|
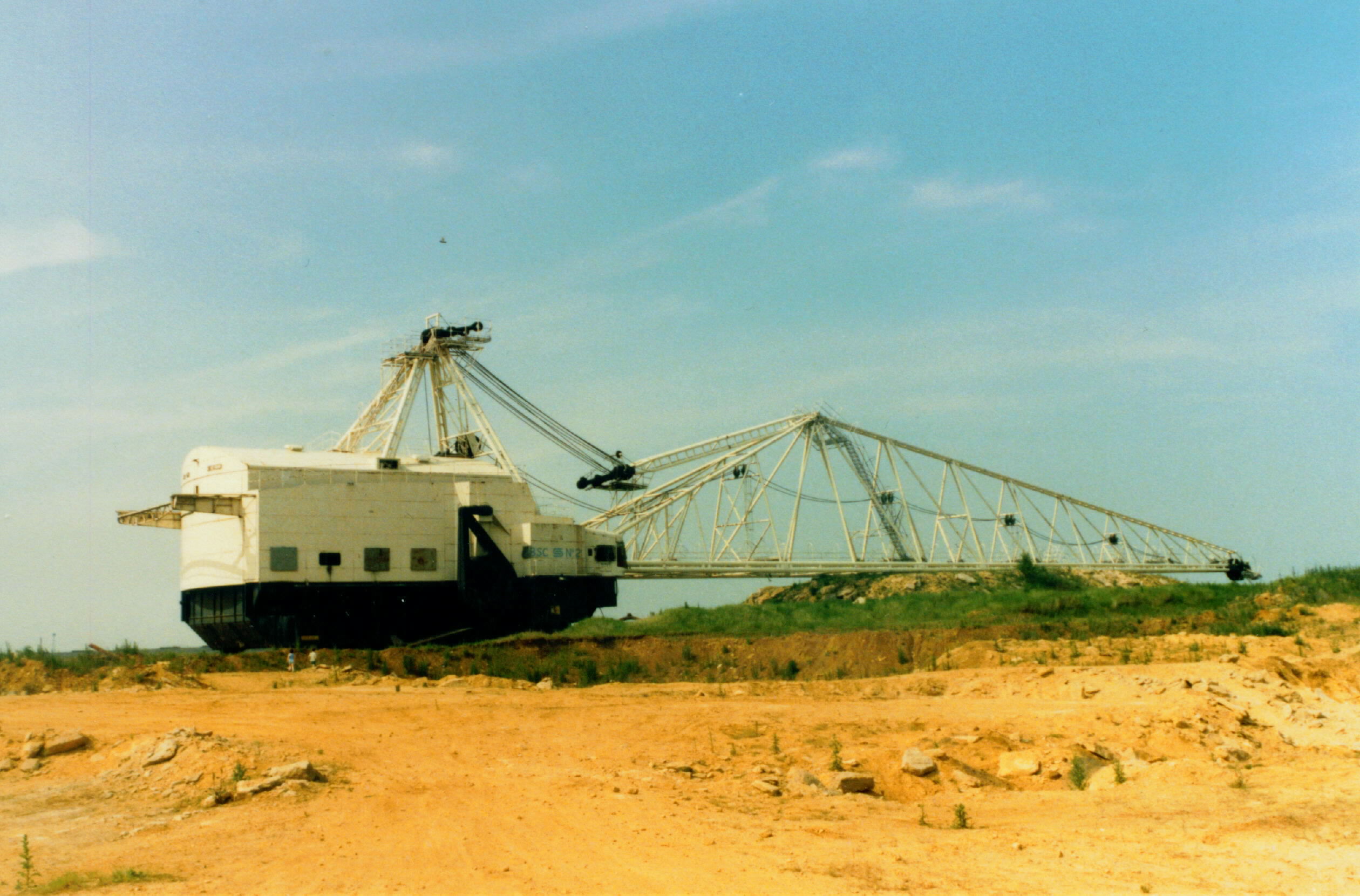
Sundew (dragline)
Sundew was a large electrically powered dragline excavator used in mining operations in Rutland and Northamptonshire in the United Kingdom. Built by Ransomes & Rapier and named after the winning horse of the 1957 Grand National, it began work in a Rutland iron ore quarry belonging to the United Steel Companies (Ore Mining Branch) that year. At the time of its construction Sundew was the largest walking dragline in the world, weighing . With a reach of and a bucket capacity of the machine was able to move a substantial amount of material in a relatively short period. Propulsion was via two large movable feet which could be used to "walk" the dragline forwards and backwards, while directional control was provided by a large circular turntable under the body of the machine. Sundew remained until operations at the quarry ceased in 1974 and plans were then devised to relocate the machine to a recently opened British Steel Corporation quarry near Corby. At a cost of £25 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sundew Dragline
''Drosera'', which is commonly known as the sundews, is one of the largest genera of carnivorous plants, with at least 194 species. 2 volumes. These members of the family Droseraceae lure, capture, and digest insects using stalked mucilaginous glands covering their leaf surfaces. The insects are used to supplement the poor mineral nutrition of the soil in which the plants grow. Various species, which vary greatly in size and form, are native to every continent except Antarctica.McPherson, S.R. 2008. ''Glistening Carnivores''. Redfern NaturalHistory Productions Ltd., Poole. Charles Darwin performed much of the early research into ''Drosera'', engaging in a long series of experiments with Drosera rotundifolia which were the first to confirm carnivory in plants. In an 1860 letter, Darwin wrote, “…at the present moment, I care more about ''Drosera'' than the origin of all the species in the world.” Both the botanical name (from the Greek δρόσος: ''drosos'' = "dew, dew ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Steel Corporation
British may refer to: Peoples, culture, and language * British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies. ** Britishness, the British identity and common culture * British English, the English language as spoken and written in the United Kingdom or, more broadly, throughout the British Isles * Celtic Britons, an ancient ethno-linguistic group * Brittonic languages, a branch of the Insular Celtic language family (formerly called British) ** Common Brittonic, an ancient language Other uses *'' Brit(ish)'', a 2018 memoir by Afua Hirsch *People or things associated with: ** Great Britain, an island ** United Kingdom, a sovereign state ** Kingdom of Great Britain (1707–1800) ** United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland (1801–1922) See also * Terminology of the British Isles * Alternative names for the British * English (other) * Britannic (other) * British Isles * Brit (other) * Br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mining Equipment
Mining is the extraction of valuable minerals or other geological materials from the Earth, usually from an ore body, lode, vein, seam, reef, or placer deposit. The exploitation of these deposits for raw material is based on the economic viability of investing in the equipment, labor, and energy required to extract, refine and transport the materials found at the mine to manufacturers who can use the material. Ores recovered by mining include metals, coal, oil shale, gemstones, limestone, chalk, dimension stone, rock salt, potash, gravel, and clay. Mining is required to obtain most materials that cannot be grown through agricultural processes, or feasibly created artificially in a laboratory or factory. Mining in a wider sense includes extraction of any non-renewable resource such as petroleum, natural gas, or even water. Modern mining processes involve prospecting for ore bodies, analysis of the profit potential of a proposed mine, extraction of the desired materials ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heritage Lottery Fund
The National Lottery Heritage Fund, formerly the Heritage Lottery Fund (HLF), distributes a share of National Lottery funding, supporting a wide range of heritage projects across the United Kingdom. History The fund's predecessor bodies were the National Land Fund, established in 1946, and the National Heritage Memorial Fund, established in 1980. The current body was established as the "Heritage Lottery Fund" in 1994. It was re-branded as the National Lottery Heritage Fund in January 2019. Activities The fund's income comes from the National Lottery which is managed by Camelot Group. Its objectives are "to conserve the UK's diverse heritage, to encourage people to be involved in heritage and to widen access and learning". As of 2019, it had awarded £7.9 billion to 43,000 projects. In 2006, the National Lottery Heritage Fund launched the Parks for People program with the aim to revitalize historic parks and cemeteries. From 2006 to 2021, the Fund had granted £254million ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rutland Railway Museum
Rutland Railway Museum, now trading as Rocks by Rail: The Living Ironstone Museum, is a heritage railway on part of a former Midland Railway mineral branch line. It is situated north east of Oakham, in Rutland, England. Overview The museum offers an open-air site dedicated to recreating an ironstone tramway system in its entirety from the extraction of iron ore from a 'first cut' quarry face reproduced in the quarry viewing area to the exchange sidings with the BR rail head. The museum aims to preserve and operate industrial locomotives and mineral wagons from local quarry railways as well as artefacts related to quarry railways in general. The museum site is based on a typical 1950s or early 1960s quarry system when both steam and diesel power was evident in the industry. The branch line linked to the Melton Mowbray to Oakham main line at Ashwell Signal Box. Exchange sidings were once located at the museum serving three separate private quarry railway systems associated wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Welland
The River Welland is a lowland river in the east of England, some long. It drains part of the Midlands eastwards to The Wash. The river rises in the Hothorpe Hills, at Sibbertoft in Northamptonshire, then flows generally northeast to Market Harborough, Stamford and Spalding, to reach The Wash near Fosdyke. It is a major waterway across the part of the Fens called South Holland, and is one of the Fenland rivers which were laid out with washlands. There are two channels between widely spaced embankments with the intention that flood waters would have space in which to spread while the tide in the estuary prevented free egress. However, after the floods of 1947, new works such as the Coronation Channel were constructed to control flooding in Spalding and the washes are no longer used solely as pasture, but may be used for arable farming. Significant improvements were made to the river in the 1660s, when a new cut with 10 locks was constructed between Stamford and Market Dee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exton, Rutland
Exton is a village in Rutland, England. The population was 607 at the 2011 census. The civil parish was abolished in 2016 and merged with Horn to form Exton and Horn. The village The village's name means 'farm/settlement which has oxen'. The village includes a tree-planted green overlooked by the Fox and Hounds pub. Close to the green is the war memorial to the dead of Exton and Whitwell and to relatives of the Earl of Gainsborough; the names include Tom Cecil Noel MC and Bar and Maurice Dease VC. The memorial was designed by Alfred Young Nutt. In the south of the parish towards Rutland Water is Barnsdale Gardens which were created by Geoff Hamilton of the BBC television series ''Gardeners' World''. Further south, on the north shore of Rutland Water, stands what was the Barnsdale country house and is now the Barnsdale Hall Hotel and Country Club. Barnsdale was a large country house, built in 1890 as a hunting lodge for Earl Fitzwilliam by architect E. J. May. It is a Grade ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exton Hall
Exton Hall is an English country house on the western edge of the village of Exton, Rutland, England, standing in its own extensive park. The Hall It was the family seat of the family of Sir James Harington and later the Noel family, Earls of Gainsborough for almost four hundred years. An earlier mansion burnt down in 1810 and is now a ruin which has grand gables and beautiful chimneys like many Elizabethan houses. The ruins are on Historic England's Heritage at Risk Register, at priority category: C - "slow decay; no solution agreed". The present Exton Hall was built in the 19th century close to the ruins of the original house. In 1869 a Roman Catholic chapel, dedicated to St Thomas of Canterbury was added, to a design by Charles Alban Buckler. The hall was used by elements of the U.S. Army Air Force during World War II. The hall is still in regular use as the private home of Henry Noel, Viscount Campden, and his family. The hall is not normally open to the public, though ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corby
Corby is a town in North Northamptonshire, England, located north-east of Northampton. From 1974 to 2021, the town served as the administrative headquarters of the Borough of Corby. At the 2011 Census, the built-up area had a population of 56,810, while the borough, which was abolished in 2021, had a population of 75,571 in 2021. Figures released in March 2010 revealed that Corby had the fastest growing population in both Northamptonshire and the whole of England. The town was at one time known locally as "Little Scotland" due to the large number of Scottish workers who came to Corby for its steelworks. Recently, Corby has undergone a large regeneration process with the opening of Corby railway station and Corby International Pool in 2009 and the Corby Cube in 2010. The Cube was home to the (former) Corby Borough Council offices and also houses a 450-seat theatre, a public library and other community amenities. History Early history Mesolithic and Neolithic artefacts h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Steel Companies
The United Steel Companies was a steelmaking, engineering, coal mining and coal by-product group based in South Yorkshire and Lincolnshire, England. History The company was registered in 1918 and the following year saw a joining together of steel makers Samuel Fox and Company of Stocksbridge; Steel, Peech and Tozer of Templeborough and Ickles in Rotherham; the Appleby-Frodingham Steel Company of Scunthorpe; and the coal mining and by-products interests of Rother Vale Collieries at Orgreave, Treeton and Thurcroft. Over the years other companies were added to the portfolio: The Sheffield Coal Company, owners of Birley Collieries, Brookhouse and North Staveley collieries, was bought by the United Steel Companies in 1937. This also included coal by-product operations at Orgreave and Brookhouse, suppliers of Metallurgical Coke for Blast Furnaces. The Kiveton Park Colliery Company was taken over in 1944 with reserves from, amongst others, the Barnsley seam being an attrac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dragline
A dragline excavator is a piece of heavy equipment used in civil engineering and surface mining. Draglines fall into two broad categories: those that are based on standard, lifting cranes, and the heavy units which have to be built on-site. Most crawler cranes, with an added winch drum on the front, can act as a dragline. These units (like other cranes) are designed to be dismantled and transported over the road on flatbed trailers. Draglines used in civil engineering are almost always of this smaller, crane type. These are used for road construction, road, port construction, pond and canal dredging, and as Deep foundation, pile driving rigs. These types are built by crane manufacturers such as Link-Belt Construction Equipment, Link-Belt and Hyster Company, Hyster. The much larger type which is built on site is commonly used in Strip mining, strip-mining operations to remove overburden above coal and more recently for oil sands mining. The largest heavy draglines are among the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quarry
A quarry is a type of open-pit mining, open-pit mine in which dimension stone, rock (geology), rock, construction aggregate, riprap, sand, gravel, or slate is excavated from the ground. The operation of quarries is regulated in some jurisdictions to reduce their environmental impact. The word ''quarry'' can also include the underground quarrying for stone, such as Bath stone. Types of rock Types of rock extracted from quarries include: *Chalk *China clay *Scoria, Cinder *Clay *Coal *Construction aggregate (sand and gravel) *Coquina *Diabase *Gabbro *Granite *Gritstone *Gypsum *Limestone *Marble *Ores *Phosphate rock *Quartz *Sandstone *Slate *Travertine Stone quarry Stone quarry is an outdated term for mining construction rocks (limestone, marble, granite, sandstone, etc.). There are open types (called quarries, or open-pit mines) and closed types (Mining, mines and caves). For thousands of years, only hand tools had been used in quarries. In the 18th century, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |