|
Fall Of The Soviet Union
The dissolution of the Soviet Union, also negatively connoted as rus, Разва́л Сове́тского Сою́за, r=Razvál Sovétskogo Soyúza, ''Ruining of the Soviet Union''. was the process of internal disintegration within the Soviet Union (USSR) which resulted in the end of the country's and its federal government's existence as a sovereign state, thereby resulting in its constituent republics gaining full sovereignty on 26 December 1991. It brought an end to General Secretary Mikhail Gorbachev's (later also President) effort to reform the Soviet political and economic system in an attempt to stop a period of political stalemate and economic backslide. The Soviet Union had experienced internal stagnation and ethnic separatism. Although highly centralized until its final years, the country was made up of fifteen top-level republics that served as homelands for different ethnicities. By late 1991, amid a catastrophic political crisis, with several republics alread ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flag Of The Soviet Union
The State Flag of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (), commonly known as the Soviet flag (), was the official state flag of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR) from 1922 to 1991. The flag's design and symbolism are derived from several sources, but emerged during the Russian Revolution. The flag is also an international symbol of the communist movement as a whole. The design is a solid field of red adorned with a unique gold emblem in the upper hoist quarter. The red flag was a traditional revolutionary symbol long before 1917, and its incorporation into the flag paid tribute to the international aspect of workers' revolution. The iconic hammer and sickle design was a modern industrial touch adopted from the Russian Revolution. The union of the hammer (workers) and the sickle (peasants) represents the victorious and enduring revolutionary alliance. The famous emblem is topped by a gold-bordered red star representing the Communist Party of the Soviet Union. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
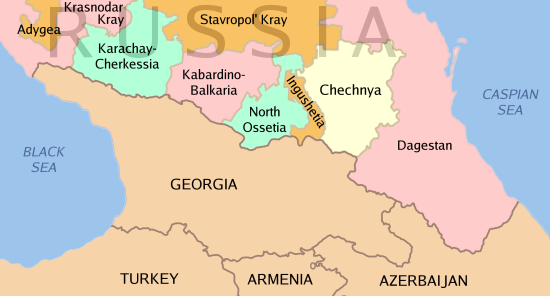
Second Chechen War
The Second Chechen War (russian: Втора́я чече́нская война́, ) took place in Chechnya and the border regions of the North Caucasus between the Russia, Russian Federation and the Chechen Republic of Ichkeria, from August 1999 to April 2009. In August 1999, Islamist fighters from Chechnya War of Dagestan, infiltrated Russia's Dagestan region, violating Russia's borders. During the initial campaign, Russians, Russian military and pro-Russian Chechens, Chechen paramilitary forces faced Chechen separatists in open combat and seized the Chechen capital Grozny after a winter Battle of Grozny (1999–2000), siege that lasted from December 1999 until February 2000. Russia established direct rule over Chechnya in May 2000 although Chechen militant Resistance movement, resistance throughout the North Caucasus region continued to inflict heavy Russian casualties and challenge Russian political control over Chechnya for several years. Both sides carried out attacks a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capitalism
Capitalism is an economic system based on the private ownership of the means of production and their operation for Profit (economics), profit. Central characteristics of capitalism include capital accumulation, competitive markets, price system, private property, Property rights (economics), property rights recognition, voluntary exchange, and wage labor. In a market economy, decision-making and investments are determined by owners of wealth, property, or ability to maneuver capital or production ability in Capital market, capital and financial markets—whereas prices and the distribution of goods and services are mainly determined by competition in goods and services markets. Economists, historians, political economists and sociologists have adopted different perspectives in their analyses of capitalism and have recognized various forms of it in practice. These include ''Laissez-faire capitalism, laissez-faire'' or free-market capitalism, anarcho-capitalism, state capi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semi-presidential Republic
A semi-presidential republic, is a republic in which a president exists alongside a prime minister and a cabinet, with the latter two being responsible to the legislature of the state. It differs from a parliamentary republic in that it has a popularly elected head of state and from the presidential system in that the cabinet, although named by the president, is responsible to the legislature, which may force the cabinet to resign through a motion of no confidence. While the Weimar Republic (1919–1933) and Finland (from 1919 to 2000) exemplified early semi-presidential systems, the term "semi-presidential" was first introduced in 1959 in an article by journalist Hubert Beuve-Méry, and popularized by a 1978 work written by political scientist Maurice Duverger, both of whom intended to describe the French Fifth Republic (established in 1958). Definition Maurice Duverger's original definition of semi-presidentialism stated that the president had to be elected, possess signi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Presidential Republic
A presidential system, or single executive system, is a form of government in which a head of government, typically with the title of president, leads an executive branch that is separate from the legislative branch in systems that use separation of powers. This head of government is in most cases also the head of state. In a presidential system, the head of government is directly or indirectly elected by a group of citizens and is not responsible to the legislature, and the legislature cannot dismiss the president except in extraordinary cases. A presidential system contrasts with a parliamentary system, where the head of government comes to power by gaining the confidence of an elected legislature. Not all presidential systems use the title of ''president''. Likewise, the title is sometimes used by other systems. It originated from a time when such a person personally presided over the governing body, as with the President of the Continental Congress in the early United S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multi Party System
In political science, a multi-party system is a political system in which multiple political parties across the political spectrum run for national elections, and all have the capacity to gain control of government offices, separately or in coalition. Apart from one-party-dominant and two-party systems, multi-party systems tend to be more common in parliamentary systems than presidential systems and far more common in countries that use proportional representation compared to countries that use first-past-the-post elections. Several parties compete for power and all of them have reasonable chance of forming government. In multi-party systems that use proportional representation, each party wins a number of legislative seats proportional to the number of votes it receives. Under first-past-the-post, the electorate is divided into a number of districts, each of which selects one person to fill one seat by a plurality of the vote. First-past-the-post is not conducive to a prolifer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internally Displaced Person
An internally displaced person (IDP) is someone who is forced to leave their home but who remains within their country's borders. They are often referred to as refugees, although they do not fall within the legal definitions of a refugee. At the end of 2014, it was estimated there were 38.2 million IDPs worldwide, the highest level since 1989, the first year for which global statistics on IDPs are available. As of 3 May 2022 the countries with the largest IDP populations were Ukraine (8 million), Syria (7.6 million), Ethiopia (5.5 million), the Democratic Republic of the Congo (5.2 million), Colombia (4.9 million), Yemen (4.3 million), Afghanistan (3.8 million), Iraq (3.6 million), Sudan (2.2 million), South Sudan (1.9 million), Pakistan (1.4 million), Nigeria (1.2 million) and Somalia (1.1 million). The United Nations and the UNHCR support monitoring and analysis of worldwide IDPs through the Geneva-based Internal Displacement Monitoring Centre. Definition Whereas 'refugee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Post-Soviet Conflicts
This article lists the post-Soviet conflicts; the violent political and ethnic conflicts in the countries of the Post-Soviet states, former Soviet Union following its Dissolution of the Soviet Union, dissolution in 1991. Some of these conflicts such as the 1993 Russian constitutional crisis or the 2013 Euromaidan protests in Ukraine were due to political crises in the successor states. Others involved separatist movements attempting to break away from one of the successor states. Frozen conflicts Some post-Soviet conflicts ended in a stalemate or without a peace treaty, and are referred to as frozen conflicts. This means that a number of Post-Soviet states, former-Soviet states are left sovereignty over the entirety of their territory De jure, in name only. De facto, In reality, they do not exercise full control over areas still under the control of rebel factions. Rebel groups are essentially left independent over large chunks of the territories they claim. In many instances, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commonwealth Of Independent States
The Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) is a regional intergovernmental organization in Eurasia. It was formed following the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991. It covers an area of and has an estimated population of 239,796,010. The CIS encourages cooperation in economic, political and military affairs and has certain powers relating to the coordination of trade, finance, lawmaking, and security. It has also promoted cooperation on cross-border crime prevention. As the Soviet Union disintegrated, Belarus, Russia and Ukraine signed the Belovezh Accords on 8 December 1991, declaring that the Union had effectively ceased to exist and proclaimed the CIS in its place. On 21 December, the Alma-Ata Protocol was signed. The Baltic states (Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania), which regard their membership in the Soviet Union as an illegal occupation, chose not to participate. Georgia withdrew its membership in 2008 following the Russo-Georgian War. Ukraine formally ended its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Post-Soviet States
The post-Soviet states, also known as the former Soviet Union (FSU), the former Soviet Republics and in Russia as the near abroad (russian: links=no, ближнее зарубежье, blizhneye zarubezhye), are the 15 sovereign states that were union republics of the Soviet Union, which emerged and re-emerged from the Soviet Union following its dissolution in 1991. Russia is the primary ''de facto'' internationally recognized successor state to the Soviet Union after the Cold War; while Ukraine has, by law, proclaimed that it is a state-successor of both the Ukrainian SSR and the Soviet Union which remained under dispute over formerly Soviet-owned properties. The three Baltic states – Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania – were the first to declare their independence from the USSR, between March and May 1990, claiming continuity from the original states that existed prior to their annexation by the Soviet Union in 1940. The remaining 12 republics all subsequently seceded, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dissolution (law)
In law, dissolution is any of several legal events that terminate a legal entity or agreement such as a marriage, adoption, corporation, or union. Dissolution is the last stage of liquidation, the process by which a company (or part of a company) is brought to an end, and the assets and property of the company are gone forever. Dissolution of a partnership is the first of two stages in the termination of a partnership. "Winding up" is the second stage.Slides 11-17 oPowerpoint for Chapter 21 from McGraw-Hill from 2nd Ed. of Kusabek Dissolution may also refer to the termination of a contract or other legal relationship; for example, a divorce is the dissolution of a marriage only if the husband or wife does not agree. If the husband and wife agree then it is a dissolution. Dissolution is also the term for the legal process by which an adoption is reversed. While this applies to the vast majority of adoptions which are terminated, they are more commonly referred to as disruptio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transnistria
Transnistria, officially the Pridnestrovian Moldavian Republic (PMR), is an unrecognised breakaway state that is internationally recognised as a part of Moldova. Transnistria controls most of the narrow strip of land between the Dniester river and the Moldovan–Ukrainian border, as well as some land on the other side of the river's bank. Its capital and largest city is Tiraspol. Transnistria has been recognised only by three other unrecognised or partially recognised breakaway states: Abkhazia, Artsakh and South Ossetia. Transnistria is officially designated by the Republic of Moldova as the Administrative-Territorial Units of the Left Bank of the Dniester ( ro, Unitățile Administrativ-Teritoriale din stînga Nistrului) or as ("Left Bank of the Dniester"). The Council of Europe considers the territory to be under military occupation by Russia. The region's origins can be traced to the Moldavian Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic, which was formed in 1924 within th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)