemen, Quran 27:6-93 Quran 34:15-18 which was believed to be the biblical land of Sheba and "the oldest and most important of the South Arabian kingdoms". The exact date of the foundation of Sabaʾ is a point of disagreement among scholars. Kenneth Kitchen dates the kingdom to between 1200 BCE and 275 CE, with its capital at Maʾrib, in what is now Yemen.Kenneth A. Kitchen ''The World of "Ancient Arabia" Series''. Documentation for Ancient Arabia. Part I. Chronological Framework and Historical Sources p.110 On the other hand, Israel Finkelstein and Neil Asher Silberman believe that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
621 Births
__NOTOC__ Year 621 ( DCXXI) was a common year starting on Thursday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. The denomination 621 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Byzantine Empire * Emperor Heraclius concludes a peace agreement (in exchange for an annual tribute) with the Avars on the Balkan Peninsula, giving him a free hand to assemble Byzantine forces in Asia Minor, for non-military expenditure against the Persian Empire. * The city of Málaga, in southern Spain in the province of Spania, is conquered by the Visigoths. Europe * King Sisebut dies after a 9-year reign and is succeeded by his son Reccared II (just a child).Roger Collins, "Visigothic Spain 409–711", p. 76 Reccared is placed on the throne by the Visigothic nobility, but dies after two months. Suintila, his half-uncle and regent, becomes king of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Year Of Birth Unknown
A year or annus is the orbital period of a planetary body, for example, the Earth, moving in its orbit around the Sun. Due to the Earth's axial tilt, the course of a year sees the passing of the seasons, marked by change in weather, the hours of daylight, and, consequently, vegetation and soil fertility. In temperate and subpolar regions around the planet, four seasons are generally recognized: spring, summer, autumn and winter. In tropical and subtropical regions, several geographical sectors do not present defined seasons; but in the seasonal tropics, the annual wet and dry seasons are recognized and tracked. A calendar year is an approximation of the number of days of the Earth's orbital period, as counted in a given calendar. The Gregorian calendar, or modern calendar, presents its calendar year to be either a common year of 365 days or a leap year of 366 days, as do the Julian calendars. For the Gregorian calendar, the average length of the calendar year ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
698 Deaths
__NOTOC__ Year 698 ( DCXCVIII) was a common year starting on Tuesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. The denomination 698 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Byzantine Empire * Spring–summer – Arab forces under Hasan ibn al-Nu'man capture Carthage, ending Byzantine rule in North Africa. The defeated Byzantine fleet revolts and proclaims Tiberios III, who deposes Leontios after a brief siege of Constantinople, Byzantine Emperor. * Autumn–winter – The Byzantine general Heraclius, brother of Tiberios III, crosses the mountain passes of the Taurus Mountains into Cilicia with an army. He launches a campaign in Syria, defeats an Arab force from Antioch, and raids as far as Samosata (modern Turkey). * Outbreak of bubonic plague in Constantinople, Syria and Mesopotamia. Theophanes the Confessor re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banu Bariq
Bariq (also transliterated as Barik or Bareq, ar, بارق) is a tribe from Bareq in south-west Saudi Arabia. It belongs to the ancient Al-Azd tribe which has many clans linked to it. As far as ancestry goes, Aws, Khazraj, Ghassān and Banu Khuza'a, and others all belong to Al-Azd. They were one of the tribes of Arabia during Muhammad's era. This tribe consists of four divisions: Al-Humaydah, Al-Musa ibn 'Ali, Al-Isba' and Al-Jibali. Their homes are located 15 miles north of Mahayil. They stretch 20 miles north and south and 30 miles east and west, and are bounded by "Banu Shihr" to the east, "Khath'm" and "Balqarn" to the north, "Al-Raysh" and "Al-Durayb" to the south and "Rabi'at al-Maqatirah" to the west. Most of them live in the villages scattered across this region. History They were a branch of the Al-Azd tribe, which was one of the two branches of Kahlan the other being Himyar. In ancient times, they inhabited Ma'rib, the capital city of the Sabaean Kingdom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
7th-century Arabic-language Poets
The 7th century is the period from 601 (DCI) through 700 ( DCC) in accordance with the Julian calendar in the Common Era. The spread of Islam and the Muslim conquests began with the unification of Arabia by Muhammad starting in 622. After Muhammad's death in 632, Islam expanded beyond the Arabian Peninsula under the Rashidun Caliphate (632–661) and the Umayyad Caliphate (661–750). The Muslim conquest of Persia in the 7th century led to the downfall of the Sasanian Empire. Also conquered during the 7th century were Syria, Palestine, Armenia, Egypt, and North Africa. The Byzantine Empire suffered setbacks during the rapid expansion of the Caliphate, a mass incursion of Slavs in the Balkans which reduced its territorial limits. The decisive victory at the Siege of Constantinople in the 670s led the empire to retain Asia Minor which assured the existence of the empire. In the Iberian Peninsula, the 7th century was known as the ''Siglo de Concilios'' (century of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poets From The Umayyad Caliphate
A poet is a person who studies and creates poetry. Poets may describe themselves as such or be described as such by others. A poet may simply be the creator ( thinker, songwriter, writer, or author) who creates (composes) poems (oral or written), or they may also perform their art to an audience. The work of a poet is essentially one of communication, expressing ideas either in a literal sense (such as communicating about a specific event or place) or metaphorically. Poets have existed since prehistory, in nearly all languages, and have produced works that vary greatly in different cultures and periods. Throughout each civilization and language, poets have used various styles that have changed over time, resulting in countless poets as diverse as the literature that (since the advent of writing systems) they have produced. History In Ancient Rome, professional poets were generally sponsored by patrons, wealthy supporters including nobility and military officials. For ins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eber
Eber ( he, , ʿĒḇer; grc-x-biblical, Ἔβερ, Éber; ar, عٰابِر, ʿĀbir) is an ancestor of the Ishmaelites and the Israelites according to the "Table of Nations" in the Book of Genesis () and the Books of Chronicles (). Lineage Eber was a great-grandson of Noah's son Shem and the father of Peleg, born when Eber was 34 years old, and of Joktan. He was the son of Shelah, a distant ancestor of Abraham. According to the Hebrew Bible, Eber died at the age of 464. In the Septuagint, the name is written as Heber/Eber (), and his father is called Sala (). His son is called Phaleg/Phalek (), born when Heber was 134 years old, and he had other sons and daughters. Heber lived to an age of 464 years. Name The Aramaic/Hebrew root () is connected with crossing over and the beyond. Considering that other names for descendants of Shem also stand for places, Eber can also be considered the name of an area, perhaps near Assyria. A number of mediaeval scholars such as Mich ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hud (prophet)
), but this is disputed , image = Prophet Hud Name.svg , image_size = 150px , alt = , caption = The name ''Hud'' written in Islamic calligraphy, followed by "Peace be upon him". , birth_name = , birth_date = , birth_place = , death_date = , death_place = , resting_place = Possibly Qabr An-Nabi Hud in Hadhramaut, South Arabia , title = Prophet , predecessor = Nuh , successor = Salih , children = , parents = , relatives = Hud (; ar, هُوْد, Hūd) was a prophet of ancient Arabia mentioned in the Quran. The eleventh chapter of the Quran, ''Hud'', is named after him, though the narrative of Hud comprises only a small portion of the chapter. Historical context Hud has sometimes been identified with Eber, an ancestor of the Ishmaelites and the Israelites who is mentioned in the Old Testament. He is s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
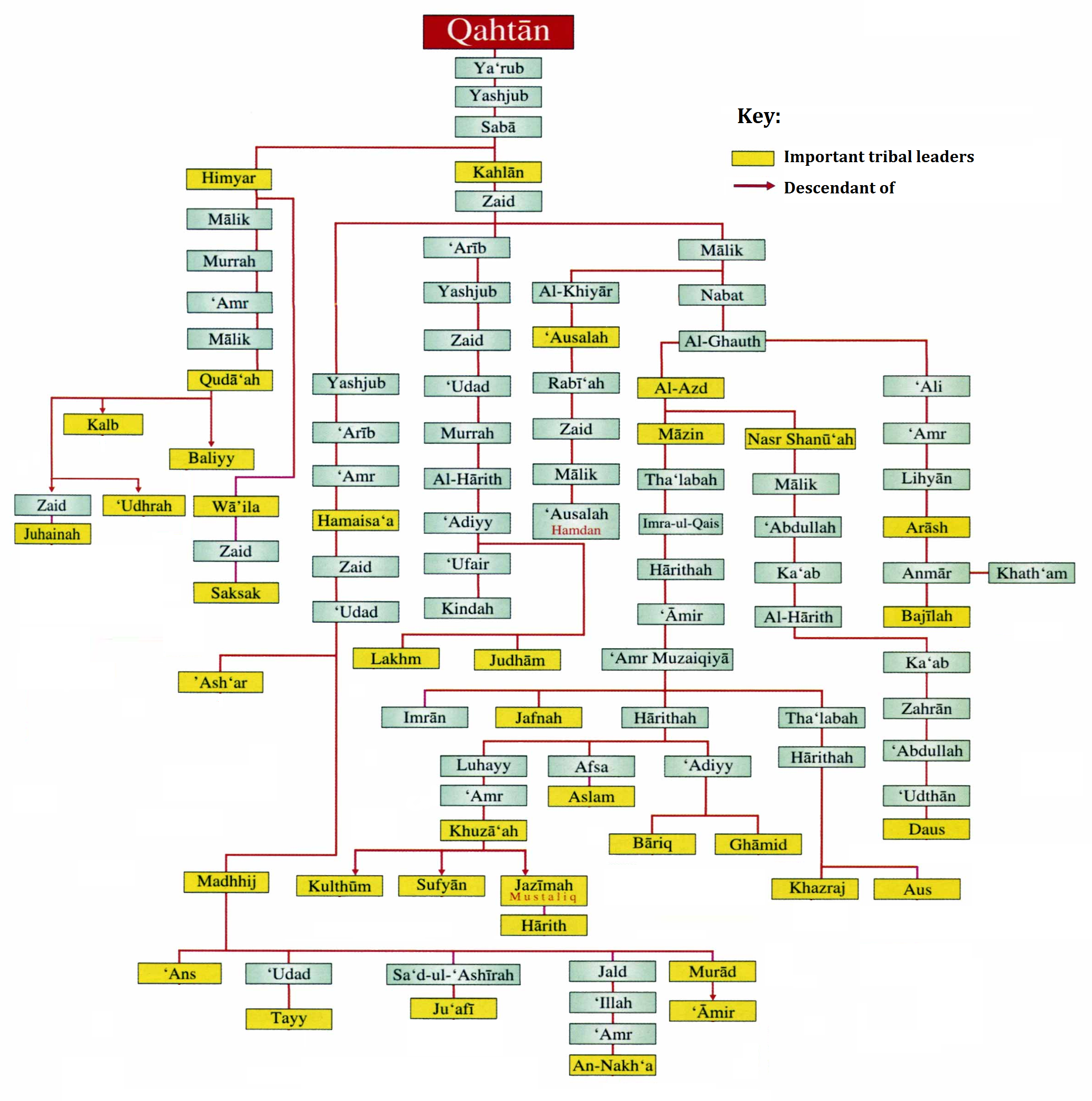
Qahtan
The terms Qahtanite and Qahtani ( ar, قَحْطَانِي; transliterated: Qaḥṭānī) refer to Arabs who originate from South Arabia. The term "Qahtan" is mentioned in multiple ancient Arabian inscriptions found in Yemen. Arab traditions believe that they are the original Arabs. Traditional Arab genealogy According to Arab tradition, the Qahtanites are from South Arabia, unlike the Adnanites who are from the north of Arabia descended from Ishmael through Adnan. "The 'arabized or arabizing Arabs', on the contrary, are believed to be the descendants of Ishmael through Adnan, but in this case the genealogy does not match the Biblical line exactly. The label 'arabized' is due to the belief that Ishmael spoke Hebrew until he got to Mecca, where he married a Yemeni woman and learnt Arabic. Both genealogical lines go back to Sem, son of Noah, but only Adnanites can claim Abraham as their ascendant, and the lineage of Mohammed, the Seal of Prophets (khatim al-anbiya'), can therefor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yarab
Ya'rub ( ar, يعرب, also spelled ''Yarob'',''Ya'rob'', ''Yarrob'', ''Yarab'' or ''Yaarub'') is an ancient Arabic personal name. He is the grandson of Abir being the son of Qahtan and the ancestor of the Himyarite and Sabaean kings of Yemen.van Donzel, 1994, p. 483. A similar account places Ya'rub as Qahtan's grandson (Ya'rub bin Yashjub bin Qahtan) and holds that he is the forefather of ''al-'Arab al-'Ariba'' ("the arab arabs" or "pure arabs"), who are generally identified with the Qahtanites and its two main tribes, the Himyar and the Kahlan.Prentiss, 2003, p. 172. Some legendary accounts relate that Ya'rub was the first to speak Arabic and that the language was named for him.Crosby, 2007, pp. 74-75.Sperl, 1989, p. 209. Shams-i Qais Razi, writing in the 12-13th century CE, traced the origins of Arabic poetry to Ya'rub and he is also credited with having invented the Kufic script.Sperl et al., 1996, p. 138.Thackston, 2001, p. 7. Ancestor of kings Ya'rub was said to be one of g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |