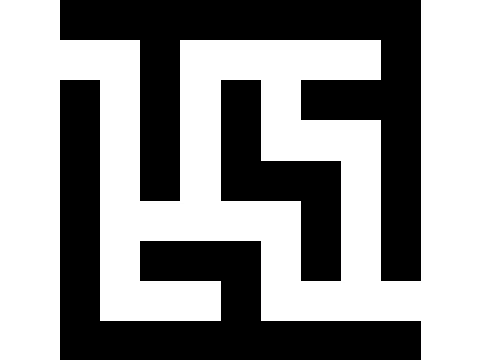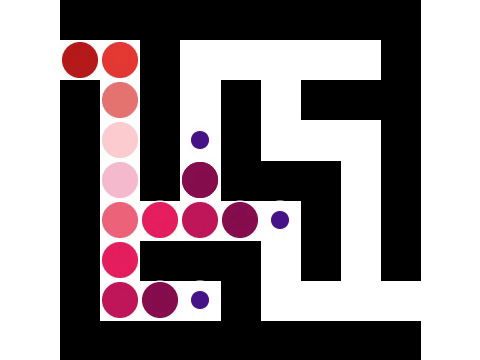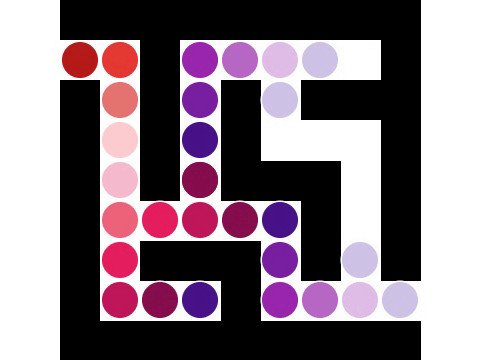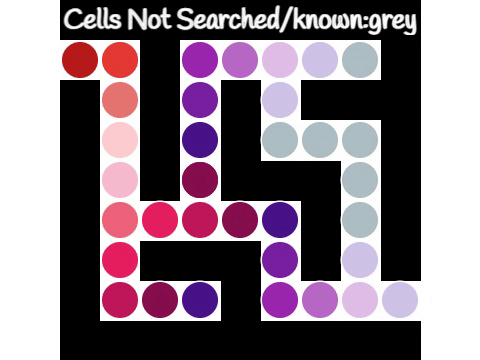
|
State-space Search
State-space search is a process used in the field of computer science, including artificial intelligence (AI), in which successive configurations or ''states'' of an instance are considered, with the intention of finding a ''goal state'' with the desired property. Problems are often modelled as a state space, a set of ''states'' that a problem can be in. The set of states forms a graph where two states are connected if there is an ''operation'' that can be performed to transform the first state into the second. State-space search often differs from traditional computer science search methods because the state space is ''implicit'': the typical state-space graph is much too large to generate and store in memory. Instead, nodes are generated as they are explored, and typically discarded thereafter. A solution to a combinatorial search instance may consist of the goal state itself, or of a path from some ''initial state'' to the goal state. Representation In state-space search ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Science
Computer science is the study of computation, information, and automation. Computer science spans Theoretical computer science, theoretical disciplines (such as algorithms, theory of computation, and information theory) to Applied science, applied disciplines (including the design and implementation of Computer architecture, hardware and Software engineering, software). Algorithms and data structures are central to computer science. The theory of computation concerns abstract models of computation and general classes of computational problem, problems that can be solved using them. The fields of cryptography and computer security involve studying the means for secure communication and preventing security vulnerabilities. Computer graphics (computer science), Computer graphics and computational geometry address the generation of images. Programming language theory considers different ways to describe computational processes, and database theory concerns the management of re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Depth-first Search
Depth-first search (DFS) is an algorithm for traversing or searching tree or graph data structures. The algorithm starts at the root node (selecting some arbitrary node as the root node in the case of a graph) and explores as far as possible along each branch before backtracking. Extra memory, usually a stack, is needed to keep track of the nodes discovered so far along a specified branch which helps in backtracking of the graph. A version of depth-first search was investigated in the 19th century by French mathematician Charles Pierre Trémaux as a strategy for solving mazes. Properties The time and space analysis of DFS differs according to its application area. In theoretical computer science, DFS is typically used to traverse an entire graph, and takes time where , V, is the number of vertices and , E, the number of edges. This is linear in the size of the graph. In these applications it also uses space O(, V, ) in the worst case to store the stack of vertices on t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State-space Planning
In artificial intelligence and computer programming, state-space planning is a process used in designing programs to search for data or solutions to problems. In a computer algorithm that searches a data structure for a piece of data, for example a program that looks up a word in a computer dictionary, the ''state space'' is a collective term for all the data to be searched. Similarly, artificial intelligence programs often employ a process of searching through a finite universe of possible procedures for reaching a goal, to find a procedure or the best procedure to achieve the goal. The universe of possible solutions to be searched is called the state space. State-space planning is the process of deciding which parts of the state space the program will search, and in what order. Definition The simplest classical planning algorithms are state-space search algorithms. These are search algorithms in which the search space is a subset of the state space: Each node corresponds to a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State Space
In computer science, a state space is a discrete space representing the set of all possible configurations of a system. It is a useful abstraction for reasoning about the behavior of a given system and is widely used in the fields of artificial intelligence and game theory. For instance, the toy problem Vacuum World has a discrete finite state space in which there are a limited set of configurations that the vacuum and dirt can be in. A "counter" system, where states are the natural numbers starting at 1 and are incremented over time has an infinite discrete state space. The angular position of an undamped pendulum is a continuous (and therefore infinite) state space. Definition State spaces are useful in computer science as a simple model of machines. Formally, a state space can be defined as a tuple [''N'', ''A'', ''S'', ''G''] where: * ''N'' is a Set (mathematics), set of states * ''A'' is a set of arcs connecting the states * ''S'' is a nonempty subset of ''N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A* Search
A* (pronounced "A-star") is a graph traversal and pathfinding algorithm that is used in many fields of computer science due to its completeness, optimality, and optimal efficiency. Given a weighted graph, a source node and a goal node, the algorithm finds the shortest path (with respect to the given weights) from source to goal. One major practical drawback is its O(b^d) space complexity where is the depth of the shallowest solution (the length of the shortest path from the source node to any given goal node) and is the branching factor (the maximum number of successors for any given state), as it stores all generated nodes in memory. Thus, in practical travel-routing systems, it is generally outperformed by algorithms that can pre-process the graph to attain better performance, as well as by memory-bounded approaches; however, A* is still the best solution in many cases. Peter Hart, Nils Nilsson and Bertram Raphael of Stanford Research Institute (now SRI International) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Best-first Search
Best-first search is a class of search algorithms which explores a graph by expanding the most promising node chosen according to a specified rule. Judea Pearl described best-first search as estimating the promise of node ''n'' by a "heuristic evaluation function f(n) which, in general, may depend on the description of ''n'', the description of the goal, the information gathered by the search up to that point, and most importantly, on any extra knowledge about the problem domain." Some authors have used "best-first search" to refer specifically to a search with a heuristic that attempts to predict how close the end of a path is to a solution (or, goal), so that paths which are judged to be closer to a solution (or, goal) are expanded first. This specific type of search is called '' greedy best-first search'' or ''pure heuristic search''. Efficient selection of the current best candidate for extension is typically implemented using a priority queue. The A* search algorithm is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heuristic Function
A heuristic or heuristic technique (''problem solving'', '' mental shortcut'', ''rule of thumb'') is any approach to problem solving that employs a pragmatic method that is not fully optimized, perfected, or rationalized, but is nevertheless "good enough" as an approximation or attribute substitution. Where finding an optimal solution is impossible or impractical, heuristic methods can be used to speed up the process of finding a satisfactory solution. Heuristics can be mental shortcuts that ease the cognitive load of making a decision. Context Gigerenzer & Gaissmaier (2011) state that sub-sets of ''strategy'' include heuristics, regression analysis, and Bayesian inference. Heuristics are strategies based on rules to generate optimal decisions, like the anchoring effect and utility maximization problem. These strategies depend on using readily accessible, though loosely applicable, information to control problem solving in human beings, machines and abstract ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dijkstra's Algorithm
Dijkstra's algorithm ( ) is an algorithm for finding the shortest paths between nodes in a weighted graph, which may represent, for example, a road network. It was conceived by computer scientist Edsger W. Dijkstra in 1956 and published three years later. Dijkstra's algorithm finds the shortest path from a given source node to every other node. It can be used to find the shortest path to a specific destination node, by terminating the algorithm after determining the shortest path to the destination node. For example, if the nodes of the graph represent cities, and the costs of edges represent the distances between pairs of cities connected by a direct road, then Dijkstra's algorithm can be used to find the shortest route between one city and all other cities. A common application of shortest path algorithms is network routing protocols, most notably IS-IS (Intermediate System to Intermediate System) and OSPF (Open Shortest Path First). It is also employed as a subroutine in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iterative Deepening Depth-first Search
In computer science, iterative deepening search or more specifically iterative deepening depth-first search (IDS or IDDFS) is a state space/graph search strategy in which a depth-limited version of depth-first search is run repeatedly with increasing depth limits until the goal is found. IDDFS is optimal, meaning that it finds the shallowest goal. Since it visits all the nodes in the search tree down to depth d before visiting any nodes at depth d + 1, the cumulative order in which nodes are first visited is effectively the same as in breadth-first search. However, IDDFS uses much less memory. Algorithm for directed graphs The following pseudocode shows IDDFS implemented in terms of a recursive depth-limited DFS (called DLS) for directed graphs. This implementation of IDDFS does not account for already-visited nodes. function IDDFS(root) is for depth from 0 to ∞ do found, remaining ← DLS(root, depth) if found ≠ null then return found ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breadth-first Search
Breadth-first search (BFS) is an algorithm for searching a tree data structure for a node that satisfies a given property. It starts at the tree root and explores all nodes at the present depth prior to moving on to the nodes at the next depth level. Extra memory, usually a queue, is needed to keep track of the child nodes that were encountered but not yet explored. For example, in a chess endgame, a chess engine may build the game tree from the current position by applying all possible moves and use breadth-first search to find a win position for White. Implicit trees (such as game trees or other problem-solving trees) may be of infinite size; breadth-first search is guaranteed to find a solution node if one exists. In contrast, (plain) depth-first search (DFS), which explores the node branch as far as possible before backtracking and expanding other nodes, may get lost in an infinite branch and never make it to the solution node. Iterative deepening depth-first search ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Set (mathematics)
In mathematics, a set is a collection of different things; the things are '' elements'' or ''members'' of the set and are typically mathematical objects: numbers, symbols, points in space, lines, other geometric shapes, variables, or other sets. A set may be finite or infinite. There is a unique set with no elements, called the empty set; a set with a single element is a singleton. Sets are ubiquitous in modern mathematics. Indeed, set theory, more specifically Zermelo–Fraenkel set theory, has been the standard way to provide rigorous foundations for all branches of mathematics since the first half of the 20th century. Context Before the end of the 19th century, sets were not studied specifically, and were not clearly distinguished from sequences. Most mathematicians considered infinity as potentialmeaning that it is the result of an endless processand were reluctant to consider infinite sets, that is sets whose number of members is not a natural number. Specific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is the capability of computer, computational systems to perform tasks typically associated with human intelligence, such as learning, reasoning, problem-solving, perception, and decision-making. It is a field of research in computer science that develops and studies methods and software that enable machines to machine perception, perceive their environment and use machine learning, learning and intelligence to take actions that maximize their chances of achieving defined goals. High-profile applications of AI include advanced web search engines (e.g., Google Search); recommendation systems (used by YouTube, Amazon (company), Amazon, and Netflix); virtual assistants (e.g., Google Assistant, Siri, and Amazon Alexa, Alexa); autonomous vehicles (e.g., Waymo); Generative artificial intelligence, generative and Computational creativity, creative tools (e.g., ChatGPT and AI art); and Superintelligence, superhuman play and analysis in strategy games (e.g., ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |