|
Substantia Ferruginea
The substantia ferruginea is an underlying patch of deeply pigmented nerve cells located in the floor of the superior part of the sulcus limitans. It was coined in 1838 and 1851. See also * Rhomboid fossa The rhomboid fossa is a rhombus-shaped depression that is the anterior part of the fourth ventricle. Its anterior wall, formed by the back of the pons and the medulla oblongata, constitutes the floor of the fourth ventricle. It is covered by a ... * Sulcus limitans * Locus ceruleus * Fourth ventricle References External linksAtlas Image of the Posterior View of the Floor of Fourth Ventricle Brainstem {{Neuroanatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulcus Limitans
The sulcus limitans is found in the fourth ventricle of the brain. It separates the cranial nerve motor nuclei (medial) from the sensory nuclei (lateral).Nolte, John. The Human Brain 6th ed. p.685. Mosby Inc. It can also be located by searching laterally from the medial eminence In the human brain, the rhomboid fossa is divided into symmetrical halves by a median sulcus which reaches from the upper to the lower angles of the fossa and is deeper below than above. On either side of this sulcus is an elevation, the medial em .... It is parallel to the median sulcus. References External links Diagram of the sulcus limitansSectional Atlas: Pons at the Abducens Nucleus - Facial Colliculus Brainstem {{Neuroanatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhomboid Fossa
The rhomboid fossa is a rhombus-shaped depression that is the anterior part of the fourth ventricle. Its anterior wall, formed by the back of the pons and the medulla oblongata, constitutes the floor of the fourth ventricle. It is covered by a thin layer of grey matter continuous with that of the spinal cord The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue, which extends from the medulla oblongata in the brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone). The backbone encloses the central canal of the spin ...; superficial to this is a thin lamina of neuroglia which constitutes the ependyma of the ventricle and supports a layer of ciliated epithelium. Parts The fossa consists of three parts, superior, intermediate, and inferior: ;The superior part :The superior part is triangular in shape and limited laterally by the superior cerebellar peduncle; its apex, directed upward, is continuous with the cerebral aqueduct; its base i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulcus Limitans
The sulcus limitans is found in the fourth ventricle of the brain. It separates the cranial nerve motor nuclei (medial) from the sensory nuclei (lateral).Nolte, John. The Human Brain 6th ed. p.685. Mosby Inc. It can also be located by searching laterally from the medial eminence In the human brain, the rhomboid fossa is divided into symmetrical halves by a median sulcus which reaches from the upper to the lower angles of the fossa and is deeper below than above. On either side of this sulcus is an elevation, the medial em .... It is parallel to the median sulcus. References External links Diagram of the sulcus limitansSectional Atlas: Pons at the Abducens Nucleus - Facial Colliculus Brainstem {{Neuroanatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
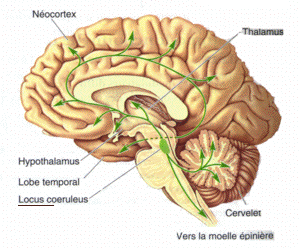
Locus Ceruleus
The locus coeruleus () (LC), also spelled locus caeruleus or locus ceruleus, is a nucleus in the pons of the brainstem involved with physiological responses to stress and panic. It is a part of the reticular activating system. The locus coeruleus, which in Latin means "blue spot", is the principal site for brain synthesis of norepinephrine (noradrenaline). The locus coeruleus and the areas of the body affected by the norepinephrine it produces are described collectively as the locus coeruleus-noradrenergic system or LC-NA system. Norepinephrine may also be released directly into the blood from the adrenal medulla. Anatomy The locus coeruleus (LC) is located in the posterior area of the rostral pons in the lateral floor of the fourth ventricle. It is composed of mostly medium-size neurons. Melanin granules inside the neurons of the LC contribute to its blue colour. Thus, it is also known as the nucleus pigmentosus pontis, meaning "heavily pigmented nucleus of the pons." ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fourth Ventricle
The fourth ventricle is one of the four connected fluid-filled cavities within the human brain. These cavities, known collectively as the ventricular system, consist of the left and right lateral ventricles, the third ventricle, and the fourth ventricle. The fourth ventricle extends from the cerebral aqueduct (''aqueduct of Sylvius'') to the obex, and is filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). The fourth ventricle has a characteristic diamond shape in cross-sections of the human brain. It is located within the pons or in the upper part of the medulla oblongata. CSF entering the fourth ventricle through the cerebral aqueduct can exit to the subarachnoid space of the spinal cord through two lateral apertures and a single, midline median aperture. Boundaries The fourth ventricle has a roof at its ''upper'' (posterior) surface and a floor at its ''lower'' (anterior) surface, and side walls formed by the cerebellar peduncles (nerve bundles joining the structure on the posteri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |