|
Suboccipital Nerve
The suboccipital nerve (first cervical dorsal ramus) is the dorsal primary ramus of the first cervical nerve (C1). It exits the spinal cord between the skull and the first cervical vertebra, the atlas. It lies within the suboccipital triangle along with the vertebral artery, where the artery enters the foramen magnum. It supplies muscles of the suboccipital triangle, the rectus capitis posterior major, obliquus capitis superior, and obliquus capitis inferior. The suboccipital nerve also innervates rectus capitis posterior minor. See also * Vertebral artery The vertebral arteries are major artery, arteries of the neck. Typically, the vertebral arteries originate from the subclavian arteries. Each vessel courses superiorly along each side of the neck, merging within the skull to form the single, m ... Additional images File:Gray792.png, Upper part of medulla spinalis and hind- and mid-brains; posterior aspect, exposed in situ. File:Suboccipital_triangle.PNG, Suboc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Occipital Bone
The occipital bone () is a neurocranium, cranial dermal bone and the main bone of the occiput (back and lower part of the skull). It is trapezoidal in shape and curved on itself like a shallow dish. The occipital bone lies over the occipital lobes of the cerebrum. At the base of the skull in the occipital bone, there is a large oval opening called the foramen magnum, which allows the passage of the spinal cord. Like the other cranial bones, it is classed as a flat bone. Due to its many attachments and features, the occipital bone is described in terms of separate parts. From its front to the back is the basilar part of occipital bone, basilar part, also called the basioccipital, at the sides of the foramen magnum are the lateral parts of occipital bone, lateral parts, also called the exoccipitals, and the back is named as the squamous part of occipital bone, squamous part. The basilar part is a thick, somewhat quadrilateral piece in front of the foramen magnum and directed toward ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertebral Artery
The vertebral arteries are major artery, arteries of the neck. Typically, the vertebral arteries originate from the subclavian arteries. Each vessel courses superiorly along each side of the neck, merging within the skull to form the single, midline basilar artery. As the supplying component of the ''vertebrobasilar vascular system'', the vertebral arteries supply blood to the upper spinal cord, brainstem, cerebellum, and Cerebral circulation#Posterior cerebral circulation, posterior part of brain. Structure The vertebral arteries usually arise from the posterosuperior aspect of the central subclavian arteries on each side of the body, then enter deep to the transverse process at the level of the 6th cervical vertebrae (C6), or occasionally (in 7.5% of cases) at the level of C7. They then proceed superiorly, in the transverse foramen of each cervical vertebra. Once they have passed through the transverse foramen of C1 (also known as the Atlas (anatomy), atlas), the vertebral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rectus Capitis Posterior Minor
The rectus capitis posterior minor (or rectus capitis posticus minor) is a muscle in the upper back part of the neck. It is one of the suboccipital muscles. Its inferior attachment is at the posterior arch of atlas; its superior attachment is onto the occipital bone at and below the inferior nuchal line. The muscle is innervated by the suboccipital nerve (the posterior ramus of first cervical spinal nerve). The muscle acts as a weak extensor of the head. Anatomy The rectus capitis posterior major muscle is one of the suboccipital muscles. The muscle extends vertically superior-ward from its inferiro attachment to its superior attachment. The muscle becomes broader superiorly. Attachments The inferior attachment is (by a narrow tendon) onto the posterior tubercle of the posterior arch of atlas. Its superior attachment is onto the medial portion of the inferior nuchal line and the external surface of the occipital bone inferior to it (between this line superiorly and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obliquus Capitis Inferior
The obliquus capitis inferior muscle () is a muscle in the upper back of the neck. It is one of the suboccipital muscles. Its inferior attachment is at the spinous process of the axis; its superior attachment is at the transverse process of the atlas. It is innervated by the suboccipital nerve (the posterior ramus of first cervical spinal nerve). The muscle rotates the head to its side. Despite what its name suggest, it is the only capitis (Latin: "head") muscle that does not actually attach to the skull. Anatomy The obliquus capitis inferior is one of the suboccipital muscles (and the only one of these to have no attachment to the skull). It is larger than the obliquus capitis superior muscle. It forms the inferolateral boundary of the suboccipital triangle. The muscle extends laterally and somewhat superiorly from its inferior attachment to its superior attachment. Attachments its inferior attachment is at the lateral external aspect of the bifid spinous process of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obliquus Capitis Superior
The obliquus capitis superior muscle () is a small muscle in the upper back part of the neck. It is one of the suboccipital muscles. It attaches inferiorly at the transverse process of the atlas (first cervical vertebra); it attaches superiorly at the external surface of the occipital bone. The muscle is innervated by the suboccipital nerve (the posterior ramus of the first cervical spinal nerve). It acts at the atlanto-occipital joint to extend the head and bend the head to the same side. Anatomy The obliquus capitis superior muscle is one of the suboccipital muscles. It forms the superolateral boundary of the suboccipital triangle. It extends superoposteriorly from its inferior attachment to its superior attachment, becoming wider superiorly. Attachments The muscle's inferior attachment is at the superior surface of the transverse process of the atlas (C1). Its superior attachment is onto the lateral portion of the external surface of the occipital bone between the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rectus Capitis Posterior Major
The rectus capitis posterior major (or rectus capitis posticus major) is a muscle in the upper back part of the neck. It is one of the suboccipital muscles. Its inferior attachment is at the spinous process of the axis (Second cervical vertebra); its superior attachment is onto the outer surface of the occipital bone on and around the side part of the inferior nuchal line. The muscle is innervated by the suboccipital nerve (the posterior ramus of cervical spinal nerve C1). The muscle acts to extend the head and rotate the head to its side. Anatomy The rectus capitis posterior major muscle is one of the suboccipital muscles. It forms the superomedial boundary of the suboccipital triangle. The muscle extends obliquely superiolaterally from its inferior attachment to its superior attachment. It becomes broader superiorly. Attachments Its inferior attachment is (via a pointed tendon) at (the external aspect of) the (bifid) spinous process of the axis (cervical vertebra C2) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscle
Muscle is a soft tissue, one of the four basic types of animal tissue. There are three types of muscle tissue in vertebrates: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle. Muscle tissue gives skeletal muscles the ability to muscle contraction, contract. Muscle tissue contains special Muscle contraction, contractile proteins called actin and myosin which interact to cause movement. Among many other muscle proteins, present are two regulatory proteins, troponin and tropomyosin. Muscle is formed during embryonic development, in a process known as myogenesis. Skeletal muscle tissue is striated consisting of elongated, multinucleate muscle cells called muscle fibers, and is responsible for movements of the body. Other tissues in skeletal muscle include tendons and perimysium. Smooth and cardiac muscle contract involuntarily, without conscious intervention. These muscle types may be activated both through the interaction of the central nervous system as well as by innervation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foramen Magnum
The foramen magnum () is a large, oval-shaped opening in the occipital bone of the skull. It is one of the several oval or circular openings (foramina) in the base of the skull. The spinal cord, an extension of the medulla oblongata, passes through the foramen magnum as it exits the cranial cavity. Apart from the transmission of the medulla oblongata and its membranes, the foramen magnum transmits the vertebral arteries, the anterior and posterior spinal arteries, the tectorial membranes and alar ligaments. It also transmits the accessory nerve into the skull. The foramen magnum is a very important feature in bipedal mammals. One of the attributes of a biped's foramen magnum is a forward shift of the anterior border of the cerebellar tentorium; this is caused by the shortening of the cranial base. Studies on the foramen magnum position have shown a connection to the functional influences of both posture and locomotion. The forward shift of the foramen magnum is apparent in b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suboccipital Triangle
The suboccipital triangle is a region of the neck bounded by the following three muscles of the suboccipital group of muscles: * Rectus capitis posterior major - above and medially * Obliquus capitis superior - above and laterally * Obliquus capitis inferior - below and laterally (Rectus capitis posterior minor is also in this region but does not form part of the triangle) It is covered by a layer of dense fibro-fatty tissue, situated beneath the semispinalis capitis. The floor is formed by the posterior atlantooccipital membrane, and the posterior arch of the atlas. In the deep groove on the upper surface of the posterior arch of the atlas are the vertebral artery and the first cervical or suboccipital nerve. In the past, the vertebral artery was accessed here in order to conduct angiography of the circle of Willis. Presently, formal angiography of the circle of Willis is performed via catheter angiography, with access usually being acquired at the common femoral artery. Alte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
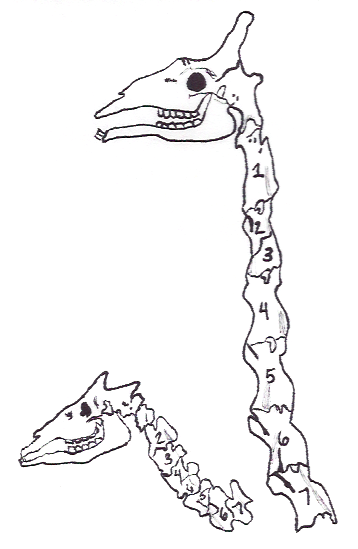
Cervical Vertebrae
In tetrapods, cervical vertebrae (: vertebra) are the vertebrae of the neck, immediately below the skull. Truncal vertebrae (divided into thoracic and lumbar vertebrae in mammals) lie caudal (toward the tail) of cervical vertebrae. In sauropsid species, the cervical vertebrae bear cervical ribs. In lizards and saurischian dinosaurs, the cervical ribs are large; in birds, they are small and completely fused to the vertebrae. The vertebral transverse processes of mammals are homologous to the cervical ribs of other amniotes. Most mammals have seven cervical vertebrae, with the only three known exceptions being the manatee with six, the two-toed sloth with five or six, and the three-toed sloth with nine. In humans, cervical vertebrae are the smallest of the true vertebrae and can be readily distinguished from those of the thoracic or lumbar regions by the presence of a transverse foramen, an opening in each transverse process, through which the vertebral artery, verteb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlas (anatomy)
In anatomy, the atlas (C1) is the most superior (first) cervical vertebra of the spine and is located in the neck. The bone is named for Atlas of Greek mythology, just as Atlas bore the weight of the heavens, the first cervical vertebra supports the head. However, the term atlas was first used by the ancient Romans for the seventh cervical vertebra (C7) due to its suitability for supporting burdens. In Greek mythology, Atlas was condemned to bear the weight of the heavens as punishment for rebelling against Zeus. Ancient depictions of Atlas show the globe of the heavens resting at the base of his neck, on C7. Sometime around 1522, anatomists decided to call the first cervical vertebra the atlas. Scholars believe that by switching the designation atlas from the seventh to the first cervical vertebra Renaissance anatomists were commenting that the point of man's burden had shifted from his shoulders to his head—that man's true burden was not a physical load, but rather, his m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cervical Vertebra
In tetrapods, cervical vertebrae (: vertebra) are the vertebrae of the neck, immediately below the skull. Truncal vertebrae (divided into thoracic and lumbar vertebrae in mammals) lie caudal (toward the tail) of cervical vertebrae. In sauropsid species, the cervical vertebrae bear cervical ribs. In lizards and saurischian dinosaurs, the cervical ribs are large; in birds, they are small and completely fused to the vertebrae. The vertebral transverse processes of mammals are homologous to the cervical ribs of other amniotes. Most mammals have seven cervical vertebrae, with the only three known exceptions being the manatee with six, the two-toed sloth with five or six, and the three-toed sloth with nine. In humans, cervical vertebrae are the smallest of the true vertebrae and can be readily distinguished from those of the thoracic or lumbar regions by the presence of a transverse foramen, an opening in each transverse process, through which the vertebral artery, vertebral veins, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |