|
String Quartet No. 6 (Babbitt)
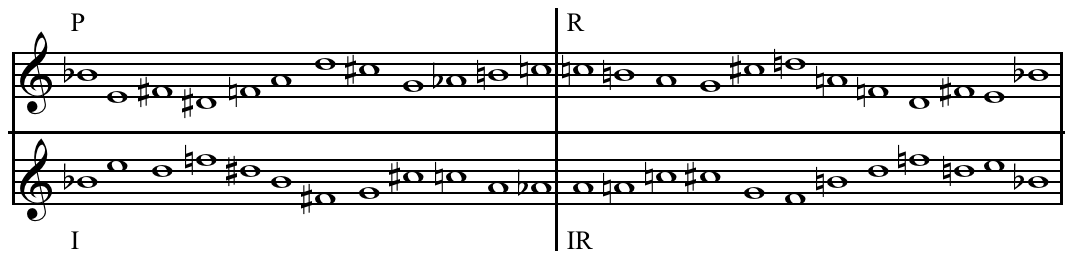
String Quartet No. 6 is the last of six chamber-music works in the string quartet medium by the American composer Milton Babbitt. Babbitt's expansive and lyrical Sixth Quartet was written in 1993. It is in two sections, in each of which the work's underlying six-part all-partition array of fifty-eight aggregates is unfolded separately in each of the four instruments. There are only momentary breaks in each part, which otherwise play continuously throughout the work, giving the sense of an endless flow of music, saturated with florid detail. Changes in muting and playing technique, usually in one instrument at a time, are used to mark off composite pitch aggregates. The work is based on an all-partition array which is (with a few swapped partitions) the M5 transform of the one used in ''The Joy of More Sextets'' (1986), for violin and piano. Recordings *Milton Babbitt: ''Occasional Variations''. Also with Babbitt: String Quartet No. 2; String Quartet No. 6; ''Composition for Gui ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
String Quartet
The term string quartet can refer to either a type of musical composition or a group of four people who play them. Many composers from the mid-18th century onwards wrote string quartets. The associated musical ensemble consists of two violinists, a violist, and a cellist. The string quartet was developed into its present form by composers such as Franz Xaver Richter, and Joseph Haydn, whose works in the 1750s established the ensemble as a group of four more-or-less equal partners. Since Haydn the string quartet has been considered a prestigious form; writing for four instruments with broadly similar characteristics both constrains and tests a composer. String quartet composition flourished in the Classical era, and Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, Ludwig van Beethoven and Franz Schubert each wrote a number of them. Many Romantic and early-twentieth-century composers composed string quartets, including Felix Mendelssohn, Robert Schumann, Johannes Brahms, Antonín Dvořák, Leoš Jan� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milton Babbitt
Milton Byron Babbitt (May 10, 1916 – January 29, 2011) was an American composer, music theorist, mathematician, and teacher. He is particularly noted for his Serialism, serial and electronic music. Biography Babbitt was born in Philadelphia to Albert E. Babbitt and Sarah Potamkin, who were Jewish. He was raised in Jackson, Mississippi, and began studying the violin when he was four but soon switched to clarinet and saxophone. Early in his life he was attracted to jazz and theater music, and "played in every pit-orchestra that came to town". Babbitt was making his own arrangements of popular songs by age 7, "wrote a lot of pop tunes for school productions", and won a local songwriting contest when he was 13. A Jackson newspaper called Babbitt a "whiz kid" and noted "that he had perfect pitch and could add up his family’s grocery bills in his head. In his teens he became a great fan of jazz cornet player Bix Beiderbecke." Babbitt's father was a mathematician, and Babbitt inten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tone Row
In music, a tone row or note row (german: Reihe or '), also series or set, is a non-repetitive ordering of a set of pitch-classes, typically of the twelve notes in musical set theory of the chromatic scale, though both larger and smaller sets are sometimes found. History and usage Tone rows are the basis of Arnold Schoenberg's twelve-tone technique and most types of serial music. Tone rows were widely used in 20th-century contemporary music, like Dmitri Shostakovich's use of twelve-tone rows, "without dodecaphonic transformations." A tone row has been identified in the A minor prelude, BWV 889, from book II of J.S. Bach's ''The Well-Tempered Clavier'' (1742) and by the late eighteenth century it is found in works such as Mozart's C major String Quartet, K. 157 (1772), String Quartet in E-flat major, K. 428, String Quintet in G minor, K. 516 (1790), and the Symphony in G minor, K. 550 (1788). Beethoven also used the technique but, on the whole, "Mozart seems to have employe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiplication (music)
The mathematical operations of multiplication have several applications to music. Other than its application to the frequency ratios of Interval (music), intervals (for example, Just intonation, and the twelfth root of two in equal temperament), it has been used in other ways for twelve-tone technique, and set theory (music), musical set theory. Additionally ring modulation is an electrical audio process involving multiplication that has been used for musical effect. A multiplicative operation is a Map (mathematics), mapping in which the Argument of a function, argument is multiplied. Multiplication originated intuitively in interval expansion, including tone row order number Rotation (mathematics), rotation, for example in the music of Béla Bartók and Alban Berg. Pitch number rotation, ''Fünferreihe'' or "five-series" and ''Siebenerreihe'' or "seven-series", was first described by Ernst Krenek in ''Über neue Musik''. Princeton-based theorists, including James K. Randall, Godf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
String Quartet No
String or strings may refer to: *String (structure), a long flexible structure made from threads twisted together, which is used to tie, bind, or hang other objects Arts, entertainment, and media Films * Strings (1991 film), ''Strings'' (1991 film), a Canadian animated short * Strings (2004 film), ''Strings'' (2004 film), a film directed by Anders Rønnow Klarlund * Strings (2011 film), ''Strings'' (2011 film), an American dramatic thriller film * Strings (2012 film), ''Strings'' (2012 film), a British film by Rob Savage * ''Bravetown'' (2015 film), an American drama film originally titled ''Strings'' * ''The String'' (2009), a French film Music Instruments * String (music), the flexible element that produces vibrations and sound in string instruments * String instrument, a musical instrument that produces sound through vibrating strings ** List of string instruments * String piano, a pianistic extended technique in which sound is produced by direct manipulation of the strings, r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RCA Mark II Sound Synthesizer
The RCA Mark II Sound Synthesizer (nicknamed ''Victor'') was the first programmable electronic synthesizer and the flagship piece of equipment at the Columbia-Princeton Electronic Music Center. Designed by Herbert Belar and Harry Olson at RCA, with contributions by Vladimir Ussachevsky and Peter Mauzey, it was installed at Columbia University in 1957. Consisting of a room-sized array of interconnected sound synthesis components, the Mark II gave the user more flexibility and had twice the number of tone oscillators as its predecessor, the Mark I. The synthesizer was funded by a large grant from the Rockefeller Foundation. Earlier 20th century electronic instruments such as the Telharmonium or the theremin were manually operated. The RCA combined diverse electronic sound generation with a music sequencer, which proved a huge attraction to composers of the day, who were growing weary of creating electronic works by splicing together individual sounds recorded on sections of magnetic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Composers Quartet
The Composers String Quartet was a string quartet best known for performances of new works by contemporary composers, including quartets by Elliott Carter and Ruth Crawford Seeger. Carter's Fourth Quartet was dedicated to the Composers Quartet, who premiered the work in 1986. The group has performed quartets by more than 60 American composers, and has toured abroad extensively. The quartet was founded in 1965, and remained active until the late 1990s. During the early 1970s it was the quartet-in-residence at New England Conservatory, where it sponsored a biennial composition prize. In 1975 the group became the quartet-in-residence at Columbia University, remaining at Columbia for at least two decades. Columbia University Record, Oct. 28, 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anahid Ajemian
Anahid Marguerite Ajemian (January 26, 1924 – June 13, 2016) was an American violinist of Armenian descent. Her career in contemporary music began from her desire to help young composers of her generation get their compositions performed. Additionally, she enjoyed performing the music of established contemporary performers. She included these composers with the traditional repertoire in her performances. Early life and education Ajemian was born in Manhattan on January 26, 1924, to Armenian immigrant parents. Her father was a physician and her mother a pianist. She began her music studies early at the Institute of Musical Art, which later merged with the Juilliard School. After graduating from the Lincoln School, Ajemian continued her education at the Juilliard School, studying violin with Édouard Dethier and chamber music with Hans Letz and Felix Salmon, and played in the Juilliard orchestra under Albert Stoessel and Edgar Shenkman. Musical career In 1946, while sti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nonesuch Records
Nonesuch Records is an American record company and label owned by Warner Music Group, distributed by Warner Records (formerly called Warner Bros. Records), and based in New York City. Founded by Jac Holzman in 1964 as a budget classical label, Nonesuch has developed into a label that records critically acclaimed music from a wide range of genres. Robert Hurwitz was president of the company from 1984 to 2017. History Founding Nonesuch was founded in early 1964 by Jac Holzman to produce "fine records at the same price as a trade paperback", which would be half the price of a normal LP. To achieve this he initially licensed European recordings of classical music as it would be too expensive to record new material. Originally the label concentrated heavily on chamber and baroque music, often with (then) unique repertory, and typically sold at less-than-premium prices. Upon its formation, Nonesuch operated as a subsidiary label of Elektra Records, which Holzman had launched in 1950. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Music Theory Spectrum
''Music Theory Spectrum'' () is a peer-reviewed, academic journal specializing in music theory and analysis. It is the official journal of the Society for Music Theory, and is published by Oxford University Press. The journal was first published in 1979 as the official organ of the Society for Music Theory, which had been founded in 1977 and had its first conference in 1978.. Unlike many other journals (music or otherwise), ''Music Theory Spectrum'' was initially published in an oblong (landscape) page format, to better accommodate such musical graphics as Schenkerian graphs. Published twice annually, ''Music Theory Spectrum'' includes research articles and book reviews. Online access to back issues of the journal up 2017 is provided through JSTOR. In a 1999 study, it was the seventh most frequently cited journal in music theses overall, and the third most frequently cited journal in music theory theses. In Spring 2014, Oxford University Press began publishing ''Music Theory Sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perspectives Of New Music
''Perspectives of New Music'' (PNM) is a peer-reviewed academic journal specializing in music theory and analysis. It was established in 1962 by Arthur Berger and Benjamin Boretz (who were its initial editors-in-chief). ''Perspectives'' was first published by the Princeton University Press, initially supported by the Fromm Music Foundation.David Carson Berry, "''Journal of Music Theory'' under Allen Forte's Editorship," ''Journal of Music Theory'' 50/1 (2006), 21, n49. The first issue was favorably reviewed in the ''Journal of Music Theory'', which observed that Berger and Boretz had produced "a first issue which sustains such a high quality of interest and cogency among its articles that one suspects the long delay preceding the yet-unborn Spring 1963 issue may reflect a scarcity of material up to their standard". However, as the journal's editorial "perspective" coalesced, Fromm became—in the words of David Gable—disenchanted with the "exclusive viewpoint hatcame to dominate" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elaine Barkin
Elaine "Ray" Barkin née Radoff (December 15, 1932 – February 22, 2023) was an American composer, writer, and educator. Early life Elaine Radoff was born in The Bronx, New York City, lived in the Amalgamated Houses, attended Bronx High School of Science, Third Street Music School Settlement, and Queens College (BA in 1954), where she studied composition and theory with Karol Rathaus, Sol Berkowitz, Leo Kraft, and Saul Novack. At Brandeis University (MFA in 1956, PhD in 1971), her mentors in composition and theory were Irving Fine, Harold Shapero, Arthur Berger, and Seymour Shifrin. In the Summer of 1955 she worked with Boris Blacher at Tanglewood and then in 1956 and 1957 at the Berlin Hochschule für Musik on a Fulbright fellowship. In 1963, Barkin was asked by Benjamin Boretz, founding editor of the composers' journal '' Perspectives of New Music'', to join as editor, a post she held until 1985. In 1972 she served as co-editor and when John Rahn became editor in 1984, sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |