|
Summer Island Site
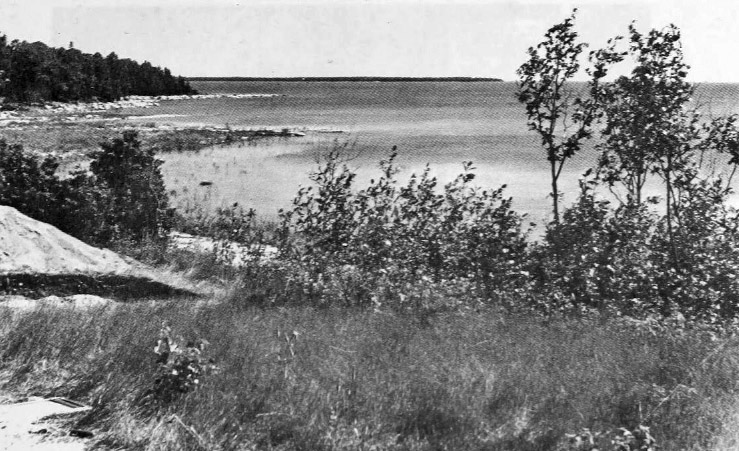
The Summer Island site, designated 20DE4, is an archaeological site located on the northwest side of Summer Island, in Delta County, Michigan. It is classified as a stratified, multi-component site with Middle Woodland (c. 100 B.C–500 A.D.), Upper Mississippian (c. 1000–1500 A. D.) and Early Historic/Protohistoric occupations (c. 1500–1700). It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1971. Site description The site lies in a sandy meadow about 20 feet above Summer Harbor on the northwest side of the island, and about "125 feet inland from the best canoe landing area in the entire bay." At the time it was first excavated, cultural material was evident on the surface of the site. Archaeological history As early as 1851, this site has been recorded as an abandoned Native American village which was occupied as late as 1770. In 1931, Wilbert B. Hinsdale included it in his ''Archaeological atlas of Michigan''. The site was first excavated by George ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Summer Island
Summer Island is an island in Lake Michigan, 2.5 miles (4 km) miles off the southern tip of the Garden Peninsula in the U.S. state of Michigan. It can easily be seen from Fairport, on the southern end of Delta County Road 483, the locally maintained extension of M-183, but is not accessible to the public. The island is part of the Niagara Escarpment archipelago in northwestern Lake Michigan. Its highest point is 710 feet (217 m) above sea level, and 129 feet (40 m) above the level of the lake. One of its most prominent shoreline features is Gravel Point, a northern headland that stretches toward the Garden Peninsula mainland. More than half the island is owned by the state of Michigan and administered as part of Lake Superior State Forest. Summer Island site On the island's northeast side, two shallow points protect Summer Harbor, a small maritime shelter and site of a former settlement. Summer Harbor is adjacent to an archeological landmark listed on the National Register ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wisconsin
Wisconsin () is a state in the upper Midwestern United States. Wisconsin is the 25th-largest state by total area and the 20th-most populous. It is bordered by Minnesota to the west, Iowa to the southwest, Illinois to the south, Lake Michigan to the east, Michigan to the northeast, and Lake Superior to the north. The bulk of Wisconsin's population live in areas situated along the shores of Lake Michigan. The largest city, Milwaukee, anchors its largest metropolitan area, followed by Green Bay and Kenosha, the third- and fourth-most-populated Wisconsin cities respectively. The state capital, Madison, is currently the second-most-populated and fastest-growing city in the state. Wisconsin is divided into 72 counties and as of the 2020 census had a population of nearly 5.9 million. Wisconsin's geography is diverse, having been greatly impacted by glaciers during the Ice Age with the exception of the Driftless Area. The Northern Highland and Western Upland along wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Superior
Lake Superior in central North America is the largest freshwater lake in the world by surface areaThe Caspian Sea is the largest lake, but is saline, not freshwater. and the third-largest by volume, holding 10% of the world's surface fresh water. The northern and westernmost of the Great Lakes of North America, it straddles the Canada–United States border with the province of Ontario to the north and east, and the states of Minnesota to the northwest and Wisconsin and Michigan to the south. It drains into Lake Huron via St. Marys River, then through the lower Great Lakes to the St. Lawrence River and the Atlantic Ocean. Name The Ojibwe name for the lake is ''gichi-gami'' (in syllabics: , pronounced ''gitchi-gami'' or ''kitchi-gami'' in different dialects), meaning "great sea". Henry Wadsworth Longfellow wrote this name as "Gitche Gumee" in the poem ''The Song of Hiawatha'', as did Gordon Lightfoot in his song " The Wreck of the ''Edmund Fitzgerald''". According to oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isle Royale
Isle Royale National Park is an American national park consisting of Isle Royale – known as Minong to the native Ojibwe – along with more than 400 small adjacent islands and the surrounding waters of Lake Superior, in the state of Michigan. Isle Royale is long and wide, with an area of , making it the fourth-largest lake island in the world. In addition, it is the largest natural island in Lake Superior, the second-largest island in the Great Lakes (after Manitoulin Island), the third-largest in the contiguous United States (after Long Island and Padre Island), and the 33rd-largest island in the United States. Isle Royale National Park was established on April 3, 1940, then additionally protected from development by wilderness area designation in 1976, declared a UNESCO International Biosphere Reserve in 1980, and added to the National Register of Historic Places in 2019 as the Minong Traditional Cultural Property. The park covers , with of land and of surroundin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
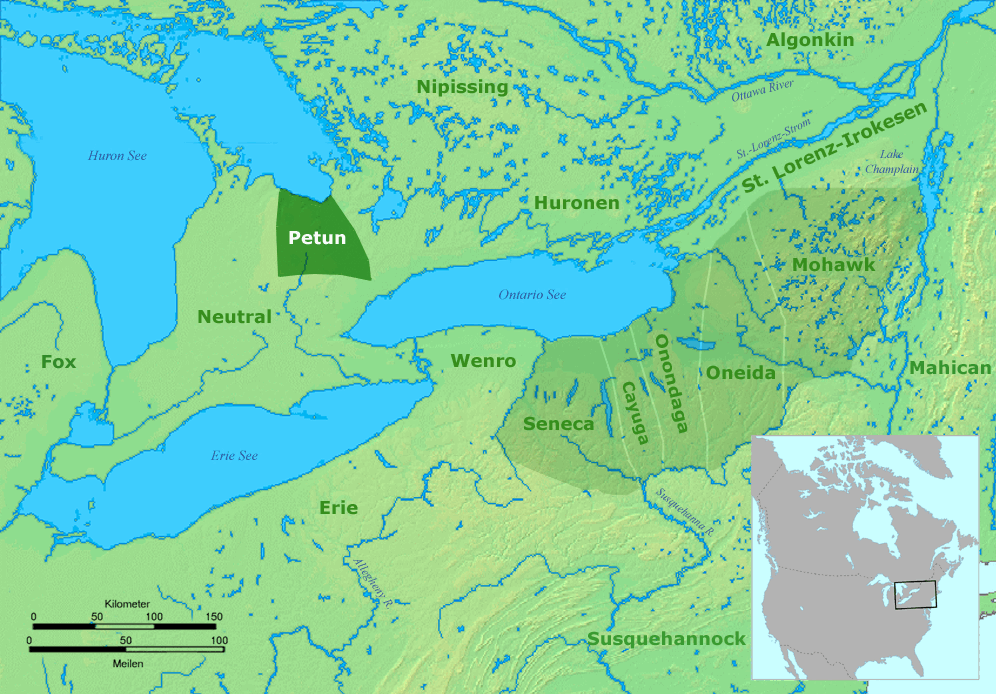
Neutral Tribe
The Neutral Confederacy (also Neutral Nation, Neutral people, or ) was a tribal confederation of Iroquoian peoples. Its heartland was in the floodplain of the Grand River in what is now Ontario, Canada. At its height, its wider territory extended toward the shores of lakes Erie, Huron, and Ontario, as well as the Niagara River in the east. To the northeast were the neighbouring territories of Huronia and the Petun Country, which were inhabited by other Iroquoian confederacies from which the term Neutrals was derived. The five-nation Iroquois Confederacy was across Lake Ontario to the southeast. Like others of Iroquoian language and culture, the tribes would raid and feud with fellow Iroquoian tribes. They were generally wary of rival Algonquian-speaking peoples, such as those who inhabited Canada to the East, along the St. Lawrence Valley basin. Iroquoian tribes were later known to historians for the fierce ways in which they waged war. A largely agrarian society, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huron Tribe
The Wyandot people, or Wyandotte and Waⁿdát, are Indigenous peoples of the Northeastern Woodlands. The Wyandot are Iroquoian Indigenous peoples of North America who emerged as a confederacy of tribes around the north shore of Lake Ontario with their original homeland extending to Georgian Bay of Lake Huron and Lake Simcoe in Ontario, Canada and occupying some territory around the western part of the lake. The Wyandot, not to be mistaken for the Huron-Wendat, predominantly descend from the Tionontati tribe. The Tionontati (or Tobacco/Petun people) never belonged to the Huron (Wendat) Confederacy. However, the Wyandot(te) have connections to the Wendat-Huron through their lineage from the Attignawantan, the founding tribe of the Huron. The four Wyandot(te) Nations are descended from remnants of the Tionontati, Attignawantan and Wenrohronon (Wenro), that were "all unique independent tribes, who united in 1649-50 after being defeated by the Iroquois Confederacy." After ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iroquois
The Iroquois ( or ), officially the Haudenosaunee ( meaning "people of the longhouse"), are an Iroquoian-speaking confederacy of First Nations peoples in northeast North America/ Turtle Island. They were known during the colonial years to the French as the Iroquois League, and later as the Iroquois Confederacy. The English called them the Five Nations, comprising the Mohawk, Oneida, Onondaga, Cayuga, and Seneca (listed geographically from east to west). After 1722, the Iroquoian-speaking Tuscarora people from the southeast were accepted into the confederacy, which became known as the Six Nations. The Confederacy came about as a result of the Great Law of Peace, said to have been composed by Deganawidah the Great Peacemaker, Hiawatha, and Jigonsaseh the Mother of Nations. For nearly 200 years, the Six Nations/Haudenosaunee Confederacy were a powerful factor in North American colonial policy, with some scholars arguing for the concept of the Middle Ground, in that Europe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ontario
Ontario ( ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada.Ontario is located in the geographic eastern half of Canada, but it has historically and politically been considered to be part of Central Canada. Located in Central Canada, it is Canada's most populous province, with 38.3 percent of the country's population, and is the second-largest province by total area (after Quebec). Ontario is Canada's fourth-largest jurisdiction in total area when the territories of the Northwest Territories and Nunavut are included. It is home to the nation's capital city, Ottawa, and the nation's most populous city, Toronto, which is Ontario's provincial capital. Ontario is bordered by the province of Manitoba to the west, Hudson Bay and James Bay to the north, and Quebec to the east and northeast, and to the south by the U.S. states of (from west to east) Minnesota, Michigan, Ohio, Pennsylvania, and New York. Almost all of Ontario's border with the United States f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moccasin Bluff Site
The Moccasin Bluff site (also designated 20BE8) is an archaeological site located along the Red Bud Trail and the St. Joseph River north of Buchanan, Michigan. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1977, and has been classified as a multi-component prehistoric site with the major component dating to the Late Woodland/Upper Mississippian period. History The terrace between Moccasin Bluff and the St. Joseph River was home to temporary camps as early as 6300 B.C. Around A.D 500, inhabitants here traded with other groups of Native Americans from Illinois and Indiana. By A.D. 1100-1400, more permanent villages were established here, and the residents farmed the local lands. By the late 1820s, European settlers moved into the area to log and farm the land. The US government then adopted a policy of moving the local Potawatomi out of the area and further west. This bluff is said to be named for Cogomoccasin, leader of one of the nearby displaced Potawatomi vi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |