|
Stenaulorhynchine
Rhynchosaurs are a group of extinct herbivorous Triassic archosauromorph reptiles, belonging to the order Rhynchosauria. Members of the group are distinguished by their triangular skulls and elongated, beak like premaxillary bones. Rhynchosaurs first appeared in the Middle Triassic or possibly the Early Triassic, before becoming abundant and globally distributed during the Carnian stage of the Late Triassic. Description Rhynchosaurs were herbivores, and at times abundant (in some fossil localities accounting for 40 to 60% of specimens found), with stocky bodies and a powerful beak. Early primitive forms, like ''Mesosuchus'' and ''Howesia'', were generally small and more typically lizard-like in build, and had skulls rather similar to the early diapsid ''Youngina'', except for the beak and a few other features. Later and more advanced genera grew to medium to medium large size, up to two meters in length. The skull in these forms were short, broad, and triangular, becoming much ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
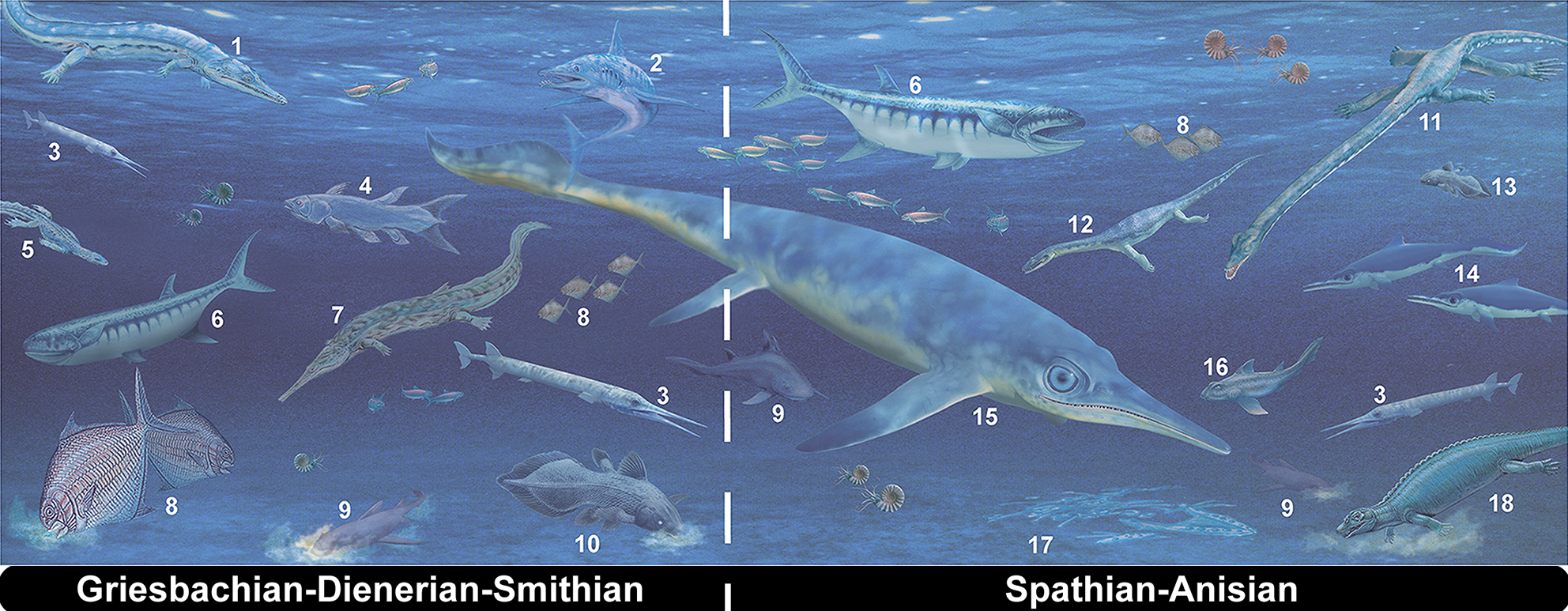
Olenekian
In the geologic timescale, the Olenekian is an age in the Early Triassic epoch; in chronostratigraphy, it is a stage in the Lower Triassic series. It spans the time between Ma and Ma (million years ago). The Olenekian is sometimes divided into the Smithian and the Spathian subages or substages. The Olenekian follows the Induan and is followed by the Anisian (Middle Triassic). The Olenekian saw the deposition of a large part of the Buntsandstein in Europe. The Olenekian is roughly coeval with the regional Yongningzhenian Stage used in China. Stratigraphic definitions The Olenekian Stage was introduced into scientific literature by Russian stratigraphers in 1956. The stage is named after Olenëk in Siberia. Before the subdivision in Olenekian and Induan became established, both stages formed the Scythian Stage, which has since disappeared from the official timescale. The base of the Olenekian is at the lowest occurrence of the ammonoids '' Hedenstroemia'' or '' Meekoceras graci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ammorhynchus
''Ammorhynchus'' is an extinct genus of hyperodapedontid rhynchosaur from Middle Triassic (Anisian stage) deposits of Navajo County, Arizona.''Ammorhynchus'' at .org It is known from the MSM 02-153/P4585, a nearly complete left and from three paratypes (MSM 00-99/P4409, a partial left maxilla; MSM 00-103/P4586, other partial maxilla and MSM 02-145/P4544, dentary fragments) from the same locality. It was found in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Premaxilla
The premaxilla (or praemaxilla) is one of a pair of small cranial bones at the very tip of the upper jaw of many animals, usually, but not always, bearing teeth. In humans, they are fused with the maxilla. The "premaxilla" of therian mammal has been usually termed as the incisive bone. Other terms used for this structure include premaxillary bone or ''os premaxillare'', intermaxillary bone or ''os intermaxillare'', and Goethe's bone. Human anatomy In human anatomy, the premaxilla is referred to as the incisive bone (') and is the part of the maxilla which bears the incisor teeth, and encompasses the anterior nasal spine and alar region. In the nasal cavity, the premaxillary element projects higher than the maxillary element behind. The palatal portion of the premaxilla is a bony plate with a generally transverse orientation. The incisive foramen is bound anteriorly and laterally by the premaxilla and posteriorly by the palatine process of the maxilla. It is formed from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
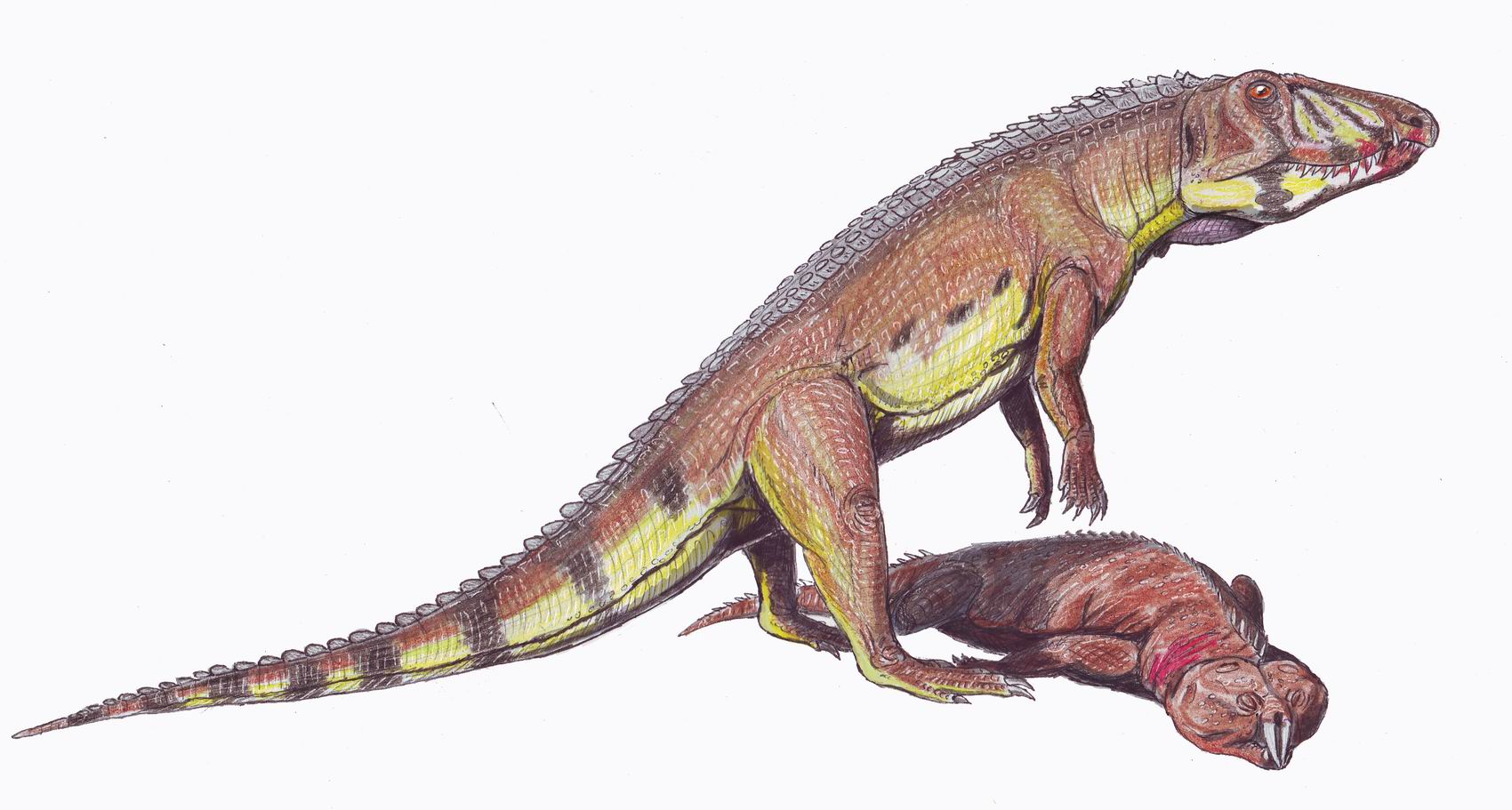
Scaphonyx
''Hyperodapedon'' is a genus of rhynchosaurs (beaked, archosaur-like reptiles) from the Late Triassic period (Carnian stage). Fossils of the genus have been found in Africa, Asia, Europe and North and South America. Its first discovery and naming was found by Thomas Henry Huxley in 1859. ''Hyperodapedon'' was a herbivore that used its beaked premaxilla and hindlimbs to dig for plants in dry land. Description ''Hyperodapedon'' was a heavily built, stocky, animal. ''H. gordoni'' had total length around with skull length of to , but largest species, ''H. huxleyi'' had lower jaw about and skull length is estimated about . Apart from its beak, it had several rows of heavy teeth on each side of the upper jaw, and a single row on each side of the lower jaw, creating a powerful chopping action when it ate. It is believed to have been herbivorous, feeding mainly on seed ferns, and died out when these plants became extinct at the end of the Triassic. The diagnosis of ''Hyperodapedon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Youngina
''Youngina'' is an extinct genus of diapsid reptile from the Late Permian Beaufort Group (''Tropidostoma''-''Dicynodon'' zones) of the Karoo Red Beds of South Africa. This, and a few related forms, make up the family Younginidae, within the Order Eosuchia (proposed by Broom in 1914). Eosuchia, having become a wastebasket taxon for many probably distantly-related primitive diapsid reptiles ranging from the Late Carboniferous to the Eocene, Romer proposed that it be replaced by Younginiformes (that included Younginidae and the Tangasauridae, ranging from the Permian to the Triassic). ''Youngina'' is known from several specimens. Many of these were attributed to as separate genera and species (such as ''Youngoides'' and ''Youngopsis''), but it was later realized that they were not distinct from ''Y. capensis''. The holotype specimen of ''Youngina'' was described briefly in 1914. The "''Youngoides romeri''" specimen was first attributed to ''Youngina'', but later given its eponymous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carnian
The Carnian (less commonly, Karnian) is the lowermost stage of the Upper Triassic Series (or earliest age of the Late Triassic Epoch). It lasted from 237 to 227 million years ago (Ma). The Carnian is preceded by the Ladinian and is followed by the Norian. Its boundaries are not characterized by major extinctions or biotic turnovers, but a climatic event (known as the Carnian pluvial episode characterized by substantial rainfall) occurred during the Carnian and seems to be associated with important extinctions or biotic radiations. Stratigraphic definitions The Carnian was named in 1869 by Mojsisovics. It is unclear if it was named after the Carnic Alps or after the Austrian region of Carinthia (''Kärnten'' in German) or after the Carnia historical region in northwestern Italy. The name, however, was first used referring to a part of the Hallstatt Limestone cropping out in Austria. The base of the Carnian Stage is defined as the place in the stratigraphic record where t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Premaxilla
The premaxilla (or praemaxilla) is one of a pair of small cranial bones at the very tip of the upper jaw of many animals, usually, but not always, bearing teeth. In humans, they are fused with the maxilla. The "premaxilla" of therian mammal has been usually termed as the incisive bone. Other terms used for this structure include premaxillary bone or ''os premaxillare'', intermaxillary bone or ''os intermaxillare'', and Goethe's bone. Human anatomy In human anatomy, the premaxilla is referred to as the incisive bone (') and is the part of the maxilla which bears the incisor teeth, and encompasses the anterior nasal spine and alar region. In the nasal cavity, the premaxillary element projects higher than the maxillary element behind. The palatal portion of the premaxilla is a bony plate with a generally transverse orientation. The incisive foramen is bound anteriorly and laterally by the premaxilla and posteriorly by the palatine process of the maxilla. It is formed from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reptile
Reptiles, as most commonly defined are the animals in the class Reptilia ( ), a paraphyletic grouping comprising all sauropsids except birds. Living reptiles comprise turtles, crocodilians, squamates (lizards and snakes) and rhynchocephalians (tuatara). As of March 2022, the Reptile Database includes about 11,700 species. In the traditional Linnaean classification system, birds are considered a separate class to reptiles. However, crocodilians are more closely related to birds than they are to other living reptiles, and so modern cladistic classification systems include birds within Reptilia, redefining the term as a clade. Other cladistic definitions abandon the term reptile altogether in favor of the clade Sauropsida, which refers to all amniotes more closely related to modern reptiles than to mammals. The study of the traditional reptile orders, historically combined with that of modern amphibians, is called herpetology. The earliest known proto-reptiles originated around ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archosauromorpha
Archosauromorpha (Greek for "ruling lizard forms") is a clade of diapsid reptiles containing all reptiles more closely related to archosaurs (such as crocodilians and dinosaurs, including birds) rather than lepidosaurs (such as tuataras, lizards, and snakes). Archosauromorphs first appeared during the late Middle Permian or Late Permian, though they became much more common and diverse during the Triassic period. Although Archosauromorpha was first named in 1946, its membership did not become well-established until the 1980s. Currently Archosauromorpha encompasses four main groups of reptiles: the stocky, herbivorous allokotosaurs and rhynchosaurs, the hugely diverse Archosauriformes, and a polyphyletic grouping of various long-necked reptiles including ''Protorosaurus'', tanystropheids, and ''Prolacerta''. Other groups including pantestudines (turtles and their extinct relatives) and the semiaquatic choristoderes have also been placed in Archosauromorpha by some authors. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triassic
The Triassic ( ) is a geologic period and system which spans 50.6 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.36 Mya. The Triassic is the first and shortest period of the Mesozoic Era. Both the start and end of the period are marked by major extinction events. The Triassic Period is subdivided into three epochs: Early Triassic, Middle Triassic and Late Triassic. The Triassic began in the wake of the Permian–Triassic extinction event, which left the Earth's biosphere impoverished; it was well into the middle of the Triassic before life recovered its former diversity. Three categories of organisms can be distinguished in the Triassic record: survivors from the extinction event, new groups that flourished briefly, and other new groups that went on to dominate the Mesozoic Era. Reptiles, especially archosaurs, were the chief terrestrial vertebrates during this time. A specialized subgroup of archo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stenaulorhynchus
''Stenaulorhynchus'' (possibly meaning "narrow tube beak") is an extinct genus of hyperodapedontid rhynchosaur known from the Middle Triassic (late Anisian stage) deposits of Tanganyika Territory, Tanzania. It was found in the Lifua Member of the Manda Formation in the Karoo Supergroup. It was named and first described by Sidney Henry Haughton in 1932. The type species is ''Stenaulorhynchus stockleyi'', a beaked herbivore measuring 1–6 meters in length. Description Dentition The teeth of ''Stenaulorhynchus'' were conical, pointed, and composed mostly of dentine, although new unworn teeth may have had a thin layer of enamel. They were set deeply into and fused with the jaw bones. They are arranged with two-to-several rows of teeth on top and only a few on bottom. The middle row of maxillary teeth only occupied the posterior third of the jaw while the other rows extended all the way forwards and sometimes down the crest of the jaw. The teeth at the front of the mouth, by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |