|
Subcutaneously
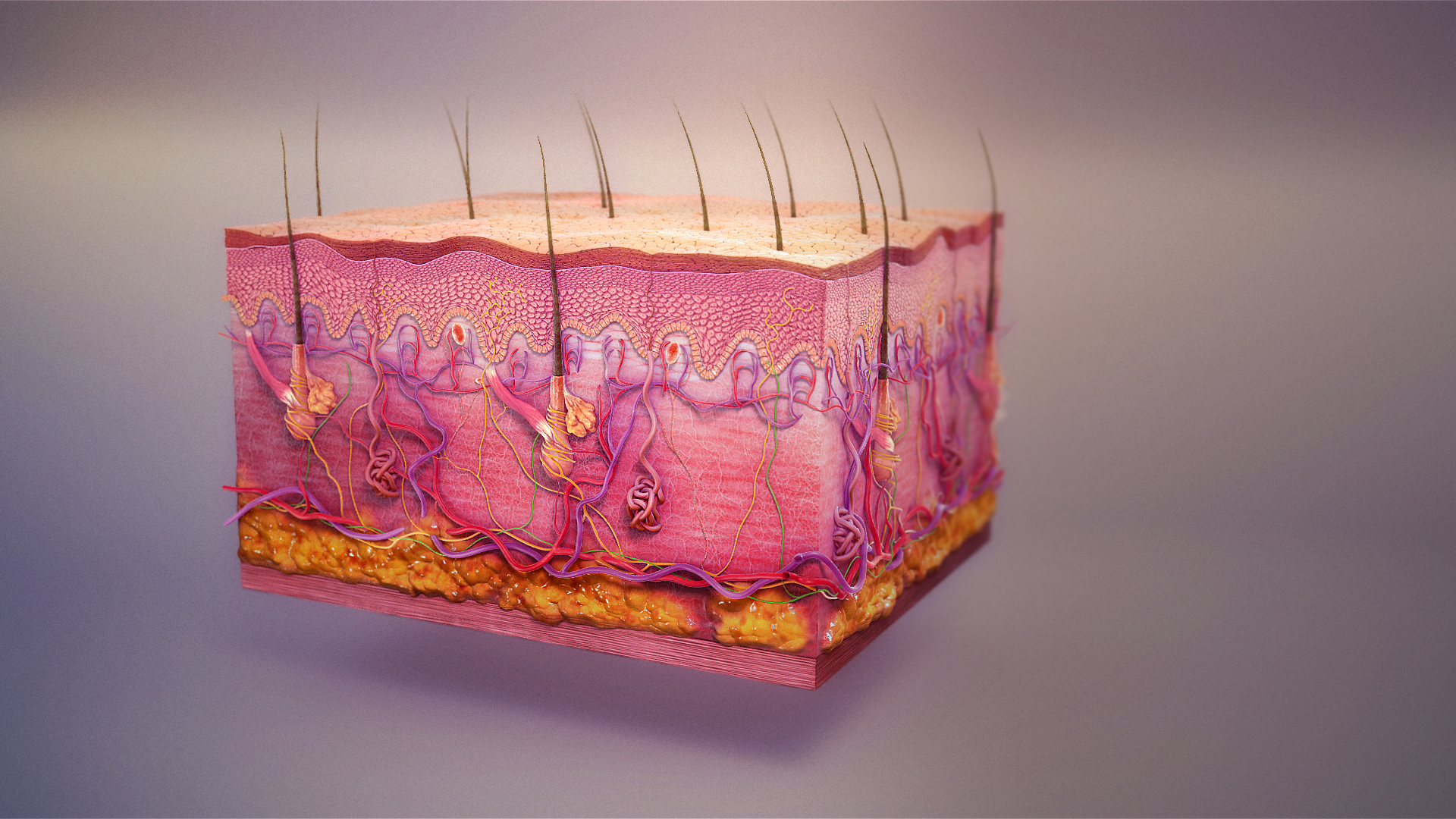
The subcutaneous tissue (), also called the hypodermis, hypoderm (), subcutis, or superficial fascia, is the lowermost layer of the integumentary system in vertebrates. The types of cells found in the layer are fibroblasts, adipose cells, and macrophages. The subcutaneous tissue is derived from the mesoderm, but unlike the dermis, it is not derived from the mesoderm's dermatome region. It consists primarily of loose connective tissue and contains larger blood vessels and nerves than those found in the dermis. It is a major site of fat storage in the body. In arthropods, a hypodermis can refer to an epidermal layer of cells that secretes the chitinous cuticle. The term also refers to a layer of cells lying immediately below the epidermis of plants. Structure * Fibrous bands anchoring the skin to the deep fascia * Collagen and elastin fibers attaching it to the dermis * Fat is absent from the eyelids, clitoris, penis, much of pinna, and scrotum * Blood vessels on route to the de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integumentary
The integumentary system is the set of organs forming the outermost layer of an animal's body. It comprises the skin and its appendages, which act as a physical barrier between the external environment and the internal environment that it serves to protect and maintain the body of the animal. Mainly it is the body's outer skin. The integumentary system includes skin, hair, Scale (zoology), scales, feathers, Hoof, hooves, claws, and Nail (anatomy), nails. It has a variety of additional functions: it may serve to maintain water balance, protect the deeper tissues, excrete wastes, and regulate Core temperature, body temperature, and is the attachment site for sensory receptors which detect pain, sensation, pressure, and temperature. Structure Skin The skin is one of the largest organs of the body. In humans, it accounts for about 12 to 15 percent of total body weight and covers 1.5 to 2 m2 of surface area. The skin (integument) is a composite organ, made up of at least two maj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elastin
Elastin is a protein encoded by the ''ELN'' gene in humans and several other animals. Elastin is a key component in the extracellular matrix of gnathostomes (jawed vertebrates). It is highly Elasticity (physics), elastic and present in connective tissue of the body to resume its shape after stretching or contracting. Elastin helps skin return to its original position whence poked or pinched. Elastin is also in important load-bearing tissue of vertebrates and used in places where storage of mechanical energy is required. Function The ''ELN'' gene encodes a protein that is one of the two components of elastic fibers. The encoded protein is rich in hydrophobic amino acids such as glycine and proline, which form mobile hydrophobic regions bounded by crosslinks between lysine residues. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. Elastin's soluble precursor is tropoelastin. Mechanism of elastic recoil The characterization of disorder is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panniculus Adiposus
The panniculus adiposus is the fatty layer of the subcutaneous tissues, superficial to a deeper vestigial layer of muscle, the panniculus carnosus.McGrath, J.A.; Eady, R.A.; Pope, F.M. (2004). ''Rook's Textbook of Dermatology'' (Seventh Edition). Blackwell Publishing. Page 3.1. . It includes structures that are considered fascia by some sources but not by others. Some examples include the fascia of Camper and the superficial cervical fascia. A group of disorders of inflammation of this layer is called panniculitis. References Skin anatomy {{dermatology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anchor Comment
An anchor is a device, normally made of metal, used to secure a Watercraft, vessel to the Seabed, bed of a body of water to prevent the craft from drifting due to Leeway, wind or Ocean current, current. The word derives from Latin ', which itself comes from the Greek language, Greek (). Anchors can either be temporary or permanent. Permanent anchors are used in the creation of a mooring (watercraft)#Permanent anchor mooring, mooring, and are rarely moved; a specialist service is normally needed to move or maintain them. Vessels carry one or more temporary anchors, which may be of different designs and weights. A sea anchor is a drag device, not in contact with the seabed, used to minimize drift of a vessel relative to the water. A drogue is a drag device used to slow or help steer a vessel Point of sail, running before a storm in a following or overtaking sea, or when crossing a bar in a breaking sea. Anchoring Anchors achieve holding power either by "hooking" i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anchor
An anchor is a device, normally made of metal, used to secure a vessel to the bed of a body of water to prevent the craft from drifting due to wind or current. The word derives from Latin ', which itself comes from the Greek (). Anchors can either be temporary or permanent. Permanent anchors are used in the creation of a mooring, and are rarely moved; a specialist service is normally needed to move or maintain them. Vessels carry one or more temporary anchors, which may be of different designs and weights. A sea anchor is a drag device, not in contact with the seabed, used to minimize drift of a vessel relative to the water. A drogue is a drag device used to slow or help steer a vessel running before a storm in a following or overtaking sea, or when crossing a bar in a breaking sea. Anchoring Anchors achieve holding power either by "hooking" into the seabed, or weight, or a combination of the two. The weight of the anchor chain can be more than that of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panniculus Carnosus
The panniculus carnosus is a part of the subcutaneous tissues in vertebrates. It is a layer of striated muscle deep to the panniculus adiposus.McGrath, J.A.; Eady, R.A.; Pope, F.M. (2004). ''Rook's Textbook of Dermatology'' (Seventh Edition). Blackwell Publishing. Page 3.1. . In humans, the platysma muscle of the neck, palmaris brevis in the hand, and the dartos muscle in the scrotum are described as a discrete muscle of the panniculus carnosus. Some of the muscles of facial expression in the head are part of the panniculus carnosus. In other parts of the body, the layer is vestigial, and may be absent or may exist only as microscopic, disconnected fibers. In other animals, the panniculus carnosus is more extensive. For example, the panniculus carnosus in the echidna covers almost its entire body, enabling it to change its shape to a certain degree, most characteristically by rolling into a ball and presenting its spines to a potential predator Predation is a biolog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mast Cells
A mast cell (also known as a mastocyte or a labrocyte) is a resident cell of connective tissue that contains many granules rich in histamine and heparin. Specifically, it is a type of granulocyte derived from the myeloid stem cell that is a part of the immune and neuroimmune systems. Mast cells were discovered by Friedrich von Recklinghausen and later rediscovered by Paul Ehrlich in 1877. Although best known for their role in allergy and anaphylaxis, mast cells play an important protective role as well, being intimately involved in wound healing, angiogenesis, immune tolerance, defense against pathogens, and vascular permeability in brain tumors. The mast cell is very similar in both appearance and function to the basophil, another type of white blood cell. Although mast cells were once thought to be tissue-resident basophils, it has been shown that the two cells develop from different hematopoietic lineages and thus cannot be the same cells. Structure Mast cells ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacinian Corpuscles
The Pacinian corpuscle (also lamellar corpuscle, or Vater–Pacini corpuscle) is a low-threshold mechanoreceptor responsive to vibration or pressure, found in the skin and other internal organs. In the skin it is one of the four main types of cutaneous receptors. The corpuscles are present in skin notably on both surfaces of the hands and feet, arms, and neck. Pacinian corpuscles are also found on periosteum, bone periosteum, joint capsules, the pancreas and other internal organs, the breast, genitals, and Lymph node, lymph nodes. Pacinian corpuscles are rapidly adapting mechanoreceptors. As phasic receptors they respond quickly but briefly to a stimulus with the response diminishing even when the stimulus is maintained. They primarily respond to vibration, and deep pressure. They are especially sensitive to high-frequency vibrations. Groups of corpuscles sense pressure changes (such as on grasping or releasing an object). They are additionally crucially involved in proprioception ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ruffini Ending
The bulbous corpuscle, Ruffini ending or Ruffini corpuscle is a slowly adapting mechanoreceptor A mechanoreceptor, also called mechanoceptor, is a sensory receptor that responds to mechanical pressure or distortion. Mechanoreceptors are located on sensory neurons that convert mechanical pressure into action potential, electrical signals tha ... located in the cutaneous tissue between the dermal papillae and the hypodermis. It is named after Angelo Ruffini. Structure Ruffini corpuscles are enlarged dendritic endings with elongated capsules. Function This spindle-shaped receptor is sensitive to skin stretch, and contributes to the kinesthetic sense of and control of finger position and movement. They are at the highest density around the fingernails where they act in monitoring slippage of objects along the surface of the skin, allowing modulation of grip on an object. Ruffini corpuscles respond to sustained pressure and show very little adaptation. Ruffinian endings are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apocrine Sweat Glands
An apocrine sweat gland (; from Greek ''apo'' 'away' and ''krinein'' 'to separate') is composed of a coiled secretory portion located at the junction of the dermis and subcutaneous fat, from which a straight portion inserts and secretes into the infundibular portion of the hair follicle. In humans, apocrine sweat glands are found only in certain locations of the body: the axillae (armpits), areola and nipples of the breast, ear canal, eyelids, wings of the nostril, perineal region, and some parts of the external genitalia. Modified apocrine glands include the ciliary glands (glands of Moll) in the eyelids; the ceruminous glands, which produce ear wax; and the mammary glands, which produce milk. They are distinct from eccrine sweat glands, which cover the whole body. Most non-primate mammals, however, have apocrine sweat glands over the greater part of their body. Domestic animals such as dogs and cats have apocrine glands at each hair follicle and even in their urinary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
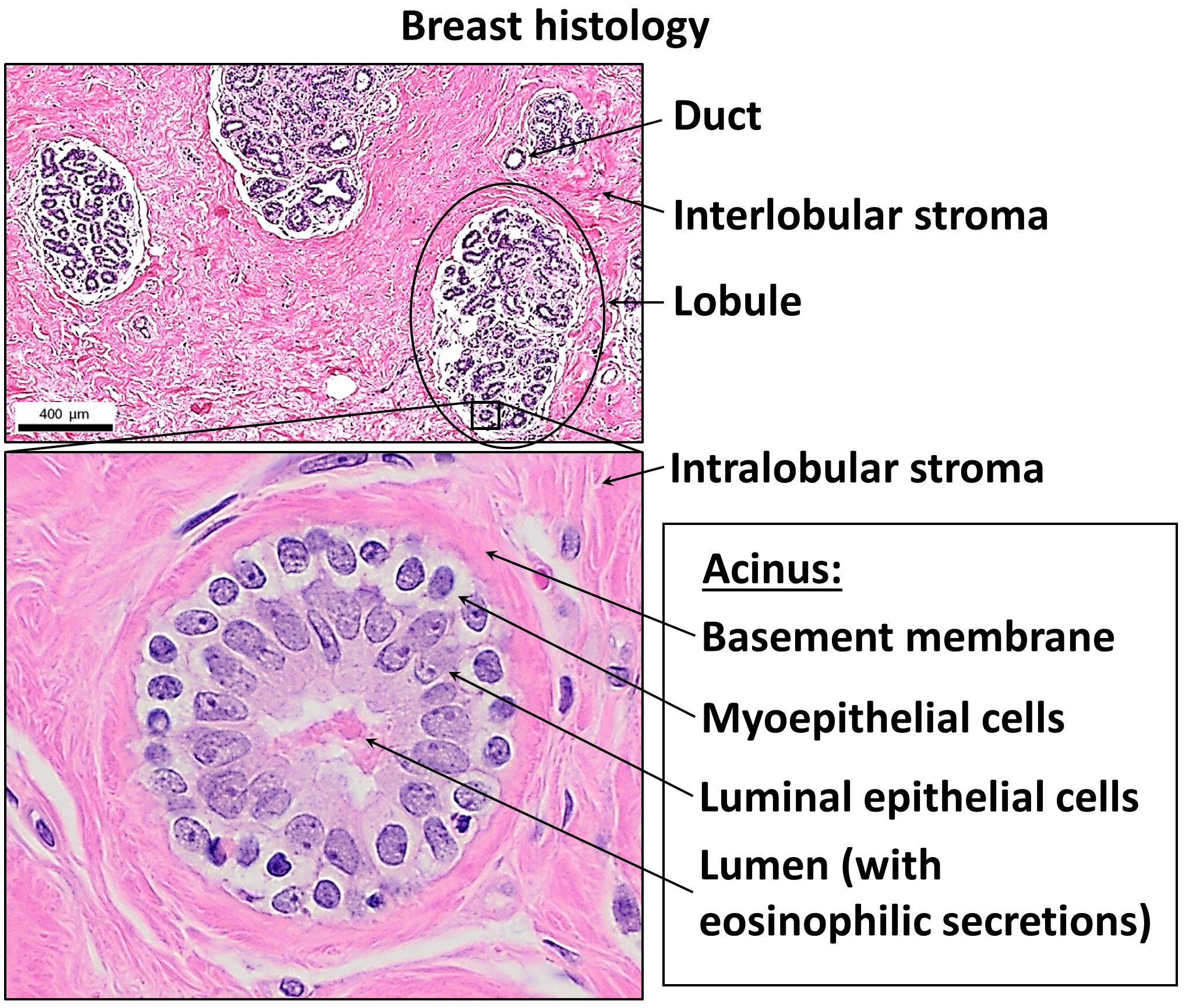
Mammary Glands
A mammary gland is an exocrine gland that produces milk in humans and other mammals. Mammals get their name from the Latin word ''mamma'', "breast". The mammary glands are arranged in organs such as the breasts in primates (for example, humans and chimpanzees), the udder in ruminants (for example, cows, goats, sheep, and deer), and the dugs of other animals (for example, dogs and cats) to feed young offspring. Lactorrhea, the occasional production of milk by the glands, can occur in any mammal, but in most mammals, lactation, the production of enough milk for nursing, occurs only in phenotypic females who have gestated in recent months or years. It is directed by hormonal guidance from sex steroids. In a few mammalian species, male lactation can occur. With humans, male lactation can occur only under specific circumstances. Mammals are divided into 3 groups: monotremes, metatherians, and eutherians. In the case of monotremes, their mammary glands are modified sebaceou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |