|
Sudan Second Division
Sudan ( or ; ar, السودان, as-Sūdān, officially the Republic of the Sudan ( ar, جمهورية السودان, link=no, Jumhūriyyat as-Sūdān), is a country in Northeast Africa. It shares borders with the Central African Republic to the southwest, Chad to the west, Egypt to the north, Eritrea to the northeast, Ethiopia to the southeast, Libya to the northwest, South Sudan to the south and the Red Sea. It has a population of 45.70 million people as of 2022 and occupies 1,886,068 square kilometres (728,215 square miles), making it Africa's third-largest country by area, and the third-largest by area in the Arab League. It was the largest country by area in Africa and the Arab League until the secession of South Sudan in 2011, since which both titles have been held by Algeria. Its capital is Khartoum and its most populated city is Omdurman (part of the metropolitan area of Khartoum). Sudan's history goes back to the Pharaonic period, witnessing the Kingdom of Kerma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flag Of Sudan
The current flag of Sudan ( ar, علم السودان, ʿalam as-Sūdān) was adopted on 20 May 1970 and consists of a horizontal red-white-black tricolour with a green triangle at the hoist. The flag is based on the Arab Liberation Flag of the Egyptian Revolution of 1952, as are the flags of Egypt, Iraq, Syria, Yemen, and Palestine and formerly of the United Arab Republic, North Yemen, South Yemen, and the Libyan Arab Republic. Whereas there is no fixed order for the Pan-Arab Colours of black, white, red, and green, flags using the Arab Liberation Colours (a subset of the Pan-Arab Colours) maintain a horizontal triband of equal stripes of red, white, and black, with green being used to distinguish the different flags from each other by way of green stars, Arabic script, or, in the case of Sudan, the green triangle along the hoist. In the original Arab Liberation Flag, green was used in the form of the flag of the Kingdom of Egypt and Sudan emblazoned on the breast of the E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Heads Of State Of Sudan
This article lists the heads of state of Sudan since the country's independence in 1956. History of the office Since independence was proclaimed on 1 January 1956, six individuals (and three multi-member sovereignty councils) have served as head of state of Sudan, currently under the title President of the Republic of the Sudan. Prior to independence, Sudan was governed as a condominium by Egypt and the United Kingdom, under the name Anglo-Egyptian Sudan. As such, executive power was vested in a dyarchy consisting of both countries' heads of state – at the time of independence, the Queen of the United Kingdom (Elizabeth II) and the Egyptian Revolutionary Command Council (headed by Gamal Abdel Nasser). Immediately following independence, the role of head of state was filled by a five-member Sovereignty Council, with rival nationalist factions unable to agree on a single candidate. In November 1958, General Ibrahim Abboud led a military coup d'état, assuming the role of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kerma Culture
The Kerma culture or Kerma kingdom was an early civilization centered in Kerma, Sudan. It flourished from around 2500 BC to 1500 BC in ancient Nubia. The Kerma culture was based in the southern part of Nubia, or "Upper Nubia" (in parts of present-day northern and central Sudan), and later extended its reach northward into Lower Nubia and the border of Egypt. The polity seems to have been one of a number of Nile Valley states during the Middle Kingdom of Egypt. In the Kingdom of Kerma's latest phase, lasting from about 1700 to 1500 BC, it absorbed the Sudanese kingdom of Sai and became a sizable, populous empire rivaling Egypt. Around 1500 BC, it was absorbed into the New Kingdom of Egypt, but rebellions continued for centuries. By the eleventh century BC, the more-Egyptianized Kingdom of Kush emerged, possibly from Kerma, and regained the region's independence from Egypt. Site The primary site of Kerma that forms the heart of the Kingdom of Kerma includes both an extensive town ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Sudan
The history of Sudan refers to both the territory of the Republic of the Sudan, including what became in 2011 the independent state of South Sudan. The territory of Sudan is geographically part of a larger African region, also known by the term "Sudan". The term is derived from ar, بلاد السودان ''bilād as-sūdān'', or "land of the black people", and has sometimes been used more widely referring to the Sahel belt of West and Central Africa. The modern Republic of the Sudan was formed in 1956 and inherited its boundaries from Anglo-Egyptian Sudan, established in 1899. For times predating 1899, usage of the term "Sudan" mainly applied to the Turkish Sudan and the Mahdist State, and a wider and changing territory between Egypt in the North and regions in the South adjacent to modern Uganda, Kenia and Ethiopia. The early history of the Kingdom of Kush, located along the Nile region in northern Sudan, is intertwined with the history of ancient Egypt, with which it was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
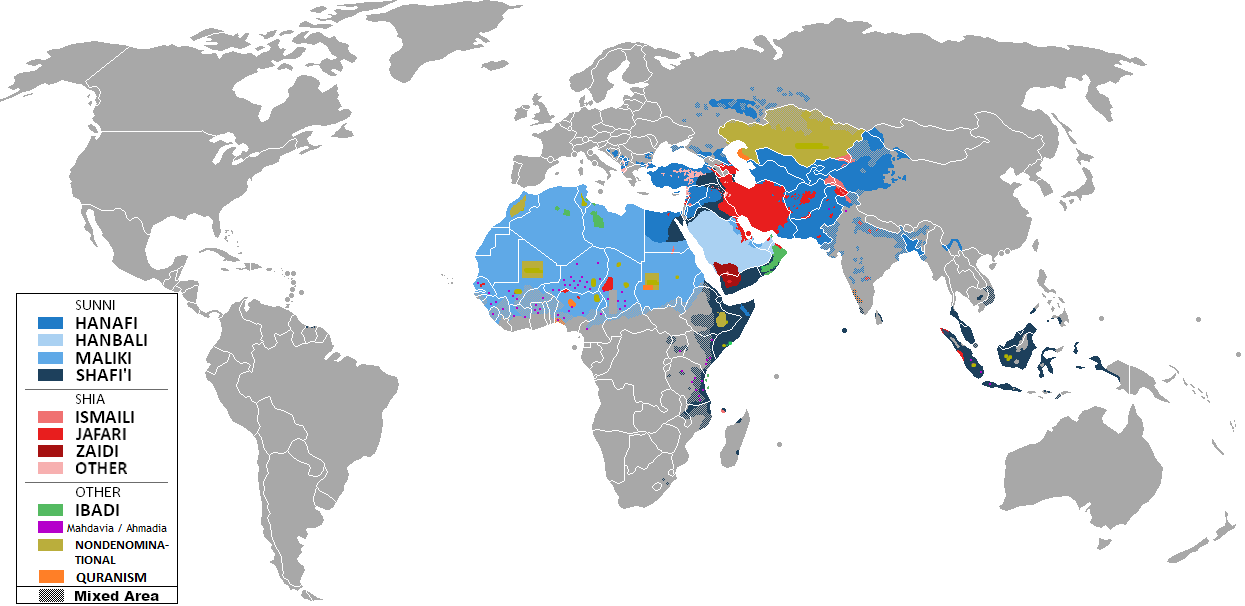
Religion In Sudan
The dominant religion in Sudan is Islam at 90.7% of the population while Christianity forms 5.4% of the population according to Pew Research Center. In September 2020, Sudan constitutionally became a secular state after Sudan's transitional government agreed to separate religion from the state, ending 30 years of Islamic rule and Islam as the official state religion in the North African nation. It also scrapped the apostasy law and public flogging. Islam Up until 2010 (before the secession of South Sudan in 2011), the country was 80% Muslim; as of 2018, the proportion grew to 90%. Most Sudanese Muslims are adherents of the Sunni branch of Islam, a vast majority following the Maliki rites, although Shafi and Hanafi rites are also present. Shiaism and its related Mahdist ideology have recently grown in popularity in Sudan. A growing number of Shias, for example, have emerged in Khartoum and surrounding villages. Sufism and Shia Islam support Prophet Muhammad's bloodline, Ahl a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Traditional African Religions
The traditional beliefs and practices of African people are highly diverse beliefs that include various ethnic religions.Encyclopedia of African Religion (Sage, 2009) Molefi Kete Asante Generally, these traditions are oral rather than scriptural and passed down from one generation to another through folk tales, songs, and festivals, include belief in an amount of higher and lower gods, sometimes including a supreme creator or force, belief in spirits, veneration of the dead, use of magic and traditional African medicine. Most religions can be described as animistic with various polytheistic and pantheistic aspects. The role of humanity is generally seen as one of harmonizing nature with the supernatural. Spread Adherents of traditional religions in Africa are distributed among 43 countries and are estimated to number over 100 million.''Britannica Book of the Year'' (2003), ''Encyclopædia Britannica'' (2003) p.306 According to the ''Encyclopædia Britannica'', as of mid-2002, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christianity In Sudan
Christianity has a long history in the region that is now Sudan and South Sudan. Ancient Nubia was reached by Coptic Christianity by the 2nd century. The Coptic Church was later influenced by Greek Christianity, particularly during the Byzantine era. From the 7th century, the Christian Nubian kingdoms were threatened by the Islamic expansion, but the southernmost of these kingdoms, Alodia, survived until 1504. Southern Sudan (including what is now South Sudan) remained long dominated by traditional (tribal) religions of the Nilotic peoples, with significant conversion to Christianity during the 20th and 21st centuries. History Coptic Christianity Christianity reached the area of present-day northern Sudan, then called Nubia, by about the end of the first century after Christ. It greatly developed under the influence of the Eastern Roman Empire. Indeed, Byzantine architecture influenced most of the Christian churches in lower Nubia. The Byzantine Emperor Justinian I (rei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islam In Sudan
Islam is the most common religion in Sudan and Muslims have dominated national government institutions since independence in 1956. According to UNDP Sudan, the Muslim population is 97%, including numerous Arab and non-Arab groups. The remaining 3% ascribe to either Christianity or traditional animist religions. Muslims predominate in all but Nuba Mountains region. The vast majority of Muslims in Sudan adhere to Sunni Islam of Maliki school of jurisprudence, deeply influenced with Sufism. There are also some Shia communities in Khartoum, the capital. The most significant divisions occur along the lines of the Sufi brotherhoods. Two popular brotherhoods, the Ansar and the Khatmia, are associated with the opposition Umma and Democratic Unionist Parties respectively. Only the Darfur region is traditionally lacking the presence of Sufi brotherhoods found in the rest of the country. Shari'a law has been installed by various military regimes, and its application to non-Muslims in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transitional Legislative Council (Sudan)
The Transitional Legislative Council of Sudan ( ar, المجلس التشريعي الانتقالي السوداني ''al majlis al tashrieiu al aintiqaliu al sudaniu'') is an interim legislative body to be formed in Sudan as part of the 2019–2024 Sudanese transition to democracy. Background Following a coup d'état in April 2019, both houses of the National Legislature of Sudan were dissolved and a Transitional Military Council was formed. In July 2019, the Transitional Military Council and the Forces of Freedom and Change coalition of civil society organisations agreed a constitutional declaration for a transition to an elected government in 2022. Under the terms of this agreement, a transitional government is to be appointed and a Transitional Legislative Council is to be formed. Composition Under the terms of the constitutional declaration, the Transitional Legislative Council is to be formed within three months of the declaration entering into force. The Forces of F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acting (law)
In law, a person is acting in a position if they are not serving in the position on a permanent basis. This may be the case if the position has not yet been formally created, the person is only occupying the position on an interim basis, the person does not have a mandate, or if the person meant to execute the role is incompetent or incapacitated. Business Organizations are advised to have a succession plan including the designation of an acting CEO if the person in that job vacates that position before a replacement has been determined. For example, the lead director on the board of directors may be designated to assume the responsibilities of the CEO until the board finds a new CEO. Politics Examples of acting positions in politics include acting mayor, acting governor, acting president, and acting prime minister. Officials in an acting position usually do not have the full powers of a properly appointed official, and are often the proper official's deputy or longest servi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osman Hussein (politician)
Osman Hussein is a Sudan politician who has served as acting prime minister of Sudan since 19 January 2022, following the resignation of Abdalla Hamdok Abdalla Hamdok Al-Kinani (also transliterated ''Abdallah'', ''Hamdouk'', '' AlKinani''; ar, عبدالله حمدوك الكناني; born 1 January 1956) is a Sudanese public administrator who served as the 15th Prime Minister of Sudan from 20 ... on 2 January. He was the general secretary of the office of Prime Minister from 13 March 2019 until 19 January 2022. References Living people Prime Ministers of Sudan 21st-century Sudanese politicians Year of birth missing (living people) National Congress Party (Sudan) politicians {{Sudan-politician-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Heads Of Government Of Sudan
This article lists the heads of government of Sudan, from the establishment of the office of Chief Minister in 1952 until the present day. The office of Prime Minister was abolished after the 1989 coup d'état, and reestablished in 2017 when Bakri Hassan Saleh was appointed Prime Minister by President Omar al-Bashir. Abdalla Hamdok was appointed as Prime Minister by the Sovereignty Council on 21 August 2019, as part of the country's transition to democracy. On 25 October 2021, Hamdok was deposed and placed under house arrest, following a coup d'état. On 21 November 2021, Hamdok was reinstated as prime minister as part of an agreement with the military. On 2 January 2022, Hamdok resigned as prime minister. Titles of heads of government * 1952–1956: Chief Minister * 1956–1989; 2017–present: Prime Minister Heads of government of Sudan (1952–present) (Dates in italics indicate ''de facto'' continuation of office) Timeline Notes See also * Politics of Sudan *Li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_001.jpg)

