|
Standard Quantum Limit
A quantum limit in physics is a limit on measurement accuracy at quantum scales. Depending on the context, the limit may be absolute (such as the Heisenberg limit), or it may only apply when the experiment is conducted with naturally occurring quantum states (e.g. the standard quantum limit in interferometry) and can be circumvented with advanced state preparation and measurement schemes. The usage of the term standard quantum limit or SQL is, however, broader than just interferometry. In principle, any linear measurement of a quantum mechanical observable of a system under study that does not commute with itself at different times leads to such limits. In short, it is the Heisenberg uncertainty principle that is the cause. A more detailed explanation would be that any measurement in quantum mechanics involves at least two parties, an Object and a Meter. The former is the system whose observable, say \hat x, we want to measure. The latter is the system we couple to the Object in o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambridge University Press
Cambridge University Press is the university press of the University of Cambridge. Granted letters patent by Henry VIII of England, King Henry VIII in 1534, it is the oldest university press A university press is an academic publishing house specializing in monographs and scholarly journals. Most are nonprofit organizations and an integral component of a large research university. They publish work that has been reviewed by schola ... in the world. It is also the King's Printer. Cambridge University Press is a department of the University of Cambridge and is both an academic and educational publisher. It became part of Cambridge University Press & Assessment, following a merger with Cambridge Assessment in 2021. With a global sales presence, publishing hubs, and offices in more than 40 Country, countries, it publishes over 50,000 titles by authors from over 100 countries. Its publishing includes more than 380 academic journals, monographs, reference works, school and uni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Noise
Quantum noise is noise arising from the indeterminate state of matter in accordance with fundamental principles of quantum mechanics, specifically the uncertainty principle and via zero-point energy fluctuations. Quantum noise is due to the apparently discrete nature of the small quantum constituents such as electrons, as well as the discrete nature of quantum effects, such as photocurrents. Quantified noise is similar to classical noise theory and will not always return an asymmetric spectral density. Shot noise as coined by J. Verdeyen is a form of quantum noise related to the statistics of photon counting, the discrete nature of electrons, and intrinsic noise generation in electronics. In contrast to shot noise, the quantum mechanical uncertainty principle sets a lower limit to a measurement. The uncertainty principle requires any amplifier or detector to have noise. Macroscopic manifestations of quantum phenomena are easily disturbed, so quantum noise is mainly observed i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classical Limit
The classical limit or correspondence limit is the ability of a physical theory to approximate or "recover" classical mechanics when considered over special values of its parameters. The classical limit is used with physical theories that predict non-classical behavior. Quantum theory A heuristic postulate called the correspondence principle was introduced to quantum theory by Niels Bohr: in effect it states that some kind of continuity argument should apply to the classical limit of quantum systems as the value of the Planck constant normalized by the action of these systems becomes very small. Often, this is approached through "quasi-classical" techniques (cf. WKB approximation). More rigorously, the mathematical operation involved in classical limits is a group contraction, approximating physical systems where the relevant action is much larger than the reduced Planck constant , so the "deformation parameter" / can be effectively taken to be zero (cf. Weyl quantization.) Thus ty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phase Space Formulation
The phase-space formulation of quantum mechanics places the position ''and'' momentum variables on equal footing in phase space. In contrast, the Schrödinger picture uses the position ''or'' momentum representations (see also position and momentum space). The two key features of the phase-space formulation are that the quantum state is described by a quasiprobability distribution (instead of a wave function, state vector, or density matrix) and operator multiplication is replaced by a star product. The theory was fully developed by Hilbrand Groenewold in 1946 in his PhD thesis, and independently by Joe Moyal, each building on earlier ideas by Hermann Weyl and Eugene Wigner. The chief advantage of the phase-space formulation is that it makes quantum mechanics appear as similar to Hamiltonian mechanics as possible by avoiding the operator formalism, thereby "'freeing' the quantization of the 'burden' of the Hilbert space". This formulation is statistical in nature and offers l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ehrenfest Theorem
The Ehrenfest theorem, named after Paul Ehrenfest, an Austrian theoretical physicist at Leiden University, relates the time derivative of the expectation values of the position and momentum operators ''x'' and ''p'' to the expectation value of the force F=-V'(x) on a massive particle moving in a scalar potential V(x), The Ehrenfest theorem is a special case of a more general relation between the expectation of any quantum mechanical operator and the expectation of the commutator of that operator with the Hamiltonian of the system where is some quantum mechanical operator and is its expectation value. It is most apparent in the Heisenberg picture of quantum mechanics, where it amounts to just the expectation value of the Heisenberg equation of motion. It provides mathematical support to the correspondence principle. The reason is that Ehrenfest's theorem is closely related to Liouville's theorem of Hamiltonian mechanics, which involves the Poisson bracket instead of a com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limit (mathematics)
In mathematics, a limit is the value that a function (or sequence) approaches as the input (or index) approaches some value. Limits are essential to calculus and mathematical analysis, and are used to define continuity, derivatives, and integrals. The concept of a limit of a sequence is further generalized to the concept of a limit of a topological net, and is closely related to limit and direct limit in category theory. In formulas, a limit of a function is usually written as : \lim_ f(x) = L, (although a few authors may use "Lt" instead of "lim") and is read as "the limit of of as approaches equals ". The fact that a function approaches the limit as approaches is sometimes denoted by a right arrow (→ or \rightarrow), as in :f(x) \to L \text x \to c, which reads "f of x tends to L as x tends to c". History Grégoire de Saint-Vincent gave the first definition of limit (terminus) of a geometric series in his work ''Opus Geometricum'' (1647): "The ''terminus'' of a pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armstrong Limit
The Armstrong limit or Armstrong's line is a measure of altitude above which atmospheric pressure is sufficiently low that water boils at the normal temperature of the human body. Exposure to pressure below this limit results in a rapid loss of consciousness, followed by a series of changes to cardiovascular and neurological functions, and eventually death, unless pressure is restored within 60–90 seconds. On Earth, the limit is around above sea level, above which atmospheric air pressure drops below 0.0618 atm (6.3 kPa, 47 mmHg, or about 1 psi). The U.S. Standard Atmospheric model sets the Armstrong pressure at an altitude of . The term is named after United States Air Force General Harry George Armstrong, who was the first to recognize this phenomenon. Effect on body fluids At or above the Armstrong limit, exposed body fluids such as saliva, tears, urine, and the liquids wetting the alveoli within the lungs—but not vascular blood (blood within the circulatory syst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classical Limit
The classical limit or correspondence limit is the ability of a physical theory to approximate or "recover" classical mechanics when considered over special values of its parameters. The classical limit is used with physical theories that predict non-classical behavior. Quantum theory A heuristic postulate called the correspondence principle was introduced to quantum theory by Niels Bohr: in effect it states that some kind of continuity argument should apply to the classical limit of quantum systems as the value of the Planck constant normalized by the action of these systems becomes very small. Often, this is approached through "quasi-classical" techniques (cf. WKB approximation). More rigorously, the mathematical operation involved in classical limits is a group contraction, approximating physical systems where the relevant action is much larger than the reduced Planck constant , so the "deformation parameter" / can be effectively taken to be zero (cf. Weyl quantization.) Thus ty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physical Review
''Physical Review'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal established in 1893 by Edward Nichols. It publishes original research as well as scientific and literature reviews on all aspects of physics. It is published by the American Physical Society (APS). The journal is in its third series, and is split in several sub-journals each covering a particular field of physics. It has a sister journal, ''Physical Review Letters'', which publishes shorter articles of broader interest. History ''Physical Review'' commenced publication in July 1893, organized by Cornell University professor Edward Nichols and helped by the new president of Cornell, J. Gould Schurman. The journal was managed and edited at Cornell in upstate New York from 1893 to 1913 by Nichols, Ernest Merritt, and Frederick Bedell. The 33 volumes published during this time constitute ''Physical Review Series I''. The American Physical Society (APS), founded in 1899, took over its publication in 1913 and star ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spectroscopy
Spectroscopy is the field of study that measures and interprets the electromagnetic spectra that result from the interaction between electromagnetic radiation and matter as a function of the wavelength or frequency of the radiation. Matter waves and acoustic waves can also be considered forms of radiative energy, and recently gravitational waves have been associated with a spectral signature in the context of the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) In simpler terms, spectroscopy is the precise study of color as generalized from visible light to all bands of the electromagnetic spectrum. Historically, spectroscopy originated as the study of the wavelength dependence of the absorption by gas phase matter of visible light dispersed by a prism. Spectroscopy, primarily in the electromagnetic spectrum, is a fundamental exploratory tool in the fields of astronomy, chemistry, materials science, and physics, allowing the composition, physical structure and e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word "laser" is an acronym for "light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation". The first laser was built in 1960 by Theodore H. Maiman at Hughes Research Laboratories, based on theoretical work by Charles Hard Townes and Arthur Leonard Schawlow. A laser differs from other sources of light in that it emits light which is ''coherent''. Spatial coherence allows a laser to be focused to a tight spot, enabling applications such as laser cutting and lithography. Spatial coherence also allows a laser beam to stay narrow over great distances (collimation), enabling applications such as laser pointers and lidar (light detection and ranging). Lasers can also have high temporal coherence, which allows them to emit light with a very narrow spectrum. Alternatively, temporal coherence can be used to produce ultrashort pulses of ligh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
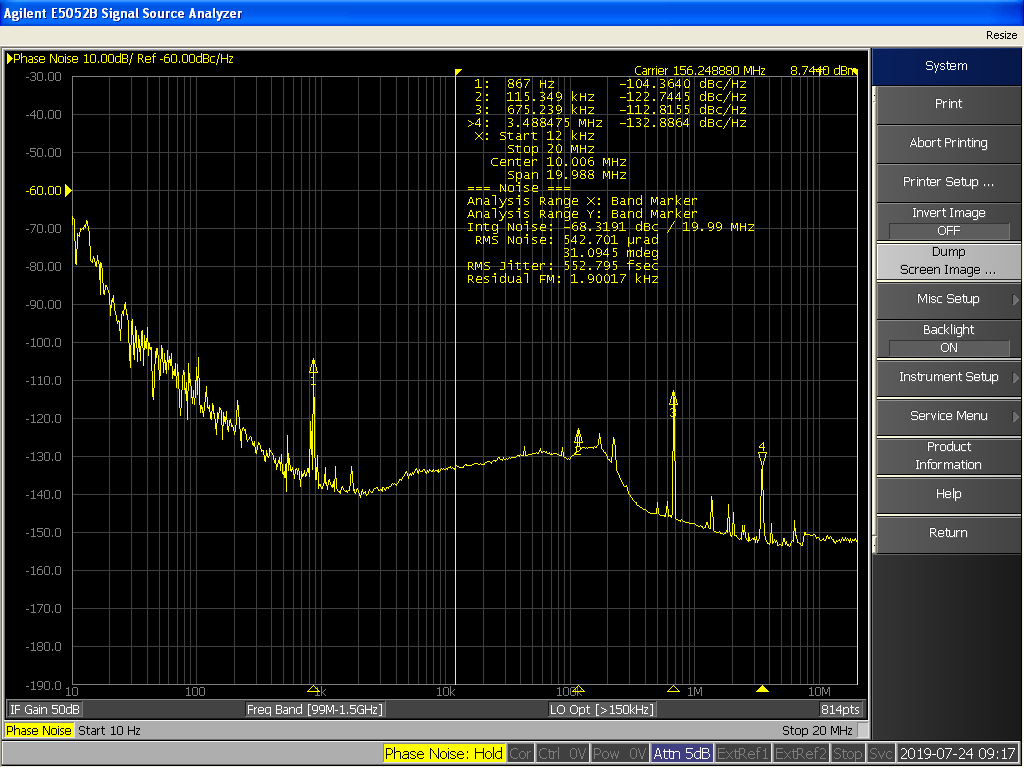
Phase Noise
In signal processing, phase noise is the frequency-domain representation of random fluctuations in the phase of a waveform, corresponding to time-domain deviations from perfect periodicity (jitter). Generally speaking, radio-frequency engineers speak of the phase noise of an oscillator, whereas digital-system engineers work with the jitter of a clock. Definitions Historically there have been two conflicting yet widely used definitions for phase noise. Some authors define phase noise to be the spectral density of a signal's phase only, while the other definition refers to the phase spectrum (which pairs up with the amplitude spectrum) resulting from the spectral estimation of the signal itself. Both definitions yield the same result at offset frequencies well removed from the carrier. At close-in offsets however, the two definitions differ. The IEEE defines phase noise as where the "phase instability" is the one-sided spectral density of a signal's phase deviation. Although ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |