|
Stirtonia Tatacoensis
''Stirtonia'' is an extinct genus of New World monkeys from the Middle Miocene (Laventan in the South American land mammal ages; 13.8 to 11.8 Ma). Its remains have been found at the Konzentrat-Lagerstätte of La Venta in the Honda Group of Colombia. Two species have been described, ''S. victoriae'' and the type species ''S. tatacoensis''.''Stirtonia victoriae'' at Fossilworks.org''Stirtonia tatacoensis'' at Fossilworks.org ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recent" because it has 18% fewer modern marine invertebrates than the Pliocene has. The Miocene is preceded by the Oligocene and is followed by the Pliocene. As Earth went from the Oligocene through the Miocene and into the Pliocene, the climate slowly cooled towards a series of ice ages. The Miocene boundaries are not marked by a single distinct global event but consist rather of regionally defined boundaries between the warmer Oligocene and the cooler Pliocene Epoch. During the Early Miocene, the Arabian Peninsula collided with Eurasia, severing the connection between the Mediterranean and Indian Ocean, and allowing a faunal interchange to occur between Eurasia and Africa, including the dispersal of proboscideans into Eurasia. During the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solimões Formation
The Pebas Formation is a lithostratigraphic unit of Miocene age, found in western Amazonia. The formation extends over , including parts of Brazil, Peru, Ecuador and Colombia.Wesselingh et al., 2006 It is interpreted as representing the deposits of a lake ("Lake Pebas") or series of lakes, formed within the foreland basin of the Andes mountain belt. It is known for its abundant fossil ostracods and molluscs and an unusually diverse group of crocodylians.Sala Gismondi et al., 2006 Fossil content Correlations Laventan Huayquerian References Bibliography * * * Further reading * {{cite LSA , first=P. , last=Antoine , first2=J.A. , last2=Abello , first3=S. , last3=Adnet , first4=A.J. , last4=Altamirano Sierra , first5=P. , last5=Baby , first6=G. , last6=Billet , first7=M. , last7=Boivin , first8=Y. , last8=Calderón , last9=Candela and J. Chabain, F. Corfu, D. A. Croft, M. Ganerød, C. Jaramillo, S. Klaus, L. Marivaux, R. E. Navarrete, M. J. Orliac, F. Par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mohanamico
''Mohanamico'' is an extinct genus of New World monkeys from the Middle Miocene (Laventan in the South American land mammal ages; 13.8 to 11.8 Ma). Its remains have been found at the Konzentrat-Lagerstätte of La Venta in the Honda Group of Colombia. The type species is ''M. hershkovitzi''. Due to the relatively few material found of ''Mohanamico'', the placement of the genus is not certain and four possible families have been proposed by different authors, Atelidae, Callitrichidae, Pitheciidae or Aotidae. Etymology ''Mohanimico hershkovitzi'' is named after the river god Mohan of the Magdalena River, in which valley the fossils were found and to honor Philip Hershkovitz for his contributions to the study of Colombian and other South American primates.Luchterhand et al., 1986, p.1757 Description Fossils of ''Mohanamico'' were discovered in the "Monkey Beds" of the Honda Group, that has been dated to the Laventan, about 12.5 Ma.Wheeler, 2010, p.133 ''Mohanamico'' was about ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micodon
''Micodon'' is an extinct genus of New World monkeys from the Middle Miocene (Laventan in the South American land mammal ages; 13.8 to 11.8 Ma). Its remains have been found at the Konzentrat-Lagerstätte of La Venta in the Honda Group of Colombia. The type species is ''M. kiotensis'',''Micodon kiotensis'' at .org a very small monkey among the New World species.Tejedor, 2013, p.29 Description Fossils of ''Micodon'' were discovered in the |
Aotus Dindensis
''Aotus dindensis'' is an extinct species of New World monkeys in the genus '' Aotus'' from the Middle Miocene (Laventan in the South American land mammal ages; 13.8 to 11.8 Ma). Its remains have been found at the Konzentrat-Lagerstätte of La Venta in the Honda Group of Colombia.''Aotus dindensis'' at .org Etymology The species has been named after the locality its fossils have been found, the El Dinde site of the "Monkey Unit" in the Honda Group, Colombia.Gebo et al., 1990, p.737Description Fossils of ''Aotus dindensis'' were discovered in 1986 in the |
Orinoco Basin
The Orinoco Basin is the part of South America drained by the Orinoco river and its tributaries. The Orinoco watershed covers an area of about 990000 km2, making it the third largest in South America, covering most of Venezuela and eastern part of Colombia. The Orinoco is one of the most important rivers in the world due to its length and flow (2140 km and more than 30000 m3/s), the extent of its basin (1 million km2) and especially its historical importance and economic and the meaning it has had for Venezuela, where most of its basin is spread, with almost two-thirds of it. It is probably the largest river in the world in relation to its basin, similar in extent to that of the Danube but five times greater in volume. Its discharge is the third largest of any river worldwide, after the Amazon and the Congo, and much greater than that of many rivers of greater length and basin area. Geography Extension The Orinoco basin covers an area of almost 989000 k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
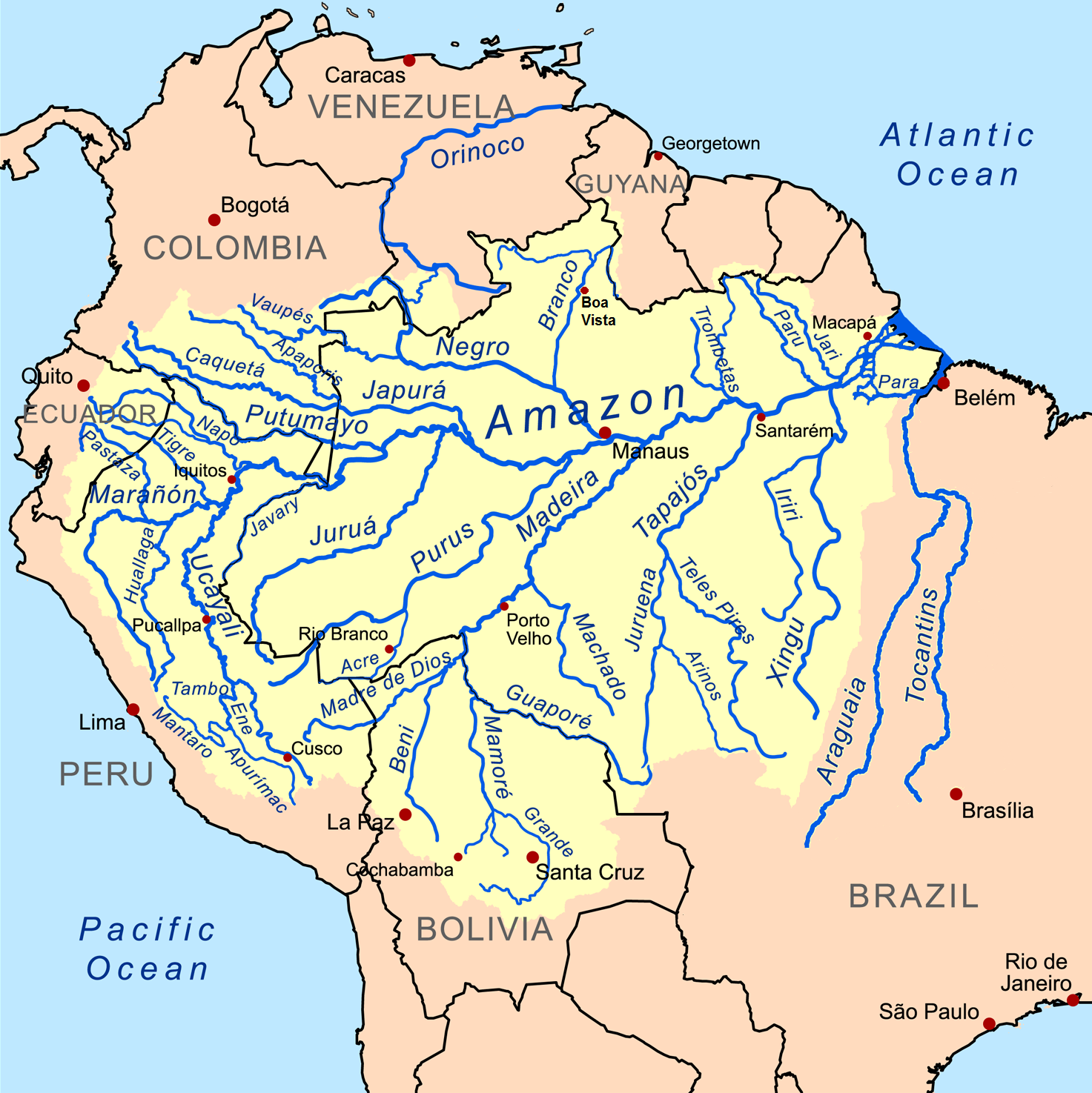
Amazon Basin
The Amazon basin is the part of South America drained by the Amazon River and its tributaries. The Amazon drainage basin covers an area of about , or about 35.5 percent of the South American continent. It is located in the countries of Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, Guyana, Peru, Suriname, and Venezuela. Most of the basin is covered by the Amazon rainforest, also known as Amazonia. With a area of dense tropical forest, this is the largest rainforest in the world. Geography The Amazon River begins in the Andes Mountains at the west of the basin with its main tributary the Marañón River and Apurimac River in Peru. The highest point in the watershed of the Amazon is the second biggest peak of Yerupajá at . With a length of about before it drains into the Atlantic Ocean, it is one of the two longest rivers in the world. A team of scientists has claimed that the Amazon is longer than the Nile, but debate about its exact length continues. The Amazon system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Fossil Primates Of South America
Various fossil primates have been found in South America and adjacent regions such as Panama and the Caribbean.Tejedor et al., 2013, p.22 Presently, 78 species of New World monkeys have been registered in South America.Rosenberger & Hartwig, 2001, p.2 Around the middle of the Cenozoic, approximately 34 million years ago,Lynch Alfaro et al., 2015, p.519 two types of mammals appeared for the first time in South America: rodents and primates. Both of these groups had already been inhabiting other continents for millions of years and they simply arrived in South America rather than originated there. Analyses of evolutionary relationships have shown that their closest relatives were living in Africa at the time. Therefore, the most likely explanation is that they somehow crossed the Atlantic Ocean, which was less wide than today, landed in South America, and founded new populations of rodents and primates. The first South American primates gave rise to an impressive evolutionary radiati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Callicebus
''Callicebus'' is a genus of monkeys known as titi monkeys. Historically, titis were monogeneric, comprising only the genus ''Callicebus'' Thomas, 1903. Owing to the great diversity found across titi monkey species, a new genus-level taxonomy was recently proposed that recognises three genera within the subfamily Callicebinae; ''Cheracebus'' Byrne et al., 2016 for the species of the ''torquatus'' group (Widow titis); ''Plecturocebus'' Byrne et al., 2016 for the Amazonian and Chaco titis of the ''moloch'' and ''donacophilus'' groups; and ''Callicebus'' Thomas, 1903 ''sensu stricto'', for species of the Atlantic Forest ''personatus'' group. In 2014, a previously unknown orange ''Callicebus'' was spotted in the Peruvian Amazon; it has not been determined whether this constitutes a color variant or a new species. Species There are 5 species in this genus: * Barbara Brown's titi monkey, ''Callicebus barbarabrownae'' * Coimbra Filho's titi monkey, ''Callicebus coimbrai'' * Coastal bla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pitheciidae
The Pitheciidae () are one of the five families of New World monkeys now recognised. Formerly, they were included in the family Atelidae. The family includes the titis, saki monkeys and uakaris. Most species are native to the Amazon region of Brazil, with some being found from Colombia in the north to Bolivia in the south. Characteristics Pithecids are small to medium-sized monkeys, ranging from 23 cm in head-body length for the smaller titis, to 44–49 cm for the uakaris. They have medium to long fur, in a wide range of colors, often with contrasting patches, especially on the face. They are diurnal and arboreal animals, found in tropical forests from low-lying swamp to mountain slopes. They are predominantly herbivorous, eating mostly fruit and seeds, although some species will also eat a small number of insects. Sakis and uakaris have a diastema between the canine and premolar teeth, but the titis, which have unusually small canines for New World monkeys, do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atelidae
The Atelidae are one of the five families of New World monkeys now recognised. It was formerly included in the family Cebidae. Atelids are generally larger monkeys; the family includes the howler, spider, woolly, and woolly spider monkeys (the latter being the largest of the New World monkeys). They are found throughout the forested regions of Central and South America, from Mexico to northern Argentina. Characteristics The Atelidae family consists of monkeys that are small to moderate in size, usually 34 to 72 cm in head-body length, with the howler monkeys being the largest members of the group, and the spider monkeys being the smallest. They have long prehensile tails with a sensitive, almost hairless, tactile pad on the underside of the distal part. The tail is frequently used as 'fifth limb' while moving through the trees where they make their homes. They also have nails on their fingers and toes, enabling them to climb. Most species have predominantly dark brown, g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type Locality (biology)
In biology, a type is a particular specimen (or in some cases a group of specimens) of an organism to which the scientific name of that organism is formally attached. In other words, a type is an example that serves to anchor or centralizes the defining features of that particular taxon. In older usage (pre-1900 in botany), a type was a taxon rather than a specimen. A taxon is a scientifically named grouping of organisms with other like organisms, a set that includes some organisms and excludes others, based on a detailed published description (for example a species description) and on the provision of type material, which is usually available to scientists for examination in a major museum research collection, or similar institution. Type specimen According to a precise set of rules laid down in the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN) and the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants (ICN), the scientific name of every taxon is almost a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)