|
Suaeda Aralocaspica
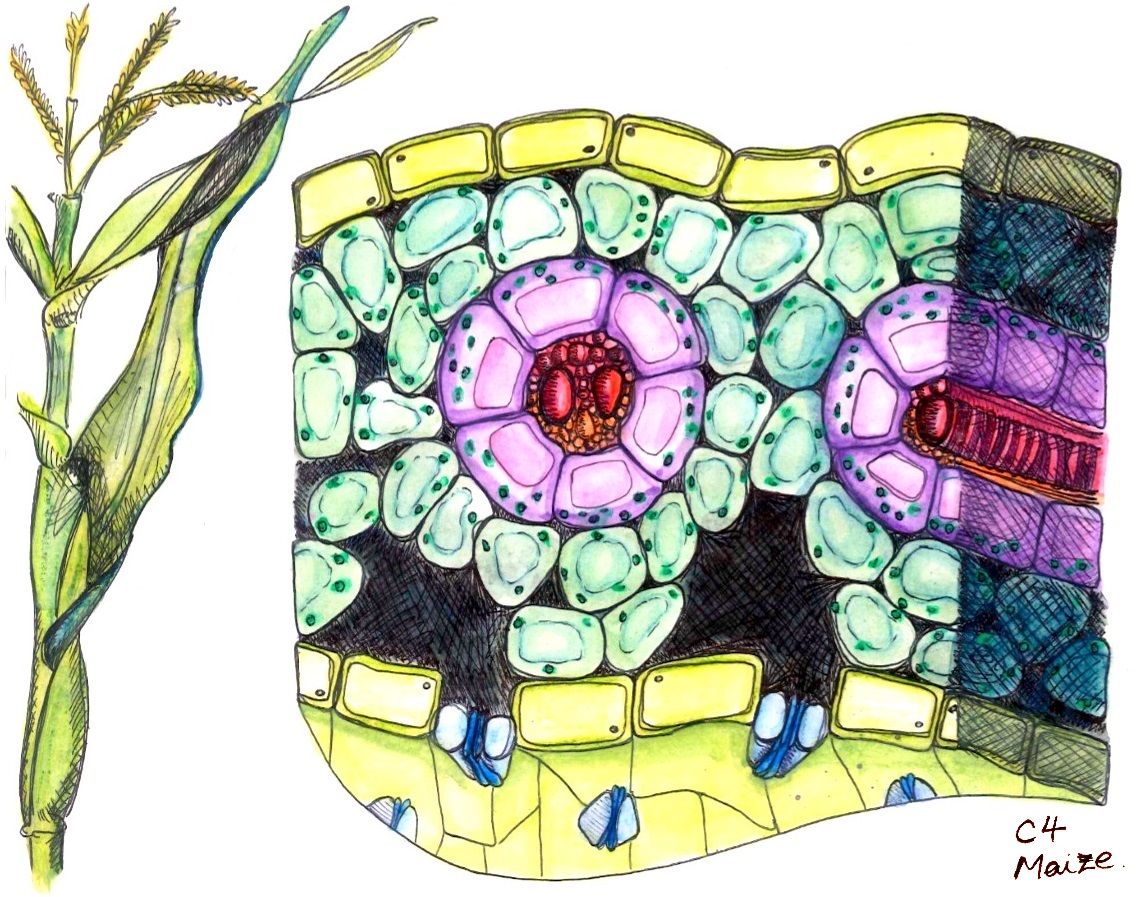
''Suaeda aralocaspica'' is a species of plant in the family Amaranthaceae that is restricted to the deserts of Central Asia. It is a halophyte and uses carbon fixation but lacks the characteristic leaf anatomy of other plants (known as kranz anatomy). Carrying out complete C4 photosynthesis within individual cells, these plants instead are known as single‐cell C4 system or SCC4 plants. This makes them distinct from typical C4 plants, which require the collaboration of two types of photosynthetic cells. SCC4 plants have features that make them potentially valuable in engineering higher photosynthetic efficiencies in agriculturally important C3 carbon fixation species such as rice. To address this, the 467 Mb genome of ''S. aralocaspica'' has been sequenced to help understanding of the evolution of SCC4 photosynthesis and contribute to the engineering of C4 photosynthesis into other economically important crops. It is monoecious, annual and grows to a height of between . ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Von Bunge
Alexander Georg von Bunge (russian: Алекса́ндр Андре́евич Бу́нге; – ) was a Russian botanist. He is best remembered for scientific expeditions into Asia and especially Siberia. Early life and education Bunge was born under the name, Alexander Andreevič von Bunge on in Kyiv as second son of a family that belonged to the German minority in Tsarist Russia. HIs father, Andreas Theodor was a pharmacist who had emigrated from East Prussia to Russia with his grandfather in the 18th century and his mother, Elisabeth von Bunge, . They moved to Dorpat in 1815 after his father's death in 1814 and attended highschool from 1818 to 1821. He was educated at Dorpat and where he passed through the gymnasium during the period of 1821–1825. Then, he studied medicine and obtained his Doctorate of Medicine from University of Tartu on 1825. He also studied botany there under Carl Friedrich von Ledebour and completed his thesis entitled ''De relatione methodi pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amaranthaceae
Amaranthaceae is a family of flowering plants commonly known as the amaranth family, in reference to its type genus ''Amaranthus''. It includes the former goosefoot family Chenopodiaceae and contains about 165 genera and 2,040 species, making it the most species-rich lineage within its parent order, Caryophyllales. Description Vegetative characters Most species in the Amaranthaceae are annual or perennial herbs or subshrubs; others are shrubs; very few species are vines or trees. Some species are succulent. Many species have stems with thickened nodes. The wood of the perennial stem has a typical "anomalous" secondary growth; only in subfamily Polycnemoideae is secondary growth normal. The leaves are simple and mostly alternate, sometimes opposite. They never possess stipules. They are flat or terete, and their shape is extremely variable, with entire or toothed margins. In some species, the leaves are reduced to minute scales. In most cases, neither basal nor terminal aggrega ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a subregion, region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes the former Soviet Union, Soviet republics of the Soviet Union, republics of Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan, which are colloquially referred to as the "-stans" as the countries all have names ending with the Persian language, Persian suffix "-stan", meaning "land of". The current geographical location of Central Asia was formerly part of the historic region of Turkestan, Turkistan, also known as Turan. In the pre-Islamic and early Islamic eras ( and earlier) Central Asia was inhabited predominantly by Iranian peoples, populated by Eastern Iranian languages, Eastern Iranian-speaking Bactrians, Sogdians, Khwarezmian language, Chorasmians and the semi-nomadic Scythians and Dahae. After expansion by Turkic peop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halophyte
A halophyte is a salt-tolerant plant that grows in soil or waters of high salinity, coming into contact with saline water through its roots or by salt spray, such as in saline semi-deserts, mangrove swamps, marshes and sloughs and seashores. The word derives from Ancient Greek ἅλας (halas) 'salt' and φυτόν (phyton) 'plant'. Halophytes have different anatomy, physiology and biochemistry than glycophytes.Physiology of halophytes, T. J. FLOWERS, Plant and Soil 89, 41-56 (1985) An example of a halophyte is the salt marsh grass ''Spartina alterniflora'' (smooth cordgrass). Relatively few plant species are halophytes—perhaps only 2% of all plant species. Information about many of the earth's halophytes can be found in thehalophdatabase. The large majority of plant species are glycophytes, which are not salt-tolerant and are damaged fairly easily by high salinity. Classification Halophytes can be classified in many ways. According to Stocker (1933), it is mainly of 3 kin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C4 Carbon Fixation
carbon fixation or the Hatch–Slack pathway is one of three known photosynthetic processes of carbon fixation in plants. It owes the names to the 1960's discovery by Marshall Davidson Hatch and Charles Roger Slack that some plants, when supplied with 14, incorporate the 14C label into four-carbon molecules first. fixation is an addition to the ancestral and more common carbon fixation. The main carboxylating enzyme in photosynthesis is called RuBisCO, which catalyses two distinct reactions using either (carboxylation) or oxygen (oxygenation) as a substrate. The latter process, oxygenation, gives rise to the wasteful process of photorespiration. photosynthesis reduces photorespiration by concentrating around RuBisCO. To ensure that RuBisCO works in an environment where there is a lot of carbon dioxide and very little oxygen, leaves generally differentiate two partially isolated compartments called mesophyll cells and bundle-sheath cells. is initially fixed in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kranz Anatomy
carbon fixation or the Hatch–Slack pathway is one of three known photosynthetic processes of carbon fixation in plants. It owes the names to the 1960's discovery by Marshall Davidson Hatch and Charles Roger Slack that some plants, when supplied with 14, incorporate the 14C label into four-carbon molecules first. fixation is an addition to the ancestral and more common carbon fixation. The main carboxylating enzyme in photosynthesis is called RuBisCO, which catalyses two distinct reactions using either (carboxylation) or oxygen (oxygenation) as a substrate. The latter process, oxygenation, gives rise to the wasteful process of photorespiration. photosynthesis reduces photorespiration by concentrating around RuBisCO. To ensure that RuBisCO works in an environment where there is a lot of carbon dioxide and very little oxygen, leaves generally differentiate two partially isolated compartments called mesophyll cells and bundle-sheath cells. is initially fixed in the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C3 Carbon Fixation
carbon fixation is the most common of three metabolic pathways for carbon fixation in photosynthesis, along with and CAM. This process converts carbon dioxide and ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP, a 5-carbon sugar) into two molecules of 3-phosphoglycerate through the following reaction: :CO2 + H2O + RuBP → (2) 3-phosphoglycerate This reaction was first discovered by Melvin Calvin, Andrew Benson and James Bassham in 1950. C3 carbon fixation occurs in all plants as the first step of the Calvin–Benson cycle. (In and CAM plants, carbon dioxide is drawn out of malate and into this reaction rather than directly from the air.) Plants that survive solely on fixation ( plants) tend to thrive in areas where sunlight intensity is moderate, temperatures are moderate, carbon dioxide concentrations are around 200 ppm or higher, and groundwater is plentiful. The plants, originating during Mesozoic and Paleozoic eras, predate the plants and still represent approximately 95% of Eart ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monoecious
Monoecy (; adj. monoecious ) is a sexual system in seed plants where separate male and female cones or flowers are present on the same plant. It is a monomorphic sexual system alongside gynomonoecy, andromonoecy and trimonoecy. Monoecy is connected to anemophily. It can prevent self-pollination in an individual flower but cannot prevent self-pollination between male and female flowers on the same plant. Monoecy in angiosperms has been of interest for evolutionary biologists since Charles Darwin. Terminology Monoecious comes from the Greek words for one house. History The term monoecy was first introduced in 1735 by Carl Linnaeus. Darwin noted that the flowers of monoecious species sometimes showed traces of the opposite sex function. Monoecious hemp was first reported in 1929. Occurrence Monoecy is most common in temperate climates and is often associated with inefficient pollinators or wind-pollinated plants. It may be beneficial to reducing pollen-stigma interferenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annual Plant
An annual plant is a plant that completes its life cycle, from germination to the production of seeds, within one growing season, and then dies. The length of growing seasons and period in which they take place vary according to geographical location, and may not correspond to the four traditional seasonal divisions of the year. With respect to the traditional seasons, annual plants are generally categorized into summer annuals and winter annuals. Summer annuals germinate during spring or early summer and mature by autumn of the same year. Winter annuals germinate during the autumn and mature during the spring or summer of the following calendar year. One seed-to-seed life cycle for an annual plant can occur in as little as a month in some species, though most last several months. Oilseed rapa can go from seed-to-seed in about five weeks under a bank of fluorescent lamps. This style of growing is often used in classrooms for education. Many desert annuals are therophytes, be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suaeda
__NOTOC__ ''Suaeda'' is a genus of plants also known as seepweeds and sea-blites. Most species are confined to saline or alkaline soil habitats, such as coastal salt-flats and tidal wetlands. Many species have thick, succulent leaves, a characteristic seen in various plant genera that thrive in salty habitats (halophile plants). There are about 110 species in the genus ''Suaeda''. The most common species in northwestern Europe is ''S. maritima''. It grows along the coasts, especially in saltmarsh areas, and is known in Britain as "common sea-blite", but as "herbaceous seepweed" in the USA. It is also common along the east coast of North America from Virginia northward. One of its varieties is common in tropical Asia on the land-side edge of mangrove tidal swamps. Another variety of this polymorphic species is common in tidal zones all around Australia (''Suaeda maritima var. australis'' is also classed as ''S. australis''). On the coasts of the Mediterranean Sea a common ''Sua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flora Of Central Asia
Flora is all the plant life present in a particular region or time, generally the naturally occurring (indigenous) native plants. Sometimes bacteria and fungi are also referred to as flora, as in the terms ''gut flora'' or '' skin flora''. Etymology The word "flora" comes from the Latin name of Flora, the goddess of plants, flowers, and fertility in Roman mythology. The technical term "flora" is then derived from a metonymy of this goddess at the end of the sixteenth century. It was first used in poetry to denote the natural vegetation of an area, but soon also assumed the meaning of a work cataloguing such vegetation. Moreover, "Flora" was used to refer to the flowers of an artificial garden in the seventeenth century. The distinction between vegetation (the general appearance of a community) and flora (the taxonomic composition of a community) was first made by Jules Thurmann (1849). Prior to this, the two terms were used indiscriminately.Thurmann, J. (1849). ''Essai de Phy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barilla Plants
''Barilla'' refers to several species of salt-tolerant (halophyte) plants that, until the 19th century, were the primary source of soda ash and hence of sodium carbonate. The word "barilla" was also used directly to refer to the soda ash obtained from plant sources. The word is an anglicization of the Spanish word ''barrilla'' for saltwort plants (a particular category of halophytes). A very early reference indicating the value placed upon soda ash in Catalonia has been given by Glick, who notes that "In 1189 the monastery of Poblet granted to the glassblower Guillem the right to gather glasswort in return for tithe and two hundred pounds of sheet glass paid annually (The site of these glassworks, at Narola, was excavated in 1935.)." By the 18th century, Spain's barilla industry was exporting large quantities of soda ash of exceptional purity; the product was refined from the ashes of barilla plants that were specifically cultivated for this purpose. Presumably the word "barilla" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)