|
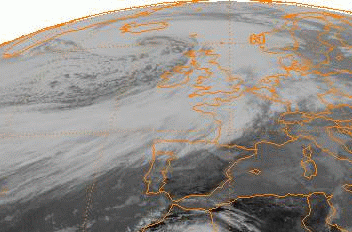
Storm Dennis
Storm Dennis was a European windstorm which, in February 2020, became one of the most intense extratropical cyclones ever recorded, reaching a minimum central pressure of . The thirteenth named storm of the 2019–20 European windstorm season, Dennis affected the Republic of Ireland and the United Kingdom less than a week after Storm Ciara, exacerbating the impacts from that storm amidst ongoing flooding in the latter country. A precursor low over North America was named by The Weather Channel, which unofficially named it ''Mabel'', moving eastwards across the southern United States. After bringing blizzard conditions to the Midwest and heavy snowfall to New England, the cyclone emerged into the north Atlantic, where it redeveloped into Storm Dennis, officially named by the Met Office on 11 February – Dennis subsequently underwent explosive cyclogenesis on 13 February, reaching its near-record low pressure south of Iceland the following day. Destructive winds and heavy rainfal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extratropical Cyclone
Extratropical cyclones, sometimes called mid-latitude cyclones or wave cyclones, are low-pressure areas which, along with the anticyclones of high-pressure areas, drive the weather over much of the Earth. Extratropical cyclones are capable of producing anything from cloudiness and mild showers to severe gales, thunderstorms, blizzards, and tornadoes. These types of cyclones are defined as large scale (synoptic) low pressure weather systems that occur in the middle latitudes of the Earth. In contrast with tropical cyclones, extratropical cyclones produce rapid changes in temperature and dew point along broad lines, called weather fronts, about the center of the cyclone. Terminology The term " cyclone" applies to numerous types of low pressure areas, one of which is the extratropical cyclone. The descriptor ''extratropical'' signifies that this type of cyclone generally occurs outside the tropics and in the middle latitudes of Earth between 30° and 60° latitude. They are term ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2019–20 United Kingdom Floods
Between November 2019 and February 2020, severe winter flooding occurred across the United Kingdom. The first wave of flooding occurred in November 2019, mainly affecting Yorkshire and the Humber, the East Midlands and the West Midlands. Further isolated flooding incidents were reported in December and January, before the second main wave of flooding, caused by Storms Ciara and Dennis, occurred in February 2020. The excessive rainfall resulted in the wettest February since records began, in 1766, in England and Wales with an average of falling across the regions, beating the record from 1833. Background Most of England received above average rainfall during October 2019, with some catchments receiving over double the average monthly total. Soils were wetter than average for the time of year across most of the country by the end of October. Monthly mean river flows were classed as exceptionally high at just over a third of indicator sites. Early on 8 November, heavy and prolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlantic Canada
Atlantic Canada, also called the Atlantic provinces (french: provinces de l'Atlantique), is the region of Eastern Canada comprising the provinces located on the Atlantic coast, excluding Quebec. The four provinces are New Brunswick, Newfoundland and Labrador, Nova Scotia, and Prince Edward Island. As of 2021, the landmass of the four Atlantic provinces was approximately 488,000 km2, and had a population of over 2.4 million people. The provinces combined had an approximate GDP of $121.888 billion in 2011. The term ''Atlantic Canada'' was popularized following the admission of Newfoundland as a Canadian province in 1949. History The first premier of Newfoundland, Joey Smallwood, coined the term "Atlantic Canada" when Newfoundland joined Canada in 1949. He believed that it would have been presumptuous for Newfoundland to assume that it could include itself within the existing term "Maritime provinces," used to describe the cultural similarities shared by New Brunswick, Prince ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five lakes, which are Lake Superior, Superior, Lake Michigan, Michigan, Lake Huron, Huron, Lake Erie, Erie, and Lake Ontario, Ontario and are in general on or near the Canada–United States border. Hydrologically, lakes Lake Michigan–Huron, Michigan and Huron are a single body joined at the Straits of Mackinac. The Great Lakes Waterway enables modern travel and shipping by water among the lakes. The Great Lakes are the largest group of freshwater lakes on Earth by total area and are second-largest by total volume, containing 21% of the world's surface fresh water by volume. The total surface is , and the total volume (measured at the low water datum) is , slightly less than the volume of Lake Baikal (, 22–23% of the world's surface fresh water ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ocean Prediction Center
The Ocean Prediction Center (OPC), established in 1995, is one of the National Centers for Environmental Prediction's (NCEP's) original six service centers. Until 2003, the name of the organization was the Marine Prediction Center.Ocean Prediction Center (2004)Ocean Prediction Center: 2003 Accomplishments. Retrieved on 2008-09-03. Its origins are traced back to the sinking of the RMS ''Titanic'' in 1912. The OPC issues forecasts up to five days in advance for ocean areas north of 31° north latitude and west of 35° west longitude in the Atlantic, and across the northeast Pacific north of 30° north latitude and east of 160° east longitude. Until recently, the OPC provided forecast points for tropical cyclones north of 20° north latitude and east of the 60° west longitude to the National Hurricane Center. OPC is composed of two branches: the Ocean Forecast Branch and the Ocean Applications Branch. History The first attempt as a marine weather program within the Unit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern England
Northern England, also known as the North of England, the North Country, or simply the North, is the northern area of England. It broadly corresponds to the former borders of Angle Northumbria, the Anglo-Scandinavian Kingdom of Jorvik, and the Celt Britonic Yr Hen Ogledd Kingdoms. The common governmental definition of the North is a grouping of three statistical regions: the North East, the North West, and Yorkshire and the Humber. These had a combined population of 14.9 million at the 2011 census, an area of and 17 cities. Northern England is culturally and economically distinct from both the Midlands and the South of England. The area's northern boundary is the border with Scotland, its western the border with Wales, and its eastern the North Sea; there are varying interpretations of where the southern border with the Midlands lies culturally; the Midlands is often also split by closeness to the North and the South. Many Industrial Revolution innovations began in N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern England
Southern England, or the South of England, also known as the South, is an area of England consisting of its southernmost part, with cultural, economic and political differences from the Midlands and the North. Officially, the area includes Greater London, the South East, the West Country (or the South West), and the East (sometimes referred to as East Anglia). The distinction between the south and rest of England and Great Britain is sometimes referred to as the north–south divide. With a population of nearly 28 million; and an area of , the south accounts for roughly 40% of the population of the United Kingdom and approximately 25% of its area. Definitions For official purposes, the UK government does not refer to the Southern England as a single entity, but the Office for National Statistics divides UK into twelve regions. In England, the North West, North East and Yorkshire and the Humber make up the North ("centre-north"); the West Midlands and East Midlands (as wel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wales
Wales ( cy, Cymru ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the Wales–England border, east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, the Celtic Sea to the south west and the Bristol Channel to the south. It had a population in 2021 of 3,107,500 and has a total area of . Wales has over of coastline and is largely mountainous with its higher peaks in the north and central areas, including Snowdon (), its highest summit. The country lies within the Temperateness, north temperate zone and has a changeable, maritime climate. The capital and largest city is Cardiff. Welsh national identity emerged among the Celtic Britons after the Roman withdrawal from Britain in the 5th century, and Wales was formed as a Kingdom of Wales, kingdom under Gruffydd ap Llywelyn in 1055. Wales is regarded as one of the Celtic nations. The Conquest of Wales by Edward I, conquest of Wales by Edward I of England was completed by 1283, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, the North Sea to the northeast and east, and the Irish Sea to the south. It also contains more than 790 islands, principally in the archipelagos of the Hebrides and the Northern Isles. Most of the population, including the capital Edinburgh, is concentrated in the Central Belt—the plain between the Scottish Highlands and the Southern Uplands—in the Scottish Lowlands. Scotland is divided into 32 administrative subdivisions or local authorities, known as council areas. Glasgow City is the largest council area in terms of population, with Highland being the largest in terms of area. Limited self-governing power, covering matters such as education, social services and roads and transportation, is devolved from the Scott ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Isles
The British Isles are a group of islands in the North Atlantic Ocean off the north-western coast of continental Europe, consisting of the islands of Great Britain, Ireland, the Isle of Man, the Inner and Outer Hebrides, the Northern Isles, and over six thousand smaller islands."British Isles", ''Encyclopædia Britannica''. They have a total area of and a combined population of almost 72 million, and include two sovereign states, the Republic of Ireland (which covers roughly five-sixths of Ireland), and the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland. The Channel Islands, off the north coast of France, are normally taken to be part of the British Isles, even though they do not form part of the archipelago. The oldest rocks are 2.7 billion years old and are found in Ireland, Wales and the northwest of Scotland. During the Silurian period, the north-western regions collided with the south-east, which had been part of a separate continental landmass. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Explosive Cyclogenesis
Explosive cyclogenesis (also referred to as a weather bomb, meteorological bomb, explosive development, bomb cyclone, or bombogenesis) is the rapid deepening of an Extratropical cyclone, extratropical cyclonic low-pressure area. The change in pressure needed to classify something as explosive cyclogenesis is latitude dependent. For example, at 60° latitude, explosive cyclogenesis occurs if the central pressure decreases by or more in 24 hours. This is a predominantly maritime, winter event, but also occurs in continental settings, This process is the extratropical equivalent of the tropical rapid deepening. Although their cyclogenesis is entirely different from that of tropical cyclones, bomb cyclones can produce winds of , the same order as the first categories of the Saffir–Simpson scale, and yield heavy precipitation. Even though only a minority of the bomb cyclones become so strong, some weaker ones have also caused significant damage. History In the 1940s and 1950s, mete ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Met Office
The Meteorological Office, abbreviated as the Met Office, is the United Kingdom's national weather service. It is an executive agency and trading fund of the Department for Business, Energy and Industrial Strategy and is led by CEO Penelope Endersby, who took on the role as Chief Executive in December 2018 and is the first woman to do so. The Met Office makes meteorological predictions across all timescales from weather forecasts to climate change. History The Met Office was established on 1 August 1854 as a small department within the Board of Trade under Vice Admiral (Royal Navy), Vice Admiral Robert FitzRoy as a service to sailor, mariners. The loss of the passenger vessel, the Royal Charter (ship), ''Royal Charter'', and 459 lives off the coast of Anglesey in a violent storm in October 1859 led to the first gale warning service. FitzRoy established a network of 15 coastal stations from which visual gale warnings could be provided for ships at sea. The new electric tele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |