|
Sufyan Ibn ò§Uyaynah
Abé¨ MuáËammad Sufyán ibn ò§Uyaynah ibn Maymé¨n al-Hilálᨠal-Ké¨fᨠ( ar, ÄÏÄ´ì ì ÄÙì Ä₤ Ä°ììÄÏì Ä´ì Ä¿ìììÄˋ Ä´ì ì ìì ìì ÄÏìììÄÏìì ÄÏììììì) (725 ã ) was a prominent eighth-century Islamic religious scholar from Mecca. He was from the third generation of Islam referred to as the Tábiò§u al-Tábiò£á¨n, "the followers of the followers". He specialized in the field of hadith and Qur'an exegesis and was described by al-Dhahabᨠas ''shaykh al-Islam''ãa preeminent Islamic authority. Some of his students achieved much renown in their own right, establishing schools of thought that have survived until the present. Biography Ibn ò§Uyaynah's father, ò§Uyaynah ibn Abᨠò£Imrán, was originally from Kufa in present day Iraq where he was a governor for Khálid ibn ò£Abdilláh al-Qasrá¨. However, when al-Qasrᨠwas removed from his position his successor sought out his governors causing ò§Uyaynah to flee to Mecca where he then settled. Ibn ò§Uyaynah was born ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islam
Islam (; ar, ÜÄÏììÄËÄ°ììÄÏì , , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ''Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad, the Muhammad in Islam, main and final Islamic prophet.Peters, F. E. 2009. "Alláh." In , edited by J. L. Esposito. Oxford: Oxford University Press. . (See alsoquick reference) "[T]he Muslims' understanding of Alláh is based...on the Qurò¢án's public witness. Alláh is Unique, the Creator, Sovereign, and Judge of mankind. It is Alláh who directs the universe through his direct action on nature and who has guided human history through his prophets, Abraham, with whom he made his covenant, Moses/Moosa, Jesus/Eesa, and MuáËammad, through all of whom he founded his chosen communities, the 'Peoples of the Book.'" It is the Major religious groups, world's second-largest religion behind Christianity, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muhammad Ibn Idris Ash-Shafiò§i
Abé¨ ò¢Abdilláh MuáËammad ibn Idrá¨s al-Sháfiò¢á¨ ( ar, ÄÈìÄ´ìì Ä¿ìÄ´ìÄ₤ì ìÝìììì ì ìÄÙìì ììÄ₤ì Ä´ììì ÄËìÄ₤ìÄÝììÄ°ì ìÝìÄÇììÄÏììÄ¿ìììì, 767ã19 January 820 CE) was an Arab Muslim theologian, writer, and scholar, who was one of the first contributors of the principles of Islamic jurisprudence (UÿÈé¨l al-fiqh). Often referred to as 'Shaykh al-Islám', al-Sháfiãᨠwas one of the four great Sunni Imams, whose legacy on juridical matters and teaching eventually led to the formation of Shafi'i school of ''fiqh'' (or Madh'hab). He was the most prominent student of Imam Malik ibn Anas, and he also served as the Governor of Najar. Born in Gaza in Palestine (Jund Filastin), he also lived in Mecca and Medina in the Hejaz, Yemen, Egypt, and Baghdad in Iraq. Introduction The biography of al-Sháfiãi is difficult to trace. Dawud al-Zahiri was said to be the first to write such a biography, but the book has been lost. The oldest surviving biography g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
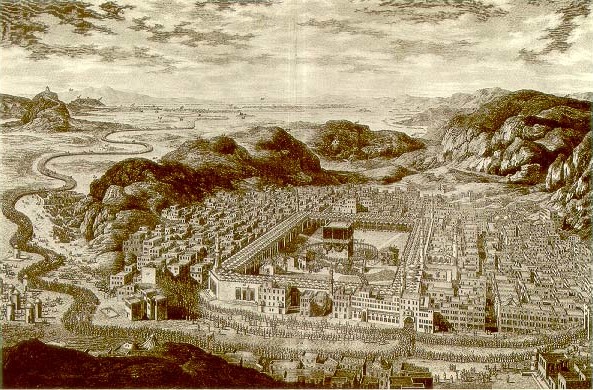
Hajj
The Hajj (; ar, ÄÙìĘì '; sometimes also spelled Hadj, Hadji or Haj in English) is an annual Islamic pilgrimage to Mecca, Saudi Arabia, the holiest city for Muslims. Hajj is a mandatory religious duty for Muslims that must be carried out at least once in their lifetime by all adult Muslims who are physically and financially capable of undertaking the journey, and of supporting their family during their absence from home. In Islamic terminology, Hajj is a pilgrimage made to the Kaaba, the "House of God", in the sacred city of Mecca in Saudi Arabia. It is one of the Five Pillars of Islam, alongside Shahadah (oath to God), Salat (prayer), Zakat (almsgiving) and Sawm (fasting of Ramadan). The Hajj is a demonstration of the solidarity of the Muslim people, and their submission to God ( Allah). The word Hajj means "to attend a journey", which connotes both the outward act of a journey and the inward act of intentions. The rites of pilgrimage are performed over five to six ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qur'an
The Quran (, ; Standard Arabic: , Quranic Arabic: , , 'the recitation'), also romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a revelation from God. It is organized in 114 chapters (pl.: , sing.: ), which consist of verses (pl.: , sing.: , cons.: ). In addition to its religious significance, it is widely regarded as the finest work in Arabic literature, and has significantly influenced the Arabic language. Muslims believe that the Quran was orally revealed by God to the final prophet, Muhammad, through the archangel Gabriel incrementally over a period of some 23 years, beginning in the month of Ramadan, when Muhammad was 40; and concluding in 632, the year of his death. Muslims regard the Quran as Muhammad's most important miracle; a proof of his prophethood; and the culmination of a series of divine messages starting with those revealed to Adam, including the Torah, the Psalms and the Gospel. The word ''Quran'' occurs so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sufyan Al-Thawri
Sufyan al-Thawri ( ar, ÄÈÄ´ì Ä¿Ä´Ä₤ ÄÏììì Ä°ììÄÏì Ä´ì Ä°Ä¿ìÄ₤ Ä´ì ì Ä°ÄÝìì ÄÏìĨìÄÝì, ò¥Abu ò¢Abd Alláh Sufyán ibn Saò£á¨d ibn Masré¨q al-Thawrᨠ; 716ã778) was a ''Tábiã al-Tábiãá¨n'' Islamic scholar, jurist, and founder of the Thawri madhhab.Steven C. Judd, ãCompetitive hagiography in biographies of al-Awzaò¢i and Sufyan al-Thawriã, Journal of the American Oriental Society 122:1 (JanãMarch, 2002). He was also a great hadith compiler (muhaddith) and was known as one of the ãEight Ascetics. Biography Sufyan ath-Thawri was born in Khorosan. His nisba ''al-Thawri'' is derived from his ancestor Thawr b. 'Abd Manat. He moved to Kufa, Iraq, for his education and in his youth supported the Family of Ali ibn Abi Talib against the dying Umayyad caliphate. By 748 he had moved to Basra, "where he met Abdallahibn 'Awn and Ayyub l-Sakhtiyani He then abandoned his Shi'i view." Afterwards, he stopped narrating the merits of Ali because he hated them in relati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fatwá
A fatwá ( ; ar, ìĈìì; plural ''fatáwá'' ) is a legal ruling on a point of Islamic law (''sharia'') given by a qualified '' Faqih'' (Islamic jurist) in response to a question posed by a private individual, judge or government. A jurist issuing fatwas is called a ''mufti'', and the act of issuing fatwas is called ''iftáòƒ''. Fatwas have played an important role throughout Islamic history, taking on new forms in the modern era. Resembling ''jus respondendi'' in Roman law and rabbinic ''responsa'', privately issued fatwas historically served to inform Muslim populations about Islam, advise courts on difficult points of Islamic law, and elaborate substantive law. In later times, public and political fatwas were issued to take a stand on doctrinal controversies, legitimize government policies or articulate grievances of the population. During the era of European colonialism, fatwas played a part in mobilizing resistance to foreign domination. Muftis acted as independent s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biographical Evaluation
Biographical evaluation ( ar, Ä¿ìììì ì ÄÏìÄÝììĘÄÏì, ò¢ilm al-rijál; literally meaning'' 'Knowledge of Men' , ''but more commonly understood as the ''Science of Narrators)'' refers to a discipline of Islamic religious studies within hadith terminology in which the narrators of hadith are evaluated. Its goal is to establish the credibility of the narrators, using both historic and religious knowledge, in order to distinguish authentic and reliable hadiths from unreliable hadiths.''Muqadimah Ibn al-Salah'', by Ibn al-Salah, edited by 'Aishah bint 'Abd al-Rahman, p. 101, ''Dar al-Ma'arif'', Cairo. is synonymous with what is commonly referred to as (discrediting and accrediting) ã the criticism and declared acceptance of hadith narrators.''Tadrib al-Rawi'', vol. 2, p. 495, ''Dar al-'Asimah'', first edition, 2003. Significance In his ''Introduction to the Science of Hadith'', Ibn al-Salah, a renowned hadith specialist, explained the importance of the study of hadit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muhammad Al-Bukhari
Muhammad ( ar, ì ìÄÙìì ììÄ₤; 570 ã 8 June 632 Common Era, CE) was an Arab religious, social, and political leader and the founder of Islam. According to Muhammad in Islam, Islamic doctrine, he was a prophet Divine inspiration, divinely inspired to preach and confirm the tawhid, monotheistic teachings of Adam in Islam, Adam, Abraham in Islam, Abraham, Moses in Islam, Moses, Jesus in Islam, Jesus, and other Prophets and messengers in Islam, prophets. He is believed to be the Seal of the Prophets within Islam. Muhammad united Arabian Peninsula, Arabia into a single Muslim polity, with the Quran as well as his teachings and practices forming the basis of Islamic religious belief. Muhammad was born approximately 570CE in Mecca. He was the son of Abdullah ibn Abd al-Muttalib and Amina bint Wahb. His father Abdullah was the son of Quraysh tribal leader Abd al-Muttalib ibn Hashim, and he died a few months before Muhammad's birth. His mother Amina died when he was six, lea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in Western Asia. It covers the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula, and has a land area of about , making it the fifth-largest country in Asia, the second-largest in the Arab world, and the largest in Western Asia and the Middle East. It is bordered by the Red Sea to the west; Jordan, Iraq, and Kuwait to the north; the Persian Gulf, Qatar and the United Arab Emirates to the east; Oman to the southeast; and Yemen to the south. Bahrain is an island country off the east coast. The Gulf of Aqaba in the northwest separates Saudi Arabia from Egypt. Saudi Arabia is the only country with a coastline along both the Red Sea and the Persian Gulf, and most of its terrain consists of arid desert, lowland, steppe, and mountains. Its capital and largest city is Riyadh. The country is home to Mecca and Medina, the two holiest cities in Islam. Pre-Islamic Arabia, the territory that constitutes modern-day Saudi Ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tihamah
Tihamah or Tihama ( ar, ĈìììÄÏì ìÄˋì ') refers to the Red Sea coastal plain of the Arabian Peninsula from the Gulf of Aqaba to the Bab el Mandeb. Etymology Tihámat is the Proto-Semitic language's term for 'sea'. Tiamat (or Tehom, in masculine form) was the ancient Mesopotamian god of the sea and of chaos. The word appears in the Hebrew Bible as tèhém (Genesis 1:2), meaning "primordial ocean, abyss". History Era of Muhammad During the era of the Islamic prophet Muhammad, many military expeditions took place here including the Battle of Hamra al-Asad and caravan raids. Beginning in January 623 CE, some of the Muslims resorted to the tradition of raiding the Meccan caravans that traveled along the eastern coast of the Red Sea from Mecca to the Syrian region. While at áÊamra' al-Asad (), Muhammad made an agreement with Mabad al-Khuzaah at Tihamah, in which Mabad pledged not to conceal anything from him. Mabad was then sent to Mecca to dissuade Abu Sufyan ibn Harb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ibn Shihab Al-Zuhri
Muhammad ibn Muslim ibn Ubaydullah ibn Abdullah ibn Shihab al-Zuhri ( ar, ì ÄÙì Ä₤ Ä´ì ì Ä°ìì Ä´ì Ä¿Ä´ÜÄ₤ ÄÏììì Ä´ì Ä¿Ä´Ä₤ ÄÏììì Ä´ì ÄÇìÄÏÄ´ ÄÏìÄýìÄÝÜ, translit=MuáËammad ibn Muslim ibn ò¢Ubayd Alláh ibn ò¢Abd Alláh b. Säýhäýiháb al-Zuhrá¨; died 124 AH/741-2 CE), also referred to as Ibn Shihab or al-Zuhri, was a ''tabi'i'' Arab jurist and traditionist credited with pioneering the development of '' sá¨ra-maghazi'' and hadith literature. Raised in Medina, he studied hadith and ''maghazi'' under Medinese traditionists before rising to prominence at the Umayyad court, where he served in a number of religious and administrative positions. He transmitted several thousand hadith included in the six canonical Sunni hadith collections and his work on ''maghazi'' forms the basis of the extant biographies of Muhammad. His relationship with the Umayyads has been debated by both early and modern Sunnis, Shias and Western specialists in Islamic studies. Biography Early ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)




