|
Study Of Health In Pomerania
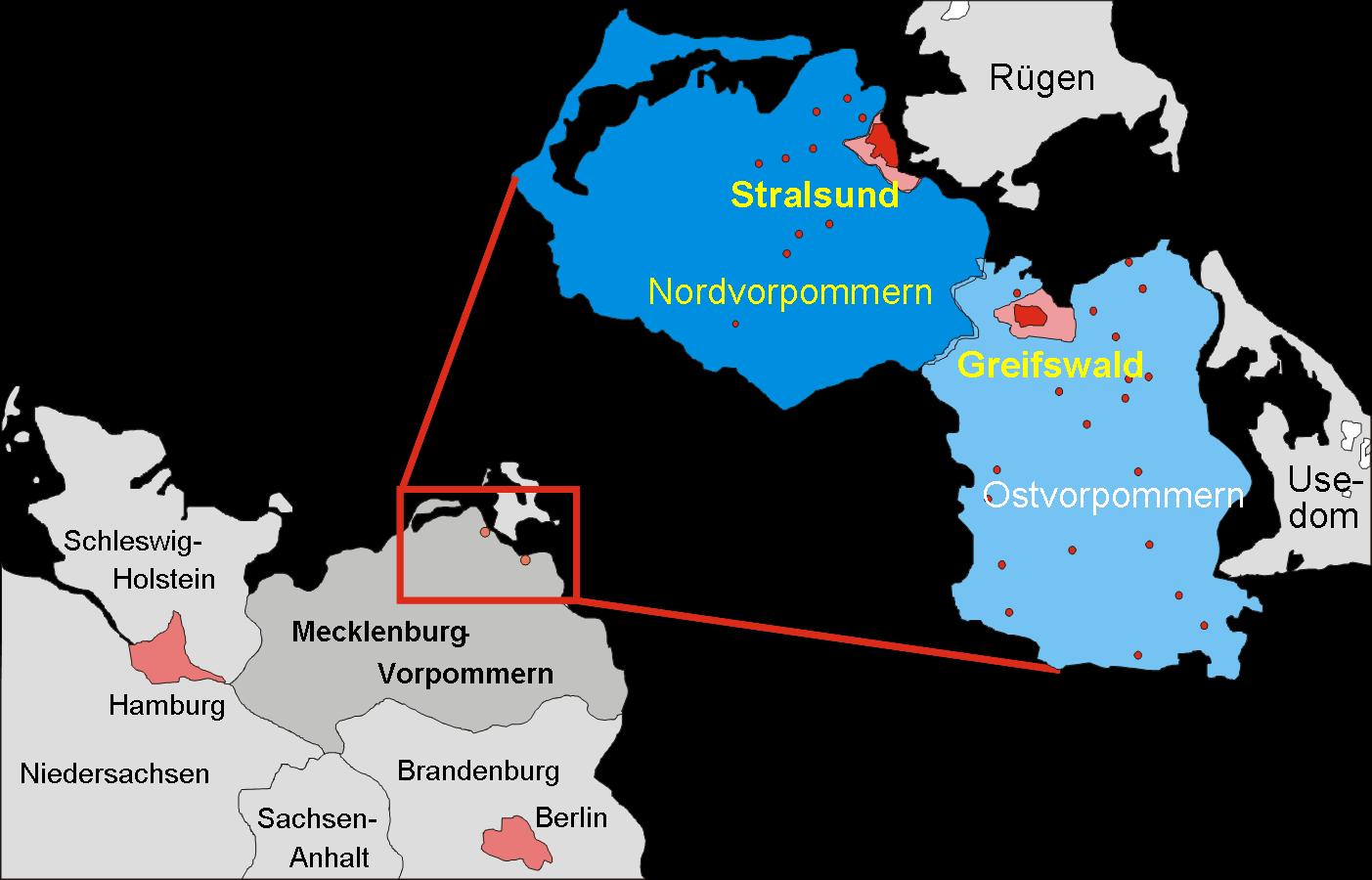
The Study of Health in Pomerania (SHIP) is a population-based epidemiological study consisting of two independent cohorts (SHIP and SHIP-TREND). The SHIP investigates common risk factors, subclinical disorders and manifest diseases with highly innovative non-invasive methods in the high-risk population of northeast Germany. The study is not interested in one specific disease. The SHIP study´s main aims include the investigation of health in all its aspects and complexity involving the collection and assessment of data relevant to the prevalence and incidence of common, population-relevant diseases and their risk factors. Design The aims of both studies are: (i) investigation of the long-term progression of subclinical findings, their determinants and prognostic values (SHIP-2); (ii) analysis of the secular trend of subclinical and overt diseases and their determinants in a high-risk population (SHIP-TREND vs SHIP-0); and (iii) assessment of the prevalence of subclinical findin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epidemiology
Epidemiology is the study and analysis of the distribution (who, when, and where), patterns and determinants of health and disease conditions in a defined population. It is a cornerstone of public health, and shapes policy decisions and evidence-based practice by identifying risk factors for disease and targets for preventive healthcare. Epidemiologists help with study design, collection, and statistical analysis of data, amend interpretation and dissemination of results (including peer review and occasional systematic review). Epidemiology has helped develop methodology used in clinical research, public health studies, and, to a lesser extent, basic research in the biological sciences. Major areas of epidemiological study include disease causation, transmission, outbreak investigation, disease surveillance, environmental epidemiology, forensic epidemiology, occupational epidemiology, screening, biomonitoring, and comparisons of treatment effects such as in clinical trials. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fatty Liver
Fatty liver disease (FLD), also known as hepatic steatosis, is a condition where excess fat builds up in the liver. Often there are no or few symptoms. Occasionally there may be tiredness or pain in the upper right side of the abdomen. Complications may include cirrhosis, liver cancer, and esophageal varices. There are two types of fatty liver disease: non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and alcoholic liver disease. NAFLD is made up of simple fatty liver and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). The primary risks include alcohol, type 2 diabetes, and obesity. Other risk factors include certain medications such as glucocorticoids, and hepatitis C. It is unclear why some people with NAFLD develop simple fatty liver and others develop NASH. Diagnosis is based on the medical history supported by blood tests, medical imaging, and occasionally liver biopsy. Treatment of NAFLD is generally by dietary changes and exercise to bring about weight loss. In those who are severely affec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallstone
A gallstone is a calculus (medicine), stone formed within the gallbladder from precipitated bile components. The term cholelithiasis may refer to the presence of gallstones or to any disease caused by gallstones, and choledocholithiasis refers to the presence of migrated gallstones within bile ducts. Most people with gallstones (about 80%) are asymptomatic. However, when a gallstone obstructs the bile duct and causes acute cholestasis, a reflexive smooth muscle spasm often occurs, resulting in an intense cramp-like visceral pain in the quadrant (abdomen), right upper part of the abdomen known as a biliary colic (or "gallbladder attack"). This happens in 1–4% of those with gallstones each year. Complications from gallstones may include inflammation of the gallbladder (cholecystitis), inflammation of the pancreas (pancreatitis), Jaundice#Post-hepatic, obstructive jaundice, and infection in bile ducts (ascending cholangitis, cholangitis). Symptoms of these complications may include ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obesity
Obesity is a medical condition, sometimes considered a disease, in which excess body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it may negatively affect health. People are classified as obese when their body mass index (BMI)—a person's weight divided by the square of the person's height—is over ; the range is defined as overweight. Some East Asian countries use lower values to calculate obesity. Obesity is a major cause of disability and is correlated with various diseases and conditions, particularly cardiovascular diseases, type 2 diabetes, obstructive sleep apnea, certain types of cancer, and osteoarthritis. Obesity has individual, socioeconomic, and environmental causes. Some known causes are diet, physical activity, automation, urbanization, genetic susceptibility, medications, mental disorders, economic policies, endocrine disorders, and exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemicals. While a majority of obese individuals at any given time are attempting to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overweight
Being overweight or fat is having more body fat than is optimally healthy. Being overweight is especially common where food supplies are plentiful and lifestyles are sedentary. , excess weight reached epidemic proportions globally, with more than 1 billion adults being either overweight or obese. In 2013, this increased to more than 2 billion. Increases have been observed across all age groups. A healthy body requires a minimum amount of fat for proper functioning of the hormonal, reproductive, and immune systems, as thermal insulation, as shock absorption for sensitive areas, and as energy for future use; however, the accumulation of too much storage fat can impair movement, flexibility, and alter the appearance of the body. Classification The degree to which a person is overweight is generally described by the body mass index (BMI). ''Overweight'' is defined as a BMI of 25 or more, thus it includes pre-obesity defined as a BMI between 25 and 29.9 and obesity as de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Population
Population typically refers to the number of people in a single area, whether it be a city or town, region, country, continent, or the world. Governments typically quantify the size of the resident population within their jurisdiction using a census, a process of collecting, analysing, compiling, and publishing data regarding a population. Perspectives of various disciplines Social sciences In sociology and population geography, population refers to a group of human beings with some predefined criterion in common, such as location, race, ethnicity, nationality, or religion. Demography is a social science which entails the statistical study of populations. Ecology In ecology, a population is a group of organisms of the same species who inhabit the same particular geographical area and are capable of interbreeding. The area of a sexual population is the area where inter-breeding is possible between any pair within the area and more probable than cross-breeding with in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Instruments Interviews SHIP
Instrument may refer to: Science and technology * Flight instruments, the devices used to measure the speed, altitude, and pertinent flight angles of various kinds of aircraft * Laboratory equipment, the measuring tools used in a scientific laboratory, often electronic in nature * Mathematical instrument, devices used in geometric construction or measurements in astronomy, surveying and navigation * Measuring instrument, a device used to measure or compare physical properties * Medical instrument, a device used to diagnose or treat diseases * Optical instrument, relies on the properties of light * Quantum instrument, a mathematical object in quantum theory combining the concepts of measurement and quantum operation * Scientific instrument, a device used to collect scientific data * Surgical instrument * Vehicle instrument, a device measuring parameters of a vehicle, such as its speed or position * Weather instrument, a device used to record aspects of the weather Music * Mus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Questionnaires 27102010
A questionnaire is a research instrument that consists of a set of questions (or other types of prompts) for the purpose of gathering information from respondents through survey or statistical study. A research questionnaire is typically a mix of close-ended questions and open-ended questions. Open-ended, long-term questions offer the respondent the ability to elaborate on their thoughts. The Research questionnaire was developed by the Statistical Society of London in 1838. Although questionnaires are often designed for statistical analysis of the responses, this is not always the case. Questionnaires have advantages over some other types of surveys in that they are cheap, do not require as much effort from the questioner as verbal or telephone surveys, and often have standardized answers that make it simple to compile data. However, such standardized answers may frustrate users as the possible answers may not accurately represent their desired responses. Questionnaires are also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Instruments SHIP 27
Instrument may refer to: Science and technology * Flight instruments, the devices used to measure the speed, altitude, and pertinent flight angles of various kinds of aircraft * Laboratory equipment, the measuring tools used in a scientific laboratory, often electronic in nature * Mathematical instrument, devices used in geometric construction or measurements in astronomy, surveying and navigation * Measuring instrument, a device used to measure or compare physical properties * Medical instrument, a device used to diagnose or treat diseases * Optical instrument, relies on the properties of light * Quantum instrument, a mathematical object in quantum theory combining the concepts of measurement and quantum operation * Scientific instrument, a device used to collect scientific data * Surgical instrument * Vehicle instrument, a device measuring parameters of a vehicle, such as its speed or position * Weather instrument, a device used to record aspects of the weather Music * Mus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Summer
Summer is the hottest of the four temperate seasons, occurring after spring and before autumn. At or centred on the summer solstice, the earliest sunrise and latest sunset occurs, daylight hours are longest and dark hours are shortest, with day length decreasing as the season progresses after the solstice. The date of the beginning of summer varies according to climate, tradition, and culture. When it is summer in the Northern Hemisphere, it is winter in the Southern Hemisphere, and vice versa. Timing From an astronomical view, the equinoxes and solstices would be the middle of the respective seasons, but sometimes astronomical summer is defined as starting at the solstice, the time of maximal insolation, often identified with the 21st day of June or December. By solar reckoning, summer instead starts on May Day and the summer solstice is Midsummer. A variable seasonal lag means that the meteorological centre of the season, which is based on average temperature pattern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autumn
Autumn, also known as fall in American English and Canadian English, is one of the four temperate seasons on Earth. Outside the tropics, autumn marks the transition from summer to winter, in September ( Northern Hemisphere) or March ( Southern Hemisphere). Autumn is the season when the duration of daylight becomes noticeably shorter and the temperature cools considerably. Day length decreases and night length increases as the season progresses until the Winter Solstice in December (Northern Hemisphere) and June (Southern Hemisphere). One of its main features in temperate climates is the striking change in colour for the leaves of deciduous trees as they prepare to shed. Date definitions Some cultures regard the autumnal equinox as "mid-autumn", while others with a longer temperature lag treat the equinox as the start of autumn. In the English-speaking world of high latitude countries, autumn traditionally began with Lammas Day and ended around Hallowe'en, the approxima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)
