|
Stryzhavka
Stryzhavka ( uk, Стрижавка, pl, Strzyżawka, russian: Стрижавка) is an urban-type settlement in the Vinnytsya oblast in Ukraine, located in the historic region of Podolia. The population is History The town is founded in 1552. Until the Partitions of Poland it was part of the Bracław Voivodeship of the Lesser Poland Province of the Polish Crown. Polish nobleman Michał Grocholski founded a Classicist palace in Strzyżawka, destroyed in 1918. Before the war, there was a significant Jewish population. On January 10, 1942, 227 Jews from the village are murdered by an Einsatzgruppen. The next day, 12 Jews are also shot in a mass execution. A memorial is built on the site of the massacre. In June 1942, the Werwolf (Wehrmacht HQ) ''Führerhauptquartier Werwolf'' was the codename used for one of Adolf Hitler's World War II Eastern Front military headquarters located in a pine forest about north of Vinnytsia, in Ukraine, which was used between 1942 and 194 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Werwolf (Wehrmacht HQ)
''Führerhauptquartier Werwolf'' was the codename used for one of Adolf Hitler's World War II Eastern Front (World War II), Eastern Front military headquarters located in a pine forest about north of Vinnytsia, in Ukraine, which was used between 1942 and 1943. It was one of a number of Führer Headquarters, ''Führer'' Headquarters throughout Europe, and the most easterly ever used by Hitler in person. Naming The name is derived from ''Werwolf'' or ''Wehrwolf'' in German, which can be translated as werewolf. The Nazis also used the term ''Werwolf'' as a codename for Clandestine operation, clandestine resistance groups which were intended to carry out guerrilla attacks against the occupying forces towards the end of World War II. The naming scheme is in accord with other code-names given to ''Führerhauptquartiere'' during the Second World War, such as ''Wolf's Lair, Wolfsschanze.'' Several were named for Hitler himself, whose nickname was ''Wolf''. The site was also the easter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urban-type Settlement
Urban-type settlementrussian: посёлок городско́го ти́па, translit=posyolok gorodskogo tipa, abbreviated: russian: п.г.т., translit=p.g.t.; ua, селище міського типу, translit=selyshche mis'koho typu, abbreviated: uk, с.м.т., translit=s.m.t.; be, пасёлак гарадскога тыпу, translit=pasiolak haradskoha typu; pl, osiedle typu miejskiego; bg, селище от градски тип, translit=selishte ot gradski tip; ro, așezare de tip orășenesc. is an official designation for a semi-urban settlement (previously called a "town A town is a human settlement. Towns are generally larger than villages and smaller than cities, though the criteria to distinguish between them vary considerably in different parts of the world. Origin and use The word "town" shares an ori ..."), used in several Eastern European countries. The term was historically used in Bulgaria, Poland, and the Soviet Union, and remains in use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bracław Voivodeship
pl, Województwo bracławskie uk, Брацлавське воєводство , subdivision = Voivodeship , nation = Poland¹ , year_start = 1566 , event_end = Third partition , year_end = 1793 , date_end = 24 October , p1 = Grand Duchy of Lithuania , image_p1 = , p2 = , flag_p2 = , s1 = , flag_s1 = , s2 = Russian Empire , image_s2 = , image_coat = Herbarz Kaspra Niesieckiego Брацлавское.svg , image_map = RON województwo bracławskie map.svg , image_map_caption = The Bracław Voivodeship (red) in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth in 1635. , capital = Bratslav , stat_area1 = 31660 , stat_year1 = , stat_pop1 = , political_subdiv = counties: 2 (3 since 1791) , footnotes = ¹ Voivodeship of the Kingdom of Poland in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. Voivodeship of Grand Duchy of Lithuania before 1569. The Bracław Voivodeship ( la, Palatinatus Braclaviensis; ; uk, Брацлавське ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vinnitsky Uyezd
Vinnitsky Uyezd (''Винницкий уезд'') was one of the uezds (uyezds or subdivisions) of the Podolian Governorate of the Russian Empire. It was situated in the northern part of the governorate. Its administrative centre was Vinnytsia (''Vinnitsa''). Demographics At the time of the Russian Empire Census of 1897, Vinnitsky Uyezd had a population of 248,314. Of these, 74.4% spoke Ukrainian language, Ukrainian, 12.4% Yiddish, 7.1% Russian language, Russian, 5.1% Polish language, Polish, 0.3% Bashkir language, Bashkir, 0.2% Tatar language, Tatar, 0.1% German language, German, 0.1% Belarusian language, Belarusian and 0.1% Czech language, Czech as their native language. References {{Reflist Vinnitsky Uyezd, Uezds of Podolia Governorate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Einsatzgruppen
(, ; also ' task forces') were (SS) paramilitary death squads of Nazi Germany that were responsible for mass murder, primarily by shooting, during World War II (1939–1945) in German-occupied Europe. The had an integral role in the implementation of the so-called "Final Solution to the Jewish question" () in territories conquered by Nazi Germany, and were involved in the murder of much of the intelligentsia and cultural elite of Poland, including members of the Catholic priesthood. Almost all of the people they murdered were civilians, beginning with the intelligentsia and swiftly progressing to Soviet political commissars, Jews, and Romani people, as well as actual or alleged partisans throughout Eastern Europe. Under the direction of Heinrich Himmler and the supervision of SS- Reinhard Heydrich, the operated in territories occupied by the Wehrmacht (German armed forces) following the invasion of Poland in September 1939 and the invasion of the Soviet Union in Ju ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classicism
Classicism, in the arts, refers generally to a high regard for a classical period, classical antiquity in the Western tradition, as setting standards for taste which the classicists seek to emulate. In its purest form, classicism is an aesthetic attitude dependent on principles based in the culture, art and literature of ancient Greece and Rome, with the emphasis on form, simplicity, proportion, clarity of structure, perfection, restrained emotion, as well as explicit appeal to the intellect. The art of classicism typically seeks to be formal and restrained: of the ''Discobolus'' Sir Kenneth Clark observed, "if we object to his restraint and compression we are simply objecting to the classicism of classic art. A violent emphasis or a sudden acceleration of rhythmic movement would have destroyed those qualities of balance and completeness through which it retained until the present century its position of authority in the restricted repertoire of visual images." Classicism, as Cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lesser Poland Province Of The Polish Crown
, subdivision = Province , nation = Poland , year_start = , event_end = Third Partition of Poland , year_end = , image_map = ProwincjaMalopolska.png , image_map_caption = Lesser Poland Province, 1635 (in red) , capital = Kraków , political_subdiv = 11 voivodeships and one duchy , today = , common_name = Lesser Poland Province ( pl, Prowincja małopolska, la, Polonia Minor) was an administrative division of the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland from 1569 until 1795 and the biggest province of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. The name of the province comes from historic land of Lesser Poland. The name of the province did not imply its size, but rather seniority. It had two administrative seats one Sudova Vyshnia for Ruthenian lands, and another Nowe Miasto Korczyn for Polonian lands. The province consisted of 11 voivodeships and one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Partitions Of Poland
The Partitions of Poland were three partitions of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth that took place toward the end of the 18th century and ended the existence of the state, resulting in the elimination of sovereign Poland and Lithuania for 123 years. The partitions were conducted by the Habsburg monarchy, the Kingdom of Prussia, and the Russian Empire, which divided up the Commonwealth lands among themselves progressively in the process of territorial seizures and annexations. The First Partition was decided on August 5, 1772 after the Bar Confederation lost the war with Russia. The Second Partition occurred in the aftermath of the Polish–Russian War of 1792 and the Targowica Confederation of 1792 when Russian and Prussian troops entered the Commonwealth and the partition treaty was signed during the Grodno Sejm on January 23, 1793 (without Austria). The Third Partition took place on October 24, 1795, in reaction to the unsuccessful Polish Kościuszko Uprising the previ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
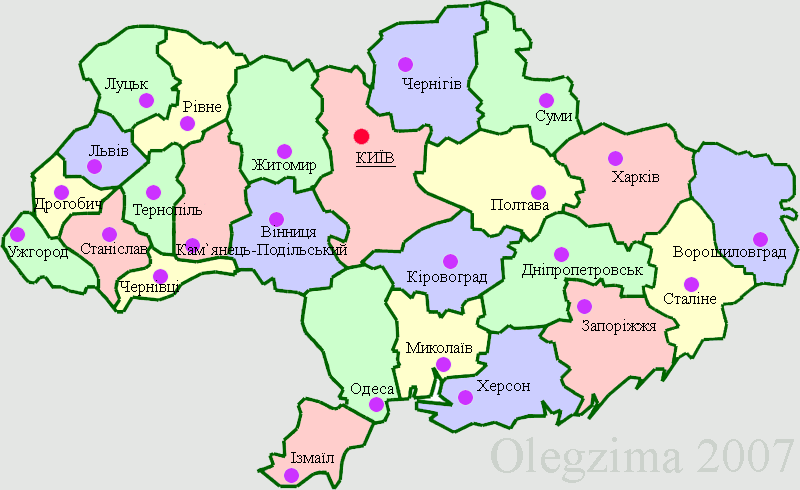
Oblasts Of Ukraine
An oblast ( uk, о́бласть; ) in Ukraine, often called a region or province, is the main type of first-level administrative division of the country. Ukraine's territory is divided into 24 oblasts, as well as one autonomous republic, Crimea, and two cities with special status, Kyiv and Sevastopol. Ukraine is a unitary state, thus the oblasts do not have much legal scope of competence other than that which is established in the Ukrainian Constitution and by law. Articles 140–146 of Chapter XI of the constitution deal directly with local authorities and their competency. Oblasts are subdivided into raions (districts), each oblast having from 3 to 10 raions following the July 2020 reform. General characteristics In Ukraine, the term ''oblast'' denotes a primary administrative division. Under the Russian Empire and into the 1920s, Ukraine was divided between several governorates. The term ''oblast'' was introduced in 1932 by Soviet authorities when the Ukrainian SSR was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Podolia
Podolia or Podilia ( uk, Поділля, Podillia, ; russian: Подолье, Podolye; ro, Podolia; pl, Podole; german: Podolien; be, Падолле, Padollie; lt, Podolė), is a historic region in Eastern Europe, located in the west-central and south-western parts of Ukraine and in northeastern Moldova (i.e. northern Transnistria). The name derives from Old Slavic ''po'', meaning "by/next to/along" and ''dol'', "valley" (see dale). Geography The area is part of the vast East European Plain, confined by the Dniester River and the Carpathian arc in the southwest. It comprises an area of about , extending for from northwest to southeast on the left bank of the Dniester. In the same direction run two ranges of relatively low hills separated by the Southern Bug, ramifications of the Avratynsk heights. The Podolian Upland, an elongated, up to high plateau stretches from the Western and Southern Bug rivers to the Dniester, and includes hill countries and mountainous regions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |