|
Stringbike
The Stringbike is a bicycle that uses a rope and pulley drive system instead of a traditional bicycle chain and sprockets. It uses two Dyneema ropes attached to pulleys attached to swinging lever and cam mechanisms, one on each side of the bike. These mechanisms replace the round sprockets found on chain-driven bikes. Unlike some traditional 10-speed gears using a derailleur, there is no slippage when changing gear ratios. The Stringbike uses a 19 gear ratio system with no duplicates and a total gear range of 3.5 to 1. The transmission ratio can be changed with a shifting knob located on the right-side handle grip. Gear ratios can be changed even when the bicycle is almost stationary. Hungarian designers from the manufacturing company Stringbike Kft., unveiled the bicycle in 2010 in Padova Padua ( ; it, Padova ; vec, Pàdova) is a city and '' comune'' in Veneto, northern Italy. Padua is on the river Bacchiglione, west of Venice. It is the capital of the province of P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stringbike 01
The Stringbike is a bicycle that uses a rope and pulley drive system instead of a traditional bicycle chain and sprockets. It uses two Dyneema ropes attached to pulleys attached to swinging lever and cam mechanisms, one on each side of the bike. These mechanisms replace the round sprockets found on chain-driven bikes. Unlike some traditional 10-speed gears using a derailleur, there is no slippage when changing gear ratios. The Stringbike uses a 19 gear ratio system with no duplicates and a total gear range of 3.5 to 1. The transmission ratio can be changed with a shifting knob located on the right-side handle grip. Gear ratios can be changed even when the bicycle is almost stationary. Hungarian designers from the manufacturing company Stringbike Kft., unveiled the bicycle in 2010 in Padova Padua ( ; it, Padova ; vec, Pàdova) is a city and '' comune'' in Veneto, northern Italy. Padua is on the river Bacchiglione, west of Venice. It is the capital of the province of P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stringbike Kft
The Stringbike is a bicycle that uses a rope and pulley drive system instead of a traditional bicycle chain and sprockets. It uses two Dyneema ropes attached to pulleys attached to swinging lever and cam mechanisms, one on each side of the bike. These mechanisms replace the round sprockets found on chain-driven bikes. Unlike some traditional 10-speed gears using a derailleur, there is no slippage when changing gear ratios. The Stringbike uses a 19 gear ratio system with no duplicates and a total gear range of 3.5 to 1. The transmission ratio can be changed with a shifting knob located on the right-side handle grip. Gear ratios can be changed even when the bicycle is almost stationary. Hungarian designers from the manufacturing company Stringbike Kft., unveiled the bicycle in 2010 in Padova Padua ( ; it, Padova ; vec, Pàdova) is a city and '' comune'' in Veneto, northern Italy. Padua is on the river Bacchiglione, west of Venice. It is the capital of the province of P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bicycle Drivetrain Systems
Bicycle drivetrain systems are used to transmit power on bicycles, tricycles, quadracycles, unicycles, or other human-powered vehicles from the riders to the drive wheels. Most also include some type of a mechanism to convert speed and torque via gear ratios. History The history of bicycle drivetrain systems is closely linked to the history of the bicycle. Major changes in bicycle form have often been initiated or accompanied by advances in drivetrain systems. Several early drivetrains used straight-cut gears that meshed directly with each other outside of the hub. Some bicycles have used a double-sided rear wheel, with different-sized sprockets on each side. To change gears, the rider would stop and dismount, remove the rear wheel and reinstall it in the reverse direction. Derailleur systems were first developed in the late 19th century, but the modern cable-operated parallelogram derailleur was invented in the 1950s. * Draisine * Penny-farthing * Safety bicycle Power ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bicycle Gearing
Bicycle gearing is the aspect of a bicycle drivetrain that determines the relation between the cadence, the rate at which the rider pedals, and the rate at which the drive wheel turns. On some bicycles there is only one gear and, therefore, the gear ratio is fixed, but most modern bicycles have multiple gears and thus multiple gear ratios. A shifting mechanism allows selection of the appropriate gear ratio for efficiency or comfort under the prevailing circumstances: for example, it may be comfortable to use a high gear when cycling downhill, a medium gear when cycling on a flat road, and a low gear when cycling uphill. Different gear ratios and gear ranges are appropriate for different people and styles of cycling. A cyclist's legs produce power optimally within a narrow pedalling speed range, or cadence. Gearing can be optimized to use this narrow range as efficiently as possible. As in other types of transmissions, the gear ratio is closely related to the mechanica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bicycle
A bicycle, also called a pedal cycle, bike or cycle, is a human-powered or motor-powered assisted, pedal-driven, single-track vehicle, having two wheels attached to a frame, one behind the other. A is called a cyclist, or bicyclist. Bicycles were introduced in the 19th century in Europe. By the early 21st century, more than 1 billion were in existence. These numbers far exceed the number of cars, both in total and ranked by the number of individual models produced. They are the principal means of transportation in many regions. They also provide a popular form of recreation, and have been adapted for use as children's toys, general fitness, military and police applications, courier services, bicycle racing, and bicycle stunts. The basic shape and configuration of a typical upright or "safety bicycle", has changed little since the first chain-driven model was developed around 1885. However, many details have been improved, especially since the advent of modern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulley
A pulley is a wheel on an axle or shaft that is designed to support movement and change of direction of a taut cable or belt, or transfer of power between the shaft and cable or belt. In the case of a pulley supported by a frame or shell that does not transfer power to a shaft, but is used to guide the cable or exert a force, the supporting shell is called a block, and the pulley may be called a sheave. A pulley may have a groove or grooves between flanges around its circumference to locate the cable or belt. The drive element of a pulley system can be a rope, cable, belt, or chain. The earliest evidence of pulleys dates back to Ancient Egypt in the Twelfth Dynasty (1991-1802 BCE) and Mesopotamia in the early 2nd millennium BCE. In Roman Egypt, Hero of Alexandria (c. 10-70 CE) identified the pulley as one of six simple machines used to lift weights. Pulleys are assembled to form a block and tackle in order to provide mechanical advantage to apply large forces. Pulleys ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bicycle Chain
A bicycle chain is a roller chain that transfers power from the pedals to the drive-wheel of a bicycle, thus propelling it. Most bicycle chains are made from plain carbon or alloy steel, but some are nickel-plated to prevent rust, or simply for aesthetics. History Obsolete chain designs previously used on bicycles included the block chain, the skip-link chain, and the Simpson lever chain. The first chains were of a simple, bushing-less design. These had inherent reliability problems and a bit more friction (and mechanical efficiency losses) than modern chains. With these limitations in mind, the Nevoigt brothers, of the German Diamant Bicycle Company, designed the roller chain in 1898, which uses bushings. More recently, the "bushingless roller chain" design has superseded the bushed chain. This design incorporates the bearing surface of the bushing into the inner side plate, with each plate creating half of the bushing. This reduces the number of parts needed to assemb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
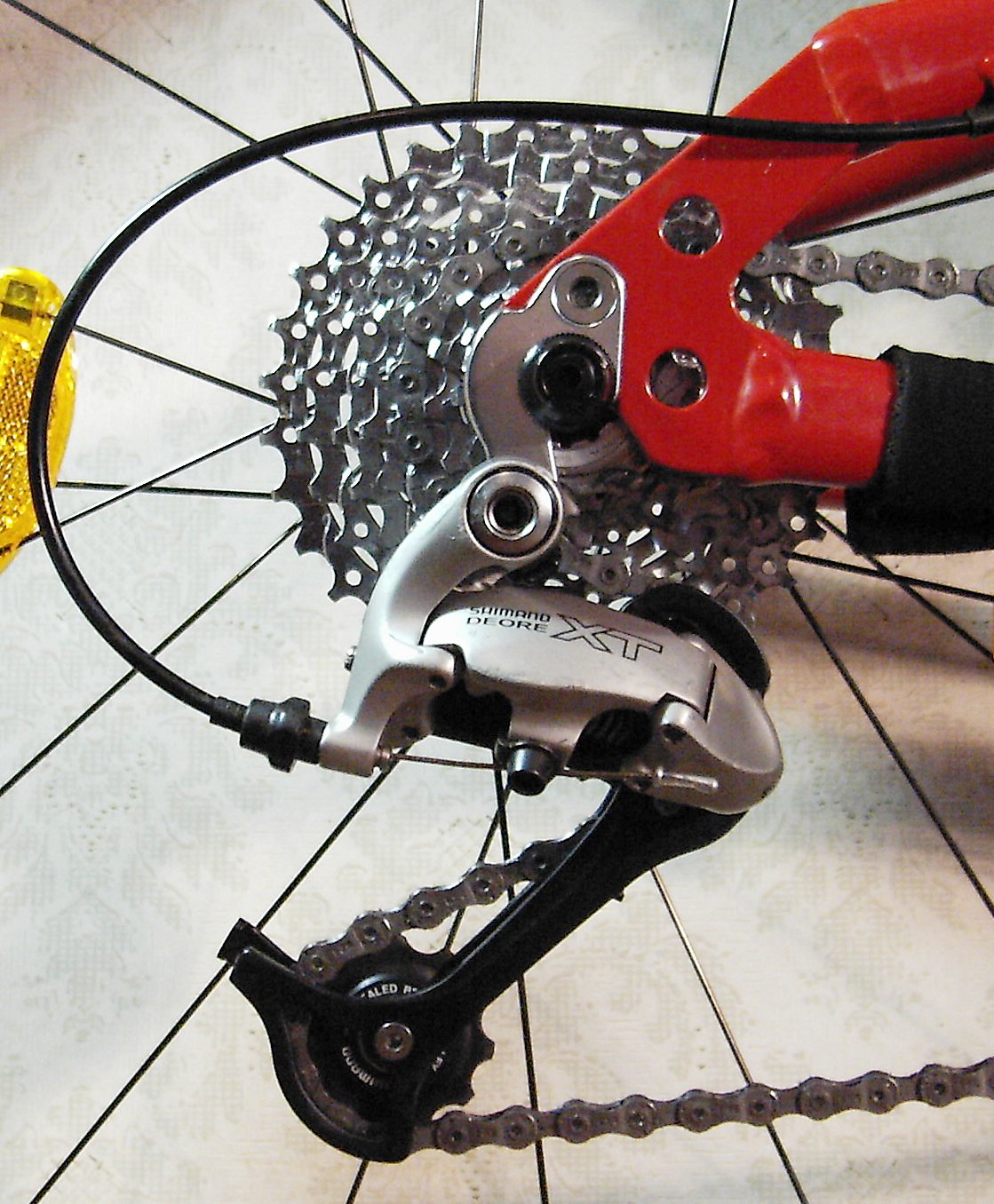
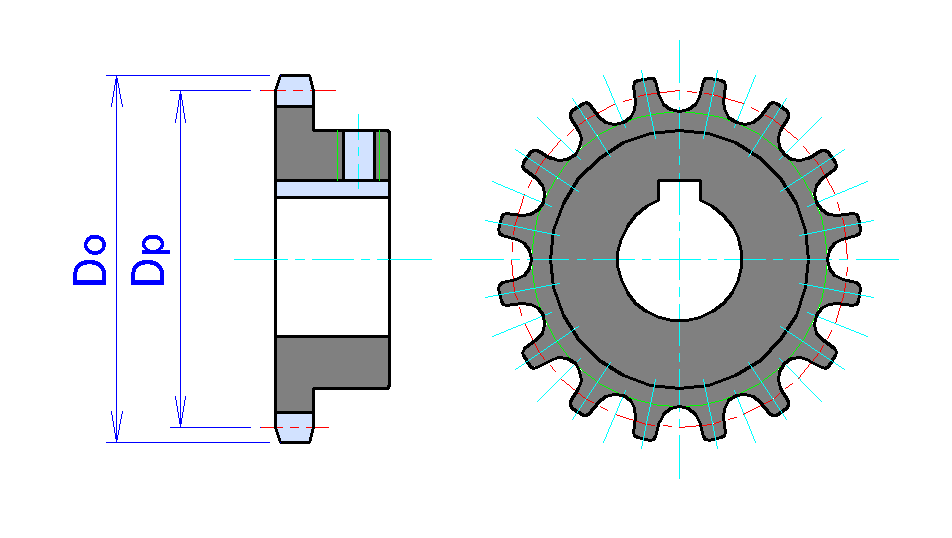
Sprocket
A sprocket, sprocket-wheel or chainwheel is a profiled wheel with teeth that mesh with a roller chain, chain, Caterpillar track, track or other perforated or indented material. The name 'sprocket' applies generally to any wheel upon which radial projections engage a chain passing over it. It is distinguished from a gear in that sprockets are never meshed together directly, and differs from a pulley in that sprockets have teeth and pulleys are smooth except for timing pulleys used with toothed belts. Sprockets are used in bicycles, motorcycles, continuous track, tracked vehicles, and other machinery either to transmit rotary motion between two shafts where gears are unsuitable or to impart linear motion to a track, tape etc. Perhaps the most common form of sprocket may be found in the bicycle, in which the pedal shaft carries a large sprocket-wheel, which drives a chain, which, in turn, drives a small sprocket on the axle of the rear wheel. Early automobiles were also largely dr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dyneema
Ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE, UHMW) is a subset of the thermoplastic polyethylene. Also known as high-modulus polyethylene, (HMPE), it has extremely long chains, with a molecular mass usually between 3.5 and 7.5 million amu. The longer chain serves to transfer load more effectively to the polymer backbone by strengthening intermolecular interactions. This results in a very tough material, with the highest impact strength of any thermoplastic presently made. UHMWPE is odorless, tasteless, and nontoxic. It embodies all the characteristics of high-density polyethylene (HDPE) with the added traits of being resistant to concentrated acids and alkalis, as well as numerous organic solvents. It is highly resistant to corrosive chemicals except oxidizing acids; has extremely low moisture absorption and a very low coefficient of friction; is self-lubricating (see boundary lubrication); and is highly resistant to abrasion, in some forms being 15 times more resistant t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Derailleur
Shimano 600 front derailleur (1980) A derailleur is a variable-ratio bicycle gearing system consisting of a chain, multiple sprockets of different sizes, and a mechanism to move the chain from one sprocket to another. Modern front and rear derailleurs typically consist of a moveable chain-guide that is operated remotely by a Bowden cable attached to a shifter mounted on the down tube, handlebar stem, or handlebar. When a rider operates the lever while pedalling, the change in cable tension moves the chain-guide from side to side, "derailing" the chain onto different sprockets. Etymology ''Dérailleur'' is a French word, derived from the derailment of a train from its tracks. Its first recorded use was 1930. History A modern road bicycle drivetrain with front and rear derailleurs Various derailleur systems were designed and built in the late 19th century. One example is the Protean two-speed derailleur available on the Whippet safety bicycle. The French bicycle to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
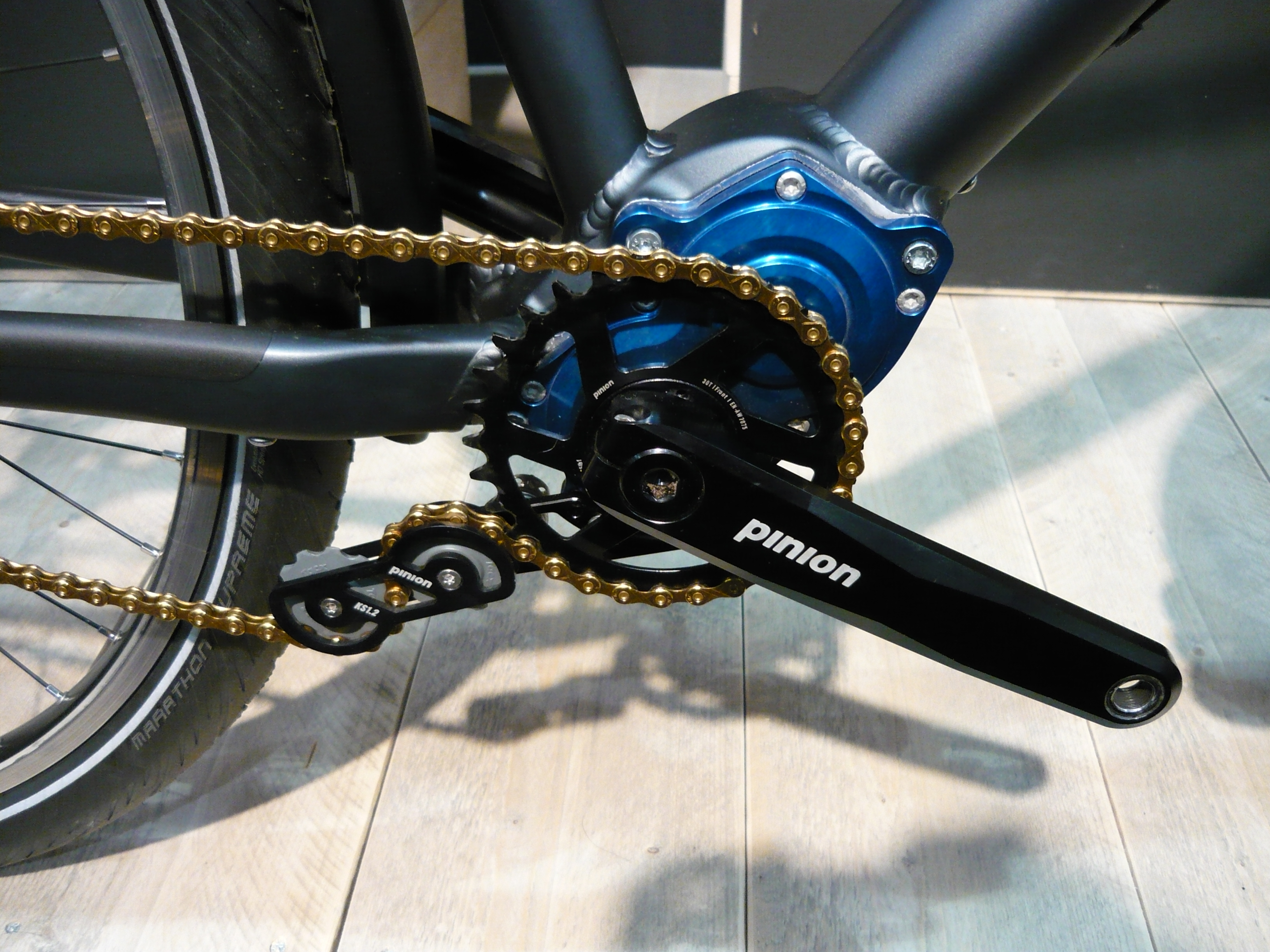
Transmission (mechanics)
Propulsion transmission is the mode of transmitting and controlling propulsion power of a machine. The term ''transmission'' properly refers to the whole drivetrain, including clutch, gearbox, prop shaft (for rear-wheel drive vehicles), differential, and final drive shafts. In the United States the term is sometimes used in casual speech to refer more specifically to the gearbox alone, and detailed usage differs. The transmission reduces the higher engine speed to the slower wheel speed, increasing torque in the process. Transmissions are also used on pedal bicycles, fixed machines, and where different rotational speeds and torques are adapted. Often, a transmission has multiple gear ratios (or simply "gears") with the ability to switch between them as the speed varies. This switching may be done manually (by the operator) or automatically (by a control unit). Directional (forward and reverse) control may also be provided. Single-ratio transmissions also exist, which simply ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hungarians
Hungarians, also known as Magyars ( ; hu, magyarok ), are a nation and ethnic group native to Hungary () and historical Hungarian lands who share a common culture, history, ancestry, and language. The Hungarian language belongs to the Uralic language family. There are an estimated 15 million ethnic Hungarians and their descendants worldwide, of whom 9.6 million live in today's Hungary. About 2–3 million Hungarians live in areas that were part of the Kingdom of Hungary before the Treaty of Trianon in 1920 and are now parts of Hungary's seven neighbouring countries, Slovakia, Ukraine, Romania, Serbia, Croatia, Slovenia, and Austria. Significant groups of people with Hungarian ancestry live in various other parts of the world, most of them in the United States, Canada, Germany, France, the United Kingdom, Chile, Brazil, Australia, and Argentina. Hungarians can be divided into several subgroups according to local linguistic and cultural characteristics; subgroups with dist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |