|
Stanford In The Vale
Stanford in the Vale is a village and civil parish in the Vale of White Horse about southeast of Faringdon and northwest of Wantage. It is part of the historic county of Berkshire, however since 1974, it has been administered as a part of Oxfordshire. The 2011 Census recorded the parish's population 2,093. Geography Stanford is a village with a clustered centre just north of the nascent River Ock, which is a tributary of the River Thames and flows from west to east through the parish. The parish is about wide north – south but extends for more than east – west along the course of the Ock and its tributaries. One tributary, Stutfield Brook, forms the southeast boundary of the parish. Another, Frogmore Brook, forms part of the northern boundary. The western boundary follows the edges of present and former fields. Stanford village is built on soil-clad Corallian Limestone, which in patches comes close to the surface through erosion. The village is on the A417 road that li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Kingdom Census 2011
A Census in the United Kingdom, census of the population of the United Kingdom is taken every ten years. The 2011 census was held in all countries of the UK on 27 March 2011. It was the first UK census which could be completed online via the Internet. The Office for National Statistics (ONS) is responsible for the census in England and Wales, the General Register Office for Scotland (GROS) is responsible for the census in Scotland, and the Northern Ireland Statistics and Research Agency (NISRA) is responsible for the census in Northern Ireland. The Office for National Statistics is the executive office of the UK Statistics Authority, a non-ministerial department formed in 2008 and which reports directly to Parliament. ONS is the UK Government's single largest statistical producer of independent statistics on the UK's economy and society, used to assist the planning and allocation of resources, policy-making and decision-making. ONS designs, manages and runs the census in England an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Britain
Roman Britain was the period in classical antiquity when large parts of the island of Great Britain were under occupation by the Roman Empire. The occupation lasted from AD 43 to AD 410. During that time, the territory conquered was raised to the status of a Roman province. Julius Caesar invaded Britain in 55 and 54 BC as part of his Gallic Wars. According to Caesar, the Britons had been overrun or culturally assimilated by other Celtic tribes during the British Iron Age and had been aiding Caesar's enemies. He received tribute, installed the friendly king Mandubracius over the Trinovantes, and returned to Gaul. Planned invasions under Augustus were called off in 34, 27, and 25 BC. In 40 AD, Caligula assembled 200,000 men at the Channel on the continent, only to have them gather seashells ('' musculi'') according to Suetonius, perhaps as a symbolic gesture to proclaim Caligula's victory over the sea. Three years later, Claudius directed four legi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Barons' War
The Second Barons' War (1264–1267) was a civil war in England between the forces of a number of barons led by Simon de Montfort against the royalist forces of King Henry III, led initially by the king himself and later by his son, the future King Edward I. The barons sought to force the king to rule with a council of barons, rather than through his favourites. The war also involved a series of massacres of Jews by de Montfort's supporters, including his sons Henry and Simon, in attacks aimed at seizing and destroying evidence of baronial debts. To bolster the initial success of his baronial regime, de Montfort sought to broaden the social foundations of parliament by extending the franchise to the commons for the first time. However, after a rule of just over a year, de Montfort was killed by forces loyal to the king at the Battle of Evesham. Causes The reign of Henry III is most remembered for the constitutional crisis in this period of civil strife, which was provoked o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert De Ferrers, 6th Earl Of Derby
Robert de Ferrers, 6th Earl of Derby (1239–1279) was an English nobleman. He was born at Tutbury Castle in Staffordshire, England, the son of William de Ferrers, 5th Earl of Derby, by his second wife Margaret de Quincy (born 1218), a daughter of Roger de Quincy, 2nd Earl of Winchester and Helen of Galloway. Early years In 1249, at the age of 10, he married the seven-year-old Mary (or Marie), daughter of Hugh XI of Lusignan Count of La Marche, the eldest of Henry III's half-brothers, at Westminster Abbey. This arranged marriage is an indication of Henry's high regard for Robert's father. William died in 1254, so Robert became a knight and inherited the title while he was still a minor. He and his estates became a ward of Prince Edward. In 1257, Edward sold the wardship to the queen and Peter of Savoy for 6000 marks, which might have been a source of the later antipathy of Ferrers for the prince. Inheritance Robert came of age in 1260 and took possession of the vast estate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
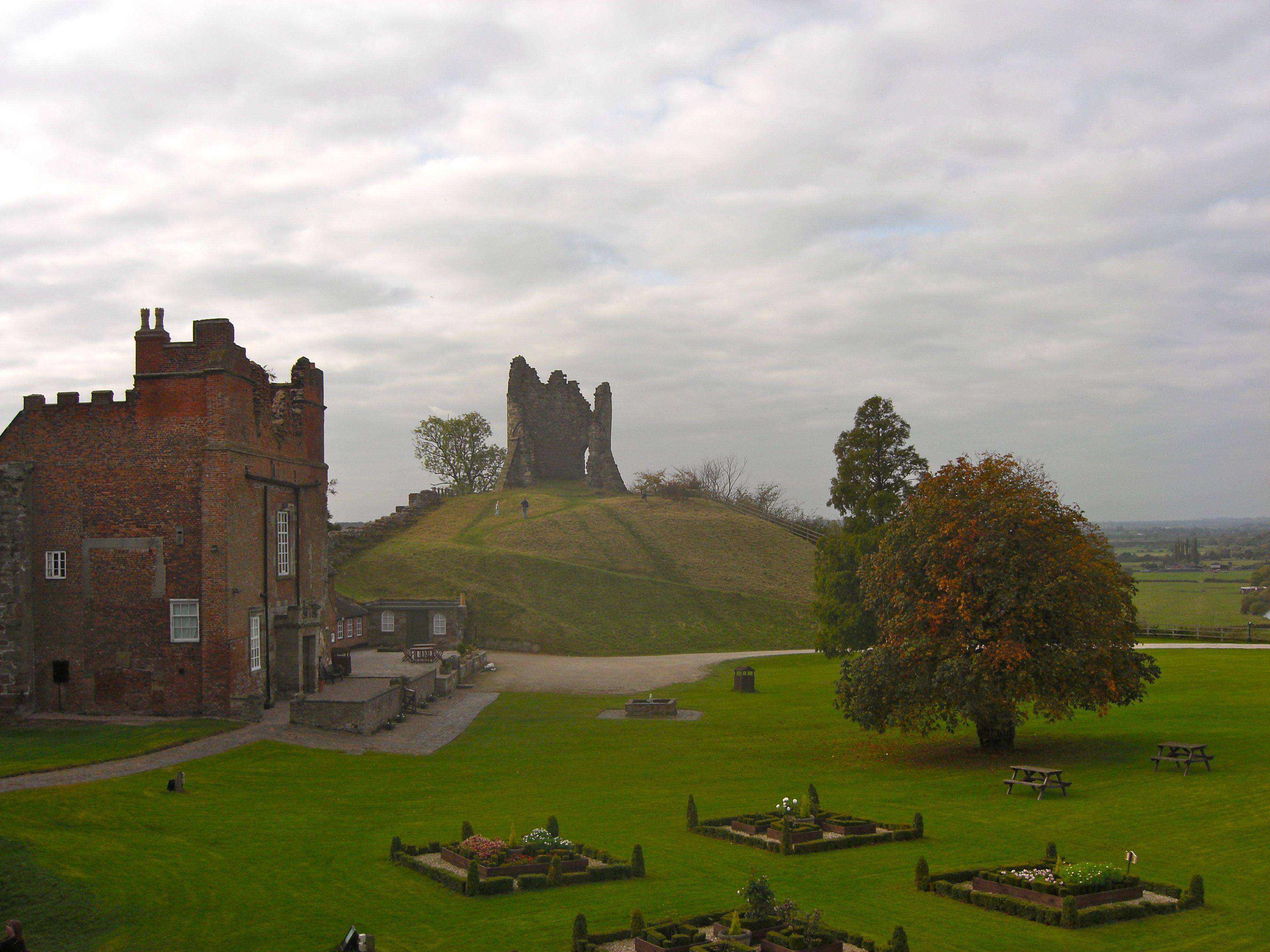
Tutbury
Tutbury is a village and civil parishes in England, civil parish in Staffordshire, England. It is north of Burton upon Trent and south of the Peak District. The village has a population of about 3,076 residents. It adjoins Hatton, Derbyshire, Hatton to the north on the Staffordshire–Derbyshire border. History Tutbury is surrounded by the agricultural countryside of both Staffordshire and Derbyshire. The site has been inhabited for over 3,000 years, with Iron Age defensive ditches encircling the main defensive hill, upon which now stand the ruins of the Norman castle. These ditches can be seen most clearly at the Park Pale and at the top of the steep hills behind Park Lane. The name Tutbury probably derives from a Scandinavian settler and subsequent chief of the hill-fort, Totta, ''bury'' being a corruption of ''burh'' the Anglo-Saxon name for 'fortified place'. Tutbury Castle became the headquarters of Henry de Ferrers and was the centre of the wapentake of Appletree, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Honour (feudal Barony)
Honour (British English) or honor (American English; see spelling differences) is the idea of a bond between an individual and a society as a quality of a person that is both of social teaching and of personal ethos, that manifests itself as a code of conduct, and has various elements such as valour, chivalry, honesty, and compassion. It is an abstract concept entailing a perceived quality of worthiness and respectability that affects both the social standing and the self-evaluation of an individual or institutions such as a family, school, regiment or nation. Accordingly, individuals (or institutions) are assigned worth and stature based on the harmony of their actions with a specific code of honour, and the moral code of the society at large. Samuel Johnson, in his ''A Dictionary of the English Language'' (1755), defined honour as having several senses, the first of which was "nobility of soul, magnanimity, and a scorn of meanness". This sort of honour derives from the percei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry De Ferrers
Henry de Ferrers (died by 1100), magnate and administrator, was a Norman who after the 1066 Norman conquest was awarded extensive lands in England. Origins He was the eldest son of Vauquelin de Ferrers and in about 1040 inherited his father's lands centred on the village of Ferrières-Saint-Hilaire. Career In England he progressively acquired landholdings, which he had to manage. As one of the leading magnates, he also served King William I of England and his successor William II in administrative capacities and is said to have been castellan of Stafford Castle. In about 1080, he and his wife founded Tutbury Priory in Staffordshire, and in 1086 he was one of the royal commissioners in charge of the Domesday survey, which records his 210 manors.''Domesday Book: A Complete Translation''. London: Penguin, 2003. p. 656-7 744-9 He died between September 1093 and September 1100 and was buried in Tutbury Priory. Landholdings His first three tranches of land came to him from dispo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norman Conquest Of England
The Norman Conquest (or the Conquest) was the 11th-century invasion and occupation of England by an army made up of thousands of Normans, Norman, Duchy of Brittany, Breton, County of Flanders, Flemish, and Kingdom of France, French troops, all led by the Duke of Normandy, later styled William the Conqueror. William's claim to the English throne derived from his familial relationship with the childless Anglo-Saxon king Edward the Confessor, who may have encouraged William's hopes for the throne. Edward died in January 1066 and was succeeded by his brother-in-law Harold Godwinson. The Norwegian king Harald Hardrada invaded northern England in September 1066 and was victorious at the Battle of Fulford on 20 September, but Godwinson's army defeated and killed Hardrada at the Battle of Stamford Bridge on 25 September. Three days later on 28 September, William's invasion force of thousands of men and hundreds of ships landed at Pevensey in Sussex in southern England. Harold march ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Domesday Book
Domesday Book () – the Middle English spelling of "Doomsday Book" – is a manuscript record of the "Great Survey" of much of England and parts of Wales completed in 1086 by order of King William I, known as William the Conqueror. The manuscript was originally known by the Latin name ''Liber de Wintonia'', meaning "Book of Winchester", where it was originally kept in the royal treasury. The '' Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' states that in 1085 the king sent his agents to survey every shire in England, to list his holdings and dues owed to him. Written in Medieval Latin, it was highly abbreviated and included some vernacular native terms without Latin equivalents. The survey's main purpose was to record the annual value of every piece of landed property to its lord, and the resources in land, manpower, and livestock from which the value derived. The name "Domesday Book" came into use in the 12th century. Richard FitzNeal wrote in the ''Dialogus de Scaccario'' ( 1179) that the book ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manorialism
Manorialism, also known as the manor system or manorial system, was the method of land ownership (or "tenure") in parts of Europe, notably France and later England, during the Middle Ages. Its defining features included a large, sometimes fortified manor house in which the lord of the manor and his dependents lived and administered a rural estate, and a population of labourers who worked the surrounding land to support themselves and the lord. These labourers fulfilled their obligations with labour time or in-kind produce at first, and later by cash payment as commercial activity increased. Manorialism is sometimes included as part of the feudal system. Manorialism originated in the Roman villa system of the Late Roman Empire, and was widely practiced in medieval western Europe and parts of central Europe. An essential element of feudal society, manorialism was slowly replaced by the advent of a money-based market economy and new forms of agrarian contract. In examining the o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward The Confessor
Edward the Confessor ; la, Eduardus Confessor , ; ( 1003 – 5 January 1066) was one of the last Anglo-Saxon English kings. Usually considered the last king of the House of Wessex, he ruled from 1042 to 1066. Edward was the son of Æthelred the Unready and Emma of Normandy. He succeeded Cnut the Great's son – and his own half-brother – Harthacnut. He restored the rule of the House of Wessex after the period of Danish rule since Cnut conquered England in 1016. When Edward died in 1066, he was succeeded by his wife's brother Harold Godwinson, who was defeated and killed in the same year by the Normans under William the Conqueror at the Battle of Hastings. Edward's young great-nephew Edgar the Ætheling of the House of Wessex was proclaimed king after the Battle of Hastings in 1066 but was never crowned and was peacefully deposed after about eight weeks. Historians disagree about Edward's fairly long 24-year reign. His nickname reflects the traditional image ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old English
Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain, Anglo-Saxon settlers in the mid-5th century, and the first Old English literature, Old English literary works date from the mid-7th century. After the Norman conquest of 1066, English was replaced, for a time, by Anglo-Norman language, Anglo-Norman (a langues d'oïl, relative of French) as the language of the upper classes. This is regarded as marking the end of the Old English era, since during this period the English language was heavily influenced by Anglo-Norman, developing into a phase known now as Middle English in England and Early Scots in Scotland. Old English developed from a set of Anglo-Frisian languages, Anglo-Frisian or Ingvaeonic dialects originally spoken by Germanic peoples, Germanic tribes traditionally known as the Angles, Sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |