|
Statist Socialism
State socialism is a political and economic ideology within the socialist movement that advocates state ownership of the means of production. This is intended either as a temporary measure, or as a characteristic of socialism in the transition from the capitalist to the socialist mode of production or to a communist society. State socialism was first theorised by Ferdinand Lassalle. It advocates a planned economy controlled by the state in which all industries and natural resources are state-owned. Aside from anarchists and other libertarian socialists, there was, in the past, confidence amongst socialists in the concept of state socialism as being the most effective form of socialism. Some early social democrats in the late 19th century and early 20th century, such as the Fabians, claimed that British society was already mostly socialist and that the economy was significantly socialist through government-run enterprises created by conservative and liberal governments which c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Political Ideology
An ideology is a set of beliefs or philosophies attributed to a person or group of persons, especially those held for reasons that are not purely epistemic, in which "practical elements are as prominent as theoretical ones." Formerly applied primarily to economic, political, or religious theories and policies, in a tradition going back to Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels, more recent use the term as mainly condemnatory. The term was coined by Antoine Destutt de Tracy, a French Enlightenment aristocrat and philosopher, who conceived it in 1796 as the "science of ideas" to develop a rational system of ideas to oppose the irrational impulses of the mob. In political science, the term is used in a descriptive sense to refer to political belief systems. Etymology and history The term ''ideology'' originates from French ''idéologie'', itself deriving from combining (; close to the Lockean sense of ''idea'') and '' -logíā'' (). The term ideology, and the system of ideas associ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
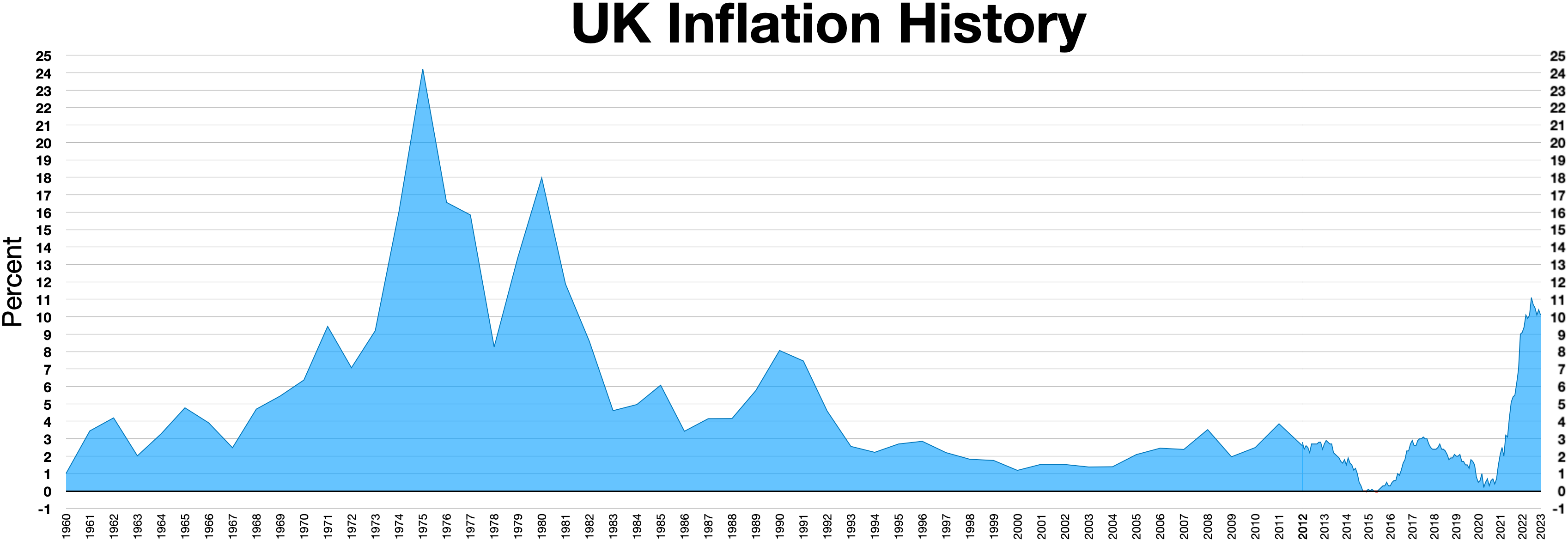
Stagflation
In economics, stagflation or recession-inflation is a situation in which the inflation rate is high or increasing, the economic growth rate slows, and unemployment remains steadily high. It presents a dilemma for economic policy, since actions intended to lower inflation may exacerbate unemployment. The term, a portmanteau of '' stagnation'' and ''inflation'', is generally attributed to Iain Macleod, a British Conservative Party politician who became Chancellor of the Exchequer in 1970. Macleod used the word in a 1965 speech to Parliament during a period of simultaneously high inflation and unemployment in the United Kingdom.Introduction, page 9. Warning the House of Commons of the gravity of the situation, he said: Macleod used the term again on 7 July 1970, and the media began also to use it, for example in ''The Economist'' on 15 August 1970, and ''Newsweek'' on 19 March 1973. John Maynard Keynes did not use the term, but some of his work refers to the conditions that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trade Unions In The Soviet Union
Trade unions in the Soviet Union, headed by the All-Union Central Council of Trade Unions (VTsSPS or ACCTU in English), had a complex relationship with industrial management, the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, and the Soviet government, given that the Soviet Union was ideologically supposed to be a state in which the members of the working class ruled the country and managed themselves. During the Russian Revolution and the Russian Civil War that immediately followed, there were all sorts of ideas about how to organize and manage industries, and many people thought that the trade unions would be the vehicle of workers' control of industries. By the Stalinist era of the 1930s, it was clear that the party and government made the rules and that the trade unions were not permitted to challenge them in any substantial way. In the decades after Stalin, the worst of the powerlessness of the unions was past, but Soviet trade unions remained something closer to company unions, ans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Truthout
Truthout is a non-profit news organization which describes itself as "dedicated to providing independent reporting and commentary on a diverse range of social justice issues". Truthout's main areas of focus include mass incarceration, prison abolition, social justice, climate change, militarism, economy and labor, LGBTQ rights and reproductive justice. Truthout's Executive Director is Ziggy West Jeffery and the Editor-in-Chief is Britney Schultz. Notable reporting and projects Controversial reporting on Karl Rove On May 13, 2006, after Jason Leopold posted on Truthout that Karl Rove had been indicted by the grand jury investigating the Plame affair, Rove spokesman Mark Corallo denied the story, calling it "a complete fabrication". Truthout defended the story, saying on May 15 they had two sources "who were explicit about the information" published, and confirmed on May 25 that they had "three independent sources confirming that attorneys for Karl Rove were handed an indict ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Libertarian
Libertarianism (from french: libertaire, "libertarian"; from la, libertas, "freedom") is a political philosophy that upholds liberty as a core value. Libertarians seek to maximize autonomy and political freedom, and minimize the state's encroachment on and violations of individual liberties; emphasizing the rule of law, pluralism, cosmopolitanism, cooperation, civil and political rights, bodily autonomy, free association, free trade, freedom of expression, freedom of choice, freedom of movement, individualism and voluntary association. Libertarians are often skeptical of or opposed to authority, state power, warfare, militarism and nationalism, but some libertarians diverge on the scope of their opposition to existing economic and political systems. Various schools of Libertarian thought offer a range of views regarding the legitimate functions of state and private power, often calling for the restriction or dissolution of coercive social institutions. Different cat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Democratic Socialism
Democratic socialism is a Left-wing politics, left-wing political philosophy that supports political democracy and some form of a socially owned economy, with a particular emphasis on economic democracy, workplace democracy, and workers' self-management within a market socialist economy or an alternative form of a decentralised planned socialist economy. Democratic socialists argue that capitalism is inherently incompatible with the values of freedom, Egalitarianism, equality, and solidarity and that these Ideal (ethics), ideals can only be achieved through the realisation of a socialist society. Although most democratic socialists seek a gradual transition to socialism, democratic socialism can support revolutionary or reformist politics to establish socialism. ''Democratic socialism'' was popularised by socialists who opposed the backsliding towards a one-party state in the Soviet Union and other nations during the 20th century. The history of democratic socialism can be trac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national republics; in practice, both its government and its economy were highly centralized until its final years. It was a one-party state governed by the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, with the city of Moscow serving as its capital as well as that of its largest and most populous republic: the Russian SFSR. Other major cities included Leningrad (Russian SFSR), Kiev (Ukrainian SSR), Minsk ( Byelorussian SSR), Tashkent (Uzbek SSR), Alma-Ata (Kazakh SSR), and Novosibirsk (Russian SFSR). It was the largest country in the world, covering over and spanning eleven time zones. The country's roots lay in the October Revolution of 1917, when the Bolsheviks, under the leadership of Vladimir Lenin, overthrew the Russian Provisional Government ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marxist–Leninist State
A communist state, also known as a Marxist–Leninist state, is a one-party state that is administered and governed by a communist party guided by Marxism–Leninism. Marxism–Leninism was the state ideology of the Soviet Union, the Comintern after Bolshevisation and the communist states within the Comecon, the Eastern Bloc and the Warsaw Pact. Marxism–Leninism currently still remains the ideology of a few parties around the world. After its peak when many communist states were established, the Revolutions of 1989 brought down most of the communist states, however, it is still the official ideology of the ruling parties of China, Cuba, Laos, and Vietnam. During most of the 20th century, before the Revolutions of 1989, around one-third of the world's population lived under communist states. Communist states are typically authoritarian and are typically administered through democratic centralism by a single centralised communist party apparatus. These parties are usually Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet-type Economic Planning
Soviet-type economic planning (STP) is the specific model of centralized planning employed by Marxist–Leninist socialist states modeled on the economy of the Soviet Union (USSR). The post-''perestroika'' analysis of the system of the Soviet economic planning describes it as the administrative-command system due to the ''de facto'' priority of highly centralized management over planning. Characteristics Institutions The major institutions of Soviet-type planning in the USSR included a planning agency (Gosplan), an organization for allocating state supplies among the various organizations and enterprises in the economy (Gossnab) and enterprises which were engaged in the production and delivery of goods and services in the economy. Enterprises comprised production associations and institutes that were linked together by the plans formulated by Gosplan. In the Eastern bloc countries (Bulgaria, Czechoslovakia, East Germany, Hungary, Poland, Romania, and Albania), economic pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State Capitalism
State capitalism is an economic system in which the state undertakes business and commercial (i.e. for-profit) economic activity and where the means of production are nationalized as state-owned enterprises (including the processes of capital accumulation, centralized management and wage labor). The definition can also include the state dominance of corporatized government agencies (agencies organized along business-management practices) or of public companies such as publicly listed corporations in which the state has controlling shares. Marxist literature defines state capitalism as a social system combining capitalism with ownership or control by a state. By this definition, a state capitalist country is one where the government controls the economy and essentially acts like a single huge corporation, extracting surplus value from the workforce in order to invest it in further production. This designation applies regardless of the political aims of the state, even if the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fall Of The Soviet Union
The dissolution of the Soviet Union, also negatively connoted as rus, Разва́л Сове́тского Сою́за, r=Razvál Sovétskogo Soyúza, ''Ruining of the Soviet Union''. was the process of internal disintegration within the Soviet Union (USSR) which resulted in the end of the country's and its federal government's existence as a sovereign state, thereby resulting in its constituent republics gaining full sovereignty on 26 December 1991. It brought an end to General Secretary Mikhail Gorbachev's (later also President) effort to reform the Soviet political and economic system in an attempt to stop a period of political stalemate and economic backslide. The Soviet Union had experienced internal stagnation and ethnic separatism. Although highly centralized until its final years, the country was made up of fifteen top-level republics that served as homelands for different ethnicities. By late 1991, amid a catastrophic political crisis, with several republics alread ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Revolutions Of 1989
The Revolutions of 1989, also known as the Fall of Communism, was a revolutionary wave that resulted in the end of most communist states in the world. Sometimes this revolutionary wave is also called the Fall of Nations or the Autumn of Nations, a play on the term Spring of Nations that is sometimes used to describe the Revolutions of 1848 in Europe. It also led to the eventual breakup of the Soviet Union—the world's largest communist state—and the abandonment of communist regimes in many parts of the world, some of which were violently overthrown. The events, especially the fall of the Soviet Union, drastically altered the world's balance of power, marking the end of the Cold War and the beginning of the post-Cold War era. The earliest recorded protests were started in Kazakhstan, then part of the Soviet Union, in 1986 with the Jeltoqsan, student demonstrations — the last chapter of these revolutions is considered to be in 1993 when Cambodia United Nations Transition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)
