|
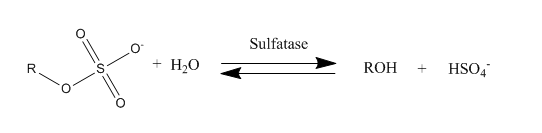
Sulfatase Hydrolysis
Sulfatases are enzymes of the esterase class that catalyze the hydrolysis of sulfate esters. These may be found on a range of substrates, including steroids, carbohydrates and proteins. Sulfate esters may be formed from various alcohols and amines. In the latter case the resultant N-sulfates can also be termed sulfamates. Sulfatases play important roles in the cycling of sulfur in the environment, in the degradation of sulfated glycosaminoglycans and glycolipids in the lysosome, and in remodelling sulfated glycosaminoglycans in the extracellular space. Together with sulfotransferases, sulfatases form the major catalytic machinery for the synthesis and breakage of sulfate esters. Occurrence and importance Sulfatases are found in lower and higher organisms. In higher organisms they are found in intracellular and extracellular spaces. Steroid sulfatase is distributed in a wide range of tissues throughout the body, enabling sulfated steroids synthesized in the adrenals and gonads t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steroid Sulfatase
Steroid sulfatase (STS), or steryl-sulfatase (EC 3.1.6.2), formerly known as arylsulfatase C, is a sulfatase enzyme involved in the metabolism of steroids. It is encoded by the ''STS'' gene. Reactions This enzyme catalysis, catalyses the following chemical reaction : 3β-hydroxyandrost-5-en-17-one 3-sulfate + H2O \rightleftharpoons 3β-hydroxyandrost-5-en-17-one + sulfate Also acts on some related steryl sulfates. Function The protein encoded by this gene catalyzes the conversion of sulfated steroid precursors to the free steroid. This includes DHEA sulfate, estrone sulfate, pregnenolone sulfate, and cholesterol sulfate, all to their unconjugated forms (DHEA, estrone, pregnenolone, and cholesterol, respectively). The encoded protein is found in the endoplasmic reticulum, where it is present as a homodimer. Clinical significance A congenital deficiency in the enzyme is associated with X-linked ichthyosis, a scaly-skin disease affecting roughly 1 in every 2,000 to 6,000 mal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glucosamine
Glucosamine (C6H13NO5) is an amino sugar and a prominent precursor in the biochemical synthesis of glycosylated proteins and lipids. Glucosamine is part of the structure of two polysaccharides, chitosan and chitin. Glucosamine is one of the most abundant monosaccharides. Produced commercially by the hydrolysis of shellfish exoskeletons or, less commonly, by fermentation of a grain such as corn or wheat, glucosamine has many names depending on country. Although a common dietary supplement, there is little evidence that it is effective for relief of arthritis or pain, and is not an approved prescription drug. Dietary supplement Oral glucosamine is a dietary supplement and is not a prescription drug. Glucosamine is marketed as a supplement to support the structure and function of joints, and the marketing is targeted to people with osteoarthritis. Commonly sold forms of glucosamine are glucosamine sulfate, glucosamine chondroitin, glucosamine hydrochloride, and ''N''-acetylglucos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
N-sulfoglucosamine Sulfohydrolase
In enzymology, a N-sulfoglucosamine sulfohydrolase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction :N-sulfo-D-glucosamine + H2O \rightleftharpoons D-glucosamine + sulfate Thus, the two substrates of this enzyme are N-sulfo-D-glucosamine and H2O, whereas its two products are D-glucosamine and sulfate. This enzyme belongs to the family of hydrolases, specifically those acting on sulfur-nitrogen bonds. The systematic name of this enzyme class is N-sulfo-D-glucosamine sulfohydrolase. Other names in common use include sulfoglucosamine sulfamidase, heparin sulfamidase, 2-desoxy-D-glucoside-2-sulphamate sulphohydrolase (sulphamate, and sulphohydrolase). This enzyme participates in glycosaminoglycan degradation and glycan structures - degradation. This enzyme can also be found at SGSH N-sulphoglucosamine sulphohydrolase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''SGSH'' gene. Clinical significance A number sign (#) is used with this entry because the phenotype is ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keratan Sulfate
Keratan sulfate (KS), also called keratosulfate, is any of several sulfated glycosaminoglycans (structural carbohydrates) that have been found especially in the cornea, cartilage, and bone. It is also synthesized in the central nervous system where it participates both in development and in the glial scar formation following an injury. Keratan sulfates are large, highly hydrated molecules which in joints can act as a cushion to absorb mechanical shock. Structure Like other glycosaminoglycans keratan sulfate is a linear polymer that consists of a repeating disaccharide unit. Keratan sulfate occurs as a proteoglycan (PG) in which KS chains are attached to cell-surface or extracellular matrix proteins, termed core proteins. KS core proteins include lumican, keratocan, mimecan, fibromodulin, PRELP, osteoadherin, and aggrecan. The basic repeating disaccharide unit within keratan sulfate is -3 Galβ1-4 GlcNAc6Sβ1-. This can be sulfated at carbon position 6 (C6) of either or both t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chondroitin Sulfate
Chondroitin sulfate is a sulfated glycosaminoglycan (GAG) composed of a chain of alternating sugars ( N-acetylgalactosamine and glucuronic acid). It is usually found attached to proteins as part of a proteoglycan. A chondroitin chain can have over 100 individual sugars, each of which can be sulfated in variable positions and quantities. Chondroitin sulfate is an important structural component of cartilage, and provides much of its resistance to compression. Along with glucosamine, chondroitin sulfate has become a widely used dietary supplement for treatment of osteoarthritis, although large clinical trials failed to demonstrate any symptomatic benefit of chondroitin. Medical use Chondroitin is used in dietary supplements as an alternative medicine to treat osteoarthritis. It is also approved and regulated as a symptomatic slow-acting drug for this disease (SYSADOA) in Europe and some other countries. It is commonly sold together with glucosamine. A 2015 Cochrane review of clini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
N-acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfatase
The enzyme ''N''-acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfatase (EC 3.1.6.4) catalyzes the chemical reaction of cleaving off the 6-sulfate groups of the ''N''-acetyl-D-galactosamine 6-sulfate units of the macromolecule chondroitin sulfate and, similarly, of the D-galactose 6-sulfate units of the macromolecule keratan sulfate. This enzyme belongs to the family of hydrolases, specifically those acting on sulfuric ester bonds. The systematic name of this enzyme class is ''N''-acetyl-D-galactosamine-6-sulfate 6-sulfohydrolase. Other names in common use include chondroitin sulfatase, chondroitinase, galactose-6-sulfate sulfatase, acetylgalactosamine 6-sulfatase, ''N''-acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfate sulfatase, and ''N''-acetylgalactosamine 6-sulfatase. This enzyme participates in glycosaminoglycan degradation and degradation of glycan structures. Deficiency Morquio syndrome is a rare birth defect caused by a deficiency in this essential enzyme. Treatment options include enzyme replacement therapy with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heparan Sulfate
Heparan sulfate (HS) is a linear polysaccharide found in all animal tissues. It occurs as a proteoglycan (HSPG, i.e. Heparan Sulfate ProteoGlycan) in which two or three HS chains are attached in close proximity to cell surface or extracellular matrix proteins. It is in this form that HS binds to a variety of protein ligands, including Wnt, and regulates a wide range of biological activities, including developmental processes, angiogenesis, blood coagulation, abolishing detachment activity by GrB (Granzyme B), and tumour metastasis. HS has also been shown to serve as cellular receptor for a number of viruses, including the respiratory syncytial virus. One study suggests that cellular heparan sulfate has a role in SARS-CoV-2 Infection, particularly when the virus attaches with ACE2. Proteoglycans The major cell membrane HSPGs are the transmembrane syndecans and the glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchored glypicans. Other minor forms of membrane HSPG include betaglycan and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iduronic Acid
-Iduronic acid (IUPAC abbr.: IdoA) is the major uronic acid component of the glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) dermatan sulfate, and heparin. It is also present in heparan sulfate, although here in a minor amount relative to its carbon-5 epimer glucuronic acid. IdoA is a hexapyranose sugar. Most hexapyranoses are stable in one of two chair conformations 1C4 or 4C1. -iduronate is different and adopts more than one solution conformation, with an equilibrium existing between three low-energy conformers. These are the 1C4 and 4C1 chair forms and an additional 2S0 skew-boat conformation. IdoA may be modified by the addition of an ''O''-sulfate group at carbon position 2 to form 2-''O''-sulfo--iduronic acid (IdoA2S). In 2000, LK Hallak described the importance of this sugar in respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) infection. Dermatan sulfate and heparan sulfate were the only GAGs containing IdoA, and they were the only ones that inhibited RSV infection in cell culture. When internally position ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |