|
Subserosa
The subserosa or tela subserosa, is a thin layer of tissue in the walls of various organs. It is a layer of connective tissue (usually of the areolar type) between the muscular layer (muscularis externa) and the serosa (serous membrane). The subserosa has clinical importance particularly in cancer staging (for example, in staging stomach cancer or uterine cancer). The subserosa ('' sub-'' + ''serosa'') is to a serous membrane what the submucosa ('' sub-'' + ''mucosa'') is to a mucous membrane A mucous membrane or mucosa is a membrane that lines various cavities in the body of an organism and covers the surface of internal organs. It consists of one or more layers of epithelial cells overlying a layer of loose connective tissue. It is .... References External links * - "Female Reproductive System: oviduct; infundibulum" Histology at uio.noDiagram at uniklinik-saarland.de Membrane biology {{Digestive-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastric Surface
The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the gastrointestinal tract of humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The stomach has a dilated structure and functions as a vital organ in the digestive system. The stomach is involved in the gastric phase of digestion, following chewing. It performs a chemical breakdown by means of enzymes and hydrochloric acid. In humans and many other animals, the stomach is located between the oesophagus and the small intestine. The stomach secretes digestive enzymes and gastric acid to aid in food digestion. The pyloric sphincter controls the passage of partially digested food (chyme) from the stomach into the duodenum, where peristalsis takes over to move this through the rest of intestines. Structure In the human digestive system, the stomach lies between the oesophagus and the duodenum (the first part of the small intestine). It is in the left upper quadrant of the abdominal cavity. The top of the stomach lies against ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Submucosa
The submucosa (or tela submucosa) is a thin layer of tissue (biology), tissue in various organ (anatomy), organs of the gastrointestinal tract, gastrointestinal, respiratory tract, respiratory, and genitourinary system, genitourinary tracts. It is the layer of dense irregular connective tissue that supports the mucosa (mucous membrane) and joins it to the muscular layer, the bulk of overlying smooth muscle (fibers running circularly within layer of longitudinal muscle). The submucosa (''wikt:sub-#Prefix, sub-'' + ''mucosa'') is to a mucous membrane what the subserosa (''wikt:sub-#Prefix, sub-'' + ''serosa'') is to a serous membrane. Structure Blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, and nerves (all supplying the mucosa) will run through here. In the intestinal wall, tiny parasympathetic ganglia are scattered around forming the submucous plexus (or "Meissner's plexus") where preganglionic parasympathetic neurons synapse with postganglionic nerve fibers that supply the muscularis mucosae. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Submucosa
The submucosa (or tela submucosa) is a thin layer of tissue (biology), tissue in various organ (anatomy), organs of the gastrointestinal tract, gastrointestinal, respiratory tract, respiratory, and genitourinary system, genitourinary tracts. It is the layer of dense irregular connective tissue that supports the mucosa (mucous membrane) and joins it to the muscular layer, the bulk of overlying smooth muscle (fibers running circularly within layer of longitudinal muscle). The submucosa (''wikt:sub-#Prefix, sub-'' + ''mucosa'') is to a mucous membrane what the subserosa (''wikt:sub-#Prefix, sub-'' + ''serosa'') is to a serous membrane. Structure Blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, and nerves (all supplying the mucosa) will run through here. In the intestinal wall, tiny parasympathetic ganglia are scattered around forming the submucous plexus (or "Meissner's plexus") where preganglionic parasympathetic neurons synapse with postganglionic nerve fibers that supply the muscularis mucosae. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastric Pits
Gastric pits are indentations in the stomach which denote entrances to 3-5"Secretions from several gastric glands flow into each gastric pit" Principals of Anatomy & Physiology 15th Ed 2017, Gerard Tortora & Bryan Derrickson tubular shaped gastric glands. They are deeper in the pylorus than they are in the other parts of the stomach. The human stomach has several million of these pits which dot the surface of the lining epithelium. Surface mucous cells line the pits themselves but give way to a series of other types of cells which then line the glands themselves. Gastric acid Gastric acid also known as ''gastric juice'' is secreted from gastric glands, which are located in narrow tube like structures called gastric pits. Gastric juice contains hydrochloric acid, pepsinogen and mucus in a healthy adult. Hydrochloric acid is secreted by parietal cells, pepsinogen is secreted by gastric chief cell A gastric chief cell (or peptic cell, or gastric zymogenic cell) is a type of gast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastric Areas
The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the gastrointestinal tract of humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The stomach has a dilated structure and functions as a vital organ in the digestive system. The stomach is involved in the gastric phase of digestion, following chewing. It performs a chemical breakdown by means of enzymes and hydrochloric acid. In humans and many other animals, the stomach is located between the oesophagus and the small intestine. The stomach secretes digestive enzymes and gastric acid to aid in food digestion. The pyloric sphincter controls the passage of partially digested food (chyme) from the stomach into the duodenum, where peristalsis takes over to move this through the rest of intestines. Structure In the human digestive system, the stomach lies between the oesophagus and the duodenum (the first part of the small intestine). It is in the left upper quadrant of the abdominal cavity. The top of the stomach lies against ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organ (anatomy)
In biology, an organ is a collection of tissues joined in a structural unit to serve a common function. In the hierarchy of life, an organ lies between tissue and an organ system. Tissues are formed from same type cells to act together in a function. Tissues of different types combine to form an organ which has a specific function. The intestinal wall for example is formed by epithelial tissue and smooth muscle tissue. Two or more organs working together in the execution of a specific body function form an organ system, also called a biological system or body system. An organ's tissues can be broadly categorized as parenchyma, the functional tissue, and stroma, the structural tissue with supportive, connective, or ancillary functions. For example, the gland's tissue that makes the hormones is the parenchyma, whereas the stroma includes the nerves that innervate the parenchyma, the blood vessels that oxygenate and nourish it and carry away its metabolic wastes, and the con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uterine Cancer
Uterine cancer, also known as womb cancer, includes two types of cancer that develop from the tissues of the uterus. Endometrial cancer forms from the lining of the uterus, and uterine sarcoma forms from the muscles or support tissue of the uterus. Endometrial cancer accounts for approximately 90% of all uterine cancers in the United States. Symptoms of endometrial cancer include changes in vaginal bleeding or pain in the pelvis. Symptoms of uterine sarcoma include unusual vaginal bleeding or a mass in the vagina. Risk factors for endometrial cancer include obesity, metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes, taking pills that contain estrogen without progesterone, a history of tamoxifen use, late menopause, and a family history of the condition. Risk factors for uterine sarcoma include prior radiation therapy to the pelvis. Diagnosis of endometrial cancer is typically based on an endometrial biopsy. A diagnosis of uterine sarcoma may be suspected based on symptoms, a pelvic exam, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stomach Cancer
Stomach cancer, also known as gastric cancer, is a cancer that develops from the lining of the stomach. Most cases of stomach cancers are gastric carcinomas, which can be divided into a number of subtypes, including gastric adenocarcinomas. Lymphomas and mesenchymal tumors may also develop in the stomach. Early symptoms may include heartburn, upper abdominal pain, nausea, and loss of appetite. Later signs and symptoms may include weight loss, yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes, vomiting, difficulty swallowing, and blood in the stool, among others. The cancer may spread from the stomach to other parts of the body, particularly the liver, lungs, bones, lining of the abdomen, and lymph nodes. The most common cause is infection by the bacterium ''Helicobacter pylori'', which accounts for more than 60% of cases. Certain types of ''H. pylori'' have greater risks than others. Smoking, dietary factors such as pickled vegetables and obesity are other risk factors. About 10% ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cancer Staging
Cancer staging is the process of determining the extent to which a cancer has developed by growing and spreading. Contemporary practice is to assign a number from I to IV to a cancer, with I being an isolated cancer and IV being a cancer that has spread to the limit of what the assessment measures. The stage generally takes into account the size of a tumor, whether it has invaded adjacent organs, how many regional (nearby) lymph nodes it has spread to (if any), and whether it has appeared in more distant locations (metastasized). The staging system is not applicable to astrocytoma, which is instead expressed as "grade I–IV". Grade IV astrocytoma, more commonly referred to as glioblastoma multiforme, is a universally fatal primary brain cancer most commonly seen in the seventh decade of life. TNM staging system Cancer staging can be divided into a clinical stage and a pathologic stage. In the TNM (Tumor, Node, Metastasis) system, clinical stage and pathologic stage are deno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
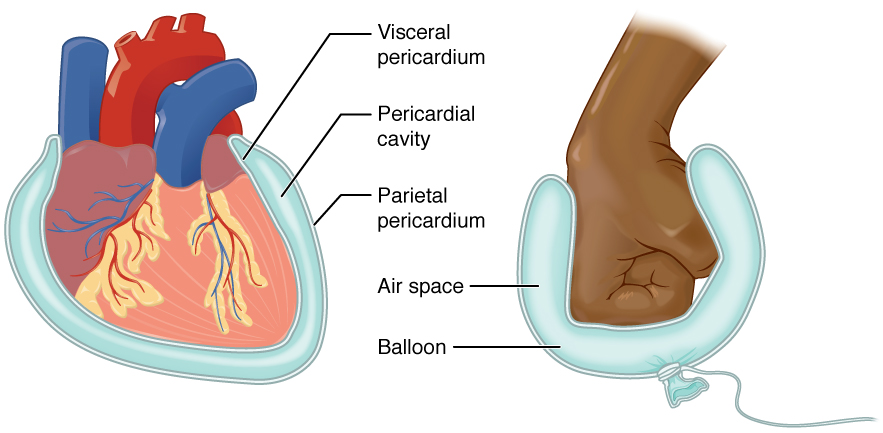
Serous Membrane
The serous membrane (or serosa) is a smooth tissue membrane of mesothelium lining the contents and inner walls of body cavities, which secrete serous fluid to allow lubricated sliding movements between opposing surfaces. The serous membrane that covers internal organs is called a ''visceral'' membrane; while the one that covers the cavity wall is called the ''parietal'' membrane. Between the two opposing serosal surfaces is often a potential space, mostly empty except for the small amount of serous fluid. The Latin anatomical name is '' tunica serosa''. Serous membranes line and enclose several body cavities, also known as serous cavities, where they secrete a lubricating fluid which reduces friction from movements. Serosa is entirely different from the adventitia, a connective tissue layer which binds together structures rather than reducing friction between them. The serous membrane covering the heart and lining the mediastinum is referred to as the pericardium, the sero ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscular Layer
The muscular layer (muscular coat, muscular fibers, muscularis propria, muscularis externa) is a region of muscle in many organs in the vertebrate body, adjacent to the submucosa. It is responsible for gut movement such as peristalsis. The Latin, tunica muscularis, may also be used. Structure It usually has two layers of smooth muscle: * inner and "circular" * outer and "longitudinal" However, there are some exceptions to this pattern. * In the stomach there are three layers to the muscular layer. Stomach contains an additional oblique muscle layer just interior to circular muscle layer. * In the upper esophagus, part of the externa is ''skeletal muscle'', rather than smooth muscle. * In the vas deferens of the spermatic cord, there are three layers: inner longitudinal, middle circular, and outer longitudinal. * In the ureter the smooth muscle orientation is opposite that of the GI tract. There is an inner longitudinal and an outer circular layer. The inner layer of the muscul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |