|
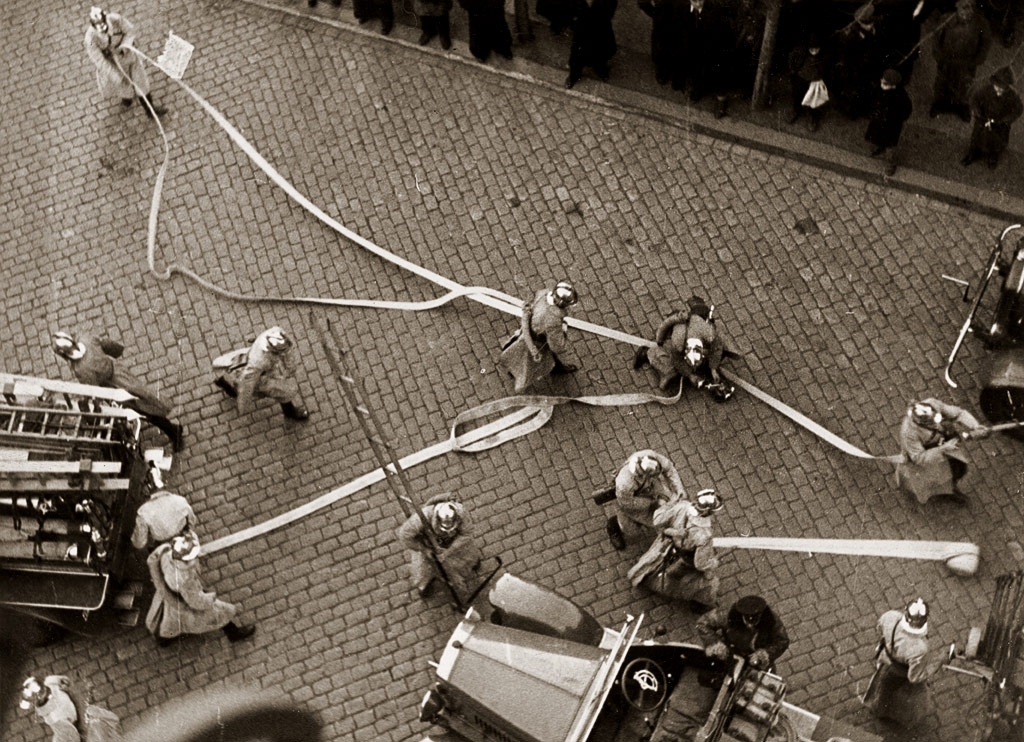
Stirrup Pump
A stirrup pump is a portable reciprocating water pump used to extinguish or control small fires. It is operated by hand. The operator places a foot on a stirrup-like bracket at the bottom of the pump to hold the pump steady, the bottom of the suction cylinder was placed inside a bucket of water.Smoke, Flame, Fire!: A History of Firefighting: A History of Firefighting. R.Apps (2018) , References External links Fire watchers Pumps Appropriate technology Human power Firefighting equipment Fire suppression Active fire protection {{firefighting-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A Female Fire Guard Using A Stirrup Pump On The Roof Of A Building In London, 1941
A, or a, is the first Letter (alphabet), letter and the first vowel of the Latin alphabet, Latin alphabet, used in the English alphabet, modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is English alphabet#Letter names, ''a'' (pronounced ), plural English alphabet#Letter names, ''aes''. It is similar in shape to the Greek alphabet#History, Ancient Greek letter alpha, from which it derives. The Letter case, uppercase version consists of the two slanting sides of a triangle, crossed in the middle by a horizontal bar. The lowercase version can be written in two forms: the double-storey a and single-storey ɑ. The latter is commonly used in handwriting and fonts based on it, especially fonts intended to be read by children, and is also found in italic type. In English grammar, "English articles, a", and its variant "English articles#Indefinite article, an", are Article (grammar)#Indefinite article, indefinite arti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
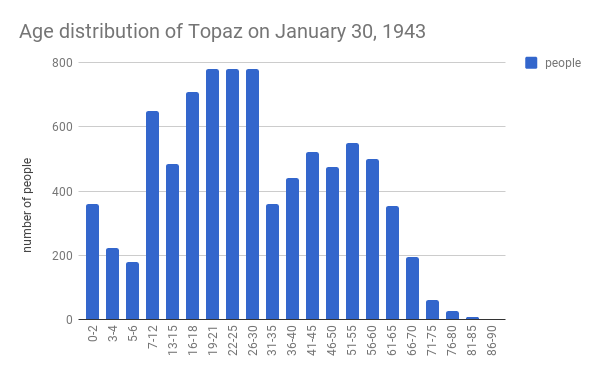
Topaz, Utah
The Topaz War Relocation Center, also known as the Central Utah Relocation Center (Topaz) and briefly as the Abraham Relocation Center, was an American concentration camp which housed Americans of Japanese descent and immigrants who had come to the United States from Japan, called '' Nikkei''. President Franklin Roosevelt signed Executive Order 9066 in February 1942, ordering people of Japanese ancestry to be incarcerated in what were euphemistically called "relocation centers" like Topaz during World War II. Most of the people incarcerated at Topaz came from the Tanforan Assembly Center and previously lived in the San Francisco Bay Area. The camp was opened in September 1942 and closed in October 1945. The camp, approximately west of Delta, Utah, consisted of , with a main living area. Most internees lived in the main living area, though some lived off-site as agricultural and industrial laborers. The approximately 9,000 internees and staff made Topaz into the fifth-larges ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Farm And Garden Annual (16200986368) (cropped)
A farm (also called an agricultural holding) is an area of land that is devoted primarily to agricultural processes with the primary objective of producing food and other crops; it is the basic facility in food production. The name is used for specialized units such as arable farms, vegetable farms, fruit farms, dairy, pig and poultry farms, and land used for the production of natural fiber, biofuel and other commodities. It includes ranches, feedlots, orchards, plantations and estates, smallholdings and hobby farms, and includes the farmhouse and agricultural buildings as well as the land. In modern times the term has been extended so as to include such industrial operations as wind farms and fish farms, both of which can operate on land or sea. There are about 570 million farms in the world, most of which are small and family-operated. Small farms with a land area of fewer than 2 hectares operate about 1% of the world's agricultural land, and family farms comprise about 75 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pumps
A pump is a device that moves fluids (liquids or gases), or sometimes slurries, by mechanical action, typically converted from electrical energy into hydraulic energy. Pumps can be classified into three major groups according to the method they use to move the fluid: ''direct lift'', ''displacement'', and ''gravity'' pumps. Mechanical pumps serve in a wide range of applications such as pumping water from wells, aquarium filtering, pond filtering and aeration, in the car industry for water-cooling and fuel injection, in the energy industry for pumping oil and natural gas or for operating cooling towers and other components of heating, ventilation and air conditioning systems. In the medical industry, pumps are used for biochemical processes in developing and manufacturing medicine, and as artificial replacements for body parts, in particular the artificial heart and penile prosthesis. When a casing contains only one revolving impeller, it is called a single-stage pump. When ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Appropriate Technology
Appropriate technology is a movement (and its manifestations) encompassing technological choice and application that is small-scale, affordable by locals, decentralized, labor-intensive, energy-efficient, environmentally sustainable, and locally autonomous. It was originally articulated as intermediate technology by the economist Ernst Friedrich "Fritz" Schumacher in his work ''Small Is Beautiful.'' Both Schumacher and many modern-day proponents of appropriate technology also emphasize the technology as people-centered. Appropriate technology has been used to address issues in a wide range of fields. Well-known examples of appropriate technology applications include: bike- and hand-powered water pumps (and other self-powered equipment), the universal nut sheller, self-contained solar lamps and streetlights, and passive solar building designs. Today appropriate technology is often developed using open source principles, which have led to ''open-source appropriate technology'' ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Power
Human power is work or energy that is produced from the human body. It can also refer to the power (rate of work per time) of a human. Power comes primarily from muscles, but body heat is also used to do work like warming shelters, food, or other humans. World records of power performance by humans are of interest to work planners and work-process engineers. The average level of human power that can be maintained over a certain duration of time is interesting to engineers designing work operations in industry. Human-powered transport includes bicycles, rowing, skiing and many other forms of mobility. Human-powered equipment is occasionally used to generate, and sometimes to store, electrical energy for use where no other source of power is available. These include the Gibson girl survival radio, wind-up or (clockwork) radio and pedal radio. Available power Normal human metabolism produces heat at a basal metabolic rate of around 80 watts. During a bicycle race, an elite cy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Firefighting Equipment
Firefighting is the act of extinguishing or preventing the spread of unwanted fires from threatening human lives and destroying property and the environment. A person who engages in firefighting is known as a firefighter. Firefighters typically undergo a high degree of technical training. This involves structural firefighting and wildland firefighting. Specialized training includes aircraft firefighting, shipboard firefighting, aerial firefighting, maritime firefighting, and proximity firefighting. Firefighting is a dangerous profession due to the toxic environment created by combustible materials, with major risks are smoke, oxygen deficiency, elevated temperatures, poisonous atmospheres, and violent air flows. To combat some of these risks, firefighters carry self-contained breathing apparatus. Additional hazards include falls — a constant peril while navigating unfamiliar layouts or confined spaces amid shifting debris under limited visibility – and structural collapse t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fire Suppression
Wildfire suppression is a range of firefighting tactics used to suppress wildfires. Firefighting efforts in wild land areas require different techniques, equipment, and training from the more familiar structure fire fighting found in populated areas. Working in conjunction with specially designed aerial firefighting aircraft, these wildfire-trained crews suppress flames, construct fire break, fire lines, and extinguish flames and areas of heat to protect resources and natural wilderness. Wildfire suppression also addresses the issues of the wildland–urban interface, where populated areas border with wild land areas. In the United States and other countries, aggressive wildfire suppression aimed at minimizing fire has contributed to accumulation of fuel loads, increasing the risk of large, catastrophic fires. History Australia Wildland fire, known in Australia as bush fire, has played a major role in Australia due to arid conditions. Notable fire services tasked with wildfire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |