|
Supra-acromial Bursa
The supra-acromial bursa is located on the superior aspect of the acromion and normally does not communicate with the glenohumeral joint.Resnick D. Diagnosis of bone and joint disorders. 3rd edition. Philadelphia: WB Saunders Company; 1995. Supra-acromial bursitis has not been receiving much attention from literature and remains described mainly as case reports of presumptive diagnosis with no histopathological correlation.Arend CF. Ultrasound of the Shoulder. Master Medical Books, 2013. Free chapter on ultrasound evaluation of the supra-acromial bursa available aShoulderUS.com/ref> Since the bursa is supra-acromial, not supraclavicular, fluid-filled masses located over the acromioclavicular joint or distal clavicle do not correspond to supra-acromial bursitis. See also * Subacromial bursa * Subcoracoid bursa The subcoracoid bursa or subcoracoid bursa of Collas is a synovial bursa located in the shoulder. It is located anterior (anatomy), anterior to the subscapularis muscle and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acromion
In human anatomy, the acromion (from Greek: ''akros'', "highest", ''ōmos'', "shoulder", plural: acromia) is a bony process on the scapula (shoulder blade). Together with the coracoid process it extends laterally over the shoulder joint. The acromion is a continuation of the scapular spine, and hooks over anteriorly. It articulates with the clavicle (collar bone) to form the acromioclavicular joint. Structure The acromion forms the summit of the shoulder, and is a large, somewhat triangular or oblong process, flattened from behind forward, projecting at first lateralward, and then curving forward and upward, so as to overhang the glenoid fossa.''Gray's Anatomy'' 1918, see infobox It starts from the base of acromion which marks its projecting point emerging from the spine of scapula. Surfaces Its superior surface, directed upward, backward, and lateralward, is convex, rough, and gives attachment to some fibers of the deltoideus, and in the rest of its extent is subcutaneous. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
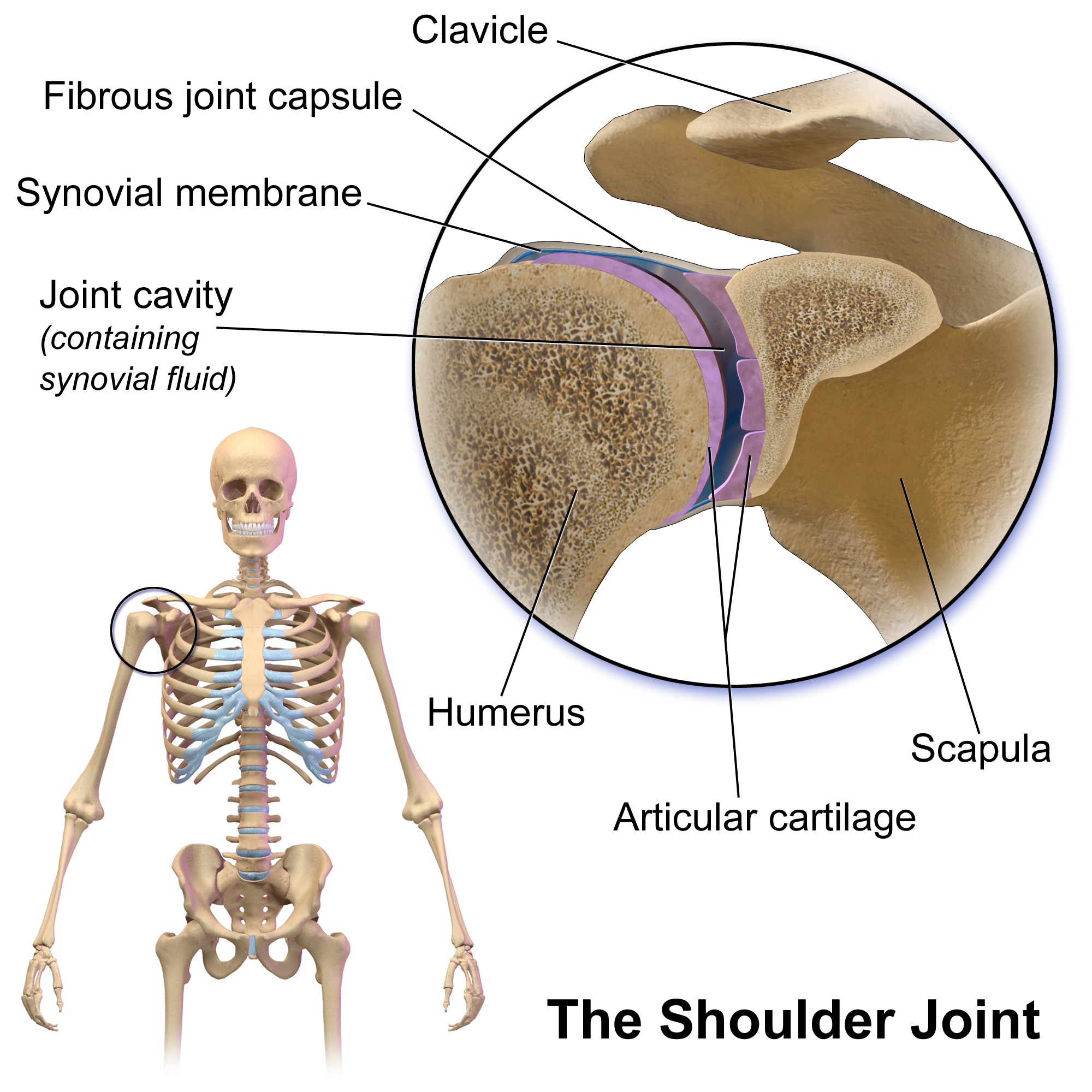
Glenohumeral Joint
The shoulder joint (or glenohumeral joint from Greek ''glene'', eyeball, + -''oid'', 'form of', + Latin ''humerus'', shoulder) is structurally classified as a synovial ball-and-socket joint and functionally as a diarthrosis and multiaxial joint. It involves an articulation between the glenoid fossa of the scapula (shoulder blade) and the head of the humerus (upper arm bone). Due to the very loose joint capsule that gives a limited interface of the humerus and scapula, it is the most mobile joint of the human body. Structure The shoulder joint is a ball-and-socket joint between the scapula and the humerus. The socket of the glenoid fossa of the scapula is itself quite shallow, but it is made deeper by the addition of the glenoid labrum. The glenoid labrum is a ring of cartilaginous fibre attached to the circumference of the cavity. This ring is continuous with the tendon of the biceps brachii above. Spaces Significant joint spaces are: * The normal glenohumeral space is 4– ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subacromial Bursa
The subacromial bursa is the synovial cavity located just below the acromion, which communicates with the subdeltoid bursa in most individuals, forming the so-called subacromial-subdeltoid bursa (SSB). The SSB bursa is located deep to the deltoid muscle and the coracoacromial arch and extends laterally beyond the humeral attachment of the rotator cuff, anteriorly to overlie the intertubercular groove, medially to the acromioclavicular joint, and posteriorly over the rotator cuff. The SSB decreases friction, and allows free motion of the rotator cuff relative to the coracoacromial arch and the deltoid muscle. French anatomist and surgeon Jean-François Jarjavay is credited as the first to describe morbid processes of the SSB in 1867. Since then, histologic studies have documented that synovial membrane may undergo inflammatory and/or degenerative changes and many now believe that they correspond to different stages in the spectrum of disease, with long-lasting inflammation leading ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subcoracoid Bursa
The subcoracoid bursa or subcoracoid bursa of Collas is a synovial bursa located in the shoulder. It is located anterior to the subscapularis muscle and inferior to the coracoid process. Its function is to reduce friction between the coracobrachialis, subscapularis and short head of the biceps tendons, thus facilitating internal and external rotation of the shoulder. The subcoracoid bursa does not communicate with the glenohumeral joint under normal circumstances, but may communicate with the subacromial bursa. As such, contrast fluid injected into the glenohumeral joint during an arthrogram that extends into the subcoracoid bursa is abnormal, and indirectly implies a full thickness rotator cuff The rotator cuff is a group of muscles and their tendons that act to stabilize the human shoulder and allow for its extensive range of motion. Of the seven scapulohumeral muscles, four make up the rotator cuff. The four muscles are the supraspi ... tear. References {{Bursae and sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |