|
Staffordia
''Staffordia'' is a genus of air-breathing land snails, terrestrial pulmonate gastropod mollusks in the family Staffordiidae. Species Species within the genus ''Staffordia'' include: * ''Staffordia daflaensis'' * ''Staffordia staffordi'' * ''Staffordia toruputuensis ''Staffordia toruputuensis'' is a species of air-breathing land snail, terrestrial pulmonate gastropod mollusk in the family Staffordiidae. The specific name ''toruputuensis'' is apparently according to its type locality, Toruputu Peak. Distr ...'' References External links {{Taxonbar, from=Q7596683 Staffordiidae ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staffordiidae
Staffordiidae is a family of air-breathing land snails, terrestrial pulmonate gastropod mollusks in the superfamily Trochomorphoidea. MolluscaBase eds. (2021). MolluscaBase. Staffordiidae Thiele, 1931. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at: http://marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=994727 on 2021-02-22 Staffordiidae is the only family in the superfamily Staffordioidea. This family has no subfamilies (according to the taxonomy of the Gastropoda by Bouchet & Rocroi, 2005). Staffordiidae is a poorly understood family, because it occurs only in the Dafla Hills area of India. The fauna and flora of that area has not been researched sufficiently. Various sources consider the family Staffordiidae as part of DyakiidaeBarker G. M. (2001) ''Gastropods on Land: Phylogeny, Diversity and Adaptive Morphology''. 1–146. In: Barker G. M. (ed.) (2001) The biology of terrestrial molluscs'. CABI Publishing, Oxon, UK, cited pages: 139–144. . or Ariophantidae/Dyakii ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
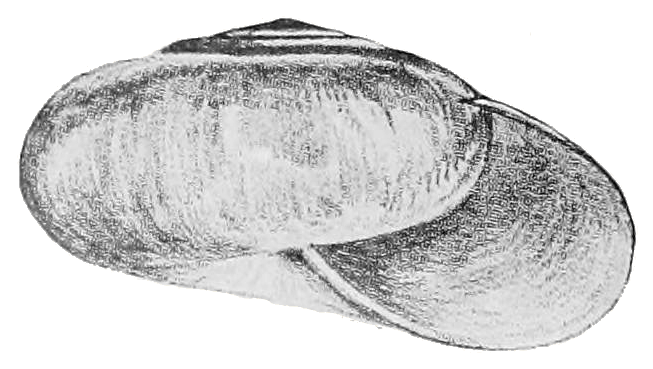
Staffordia Toruputuensis
''Staffordia toruputuensis'' is a species of air-breathing land snail, terrestrial pulmonate gastropod mollusk in the family Staffordiidae. The specific name ''toruputuensis'' is apparently according to its type locality, Toruputu Peak. Distribution The type locality of this species is " Toruputu Peak". The altitude was not specified, but it can vary from 1750 m (birdwatching of the same author)"BEAUTIFUL NUTHATCH ''Sitta formosa''". page 2279. In: ''Threatened birds of Asia''PDF to (locality of related species '' Staffordia staffordi''). It is in Dafla Hills in India, because whole family Staffordiidae is endemic to Dafla Hills.Hausdorf B. (2000). "Biogeography of the Limacoidea sensu lato (Gastropoda: Stylommatophora): Vicariance Events and Long-Distance Dispersal". ''Journal of Biogeography'' 27(2): 379-390. JSTOR Description The shell is globose with oblique columellar margin. The shell of the type specimen is not fully grown. The sculpture Sculpture is the br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staffordia Staffordi
''Staffordia staffordi'' is a species of air-breathing land snail, terrestrial pulmonate gastropod mollusk in the family Staffordiidae. The specific name ''staffordi'' as well as generic name ''Staffordia'' is in honor of Brigadier-General Stafford, who was in command of the punitive force which entered the Dafla Hills for the first time in the winter of 1874-1875. Distribution The type locality of this species is Toruputu Peak, Dafla Hills, , in India. Description The shell is moderately solid, with a thick epidermis, very globosely conoid, rounded below. The umbilicus almost hidden. The sculpture is small. Elongate papillae arearranged longitudinally, and differing from all the other species collected in the Dafla Hills. The color is olivaceous ochre. The spire is low. The suture is shallow. The shell has 5 whorls with sides convex above, rather flattened on the periphery of the last whorl. The aperture is lunate, narrow, subvertical, milky white within, rounded below. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staffordia Daflaensis
''Staffordia daflaensis'' is a species of air-breathing land snail, terrestrial pulmonate gastropod mollusk in the family Staffordiidae. The specific name ''daflaensis'' is apparently according to its area of distribution, Dafla Hills in India. Distribution The type locality of this species is " Shengorh Peak", , Dafla Hills in India. Godwin-Austen (1907) have found this species very abundant in Dafla Hills. Description The shell is depressedly tumidly conoid, umbilicated, solid, rather flat on base. The sculpture is very regular, longitudinal, sharply defined, broad-ridged ribbing. Color is rich olivaceous with ochre tint. It vary in colour and size, often being of a pale ochraceous-grey tint. The spire is low, sides convex. The suture is shallow, adpressed. The shell has 6 whorls, that are rapidly increasing. The last whorl is rounded. The aperture In optics, an aperture is a hole or an opening through which light travels. More specifically, the aperture and f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Haversham Godwin-Austen
Lieutenant-Colonel Henry Haversham Godwin-Austen FRS FZS FRGS MBOU (6 July 1834 – 2 December 1923), known until 1854 as Henry Haversham Austen, was an English topographer, surveyor, naturalist and geologist. He explored the mountains in the Himalayas and surveyed the glaciers at the base of K2, also known as Mount Godwin-Austen. Geographer Kenneth Mason called Godwin-Austen "probably the greatest mountaineer of his day". He also remains the most important investigator of the terrestrial molluscs of the Indian subcontinent. Early life The eldest son of the geologist Robert Austen, who in 1854 added Godwin to his surname by royal licence, Henry Haversham Austen was probably born at Ogwell House, near Newton Abbot, Devon, where his father had recently taken up residence. His father's family, landowners in Cheshire and Surrey since the 12th century, was a family of merchant venturers, soldiers, scholars, and collectors. His grandfather, Sir Henry Edmund Austen (1785– ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family (taxonomy), family. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. ''Panthera leo'' (lion) and ''Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomy (biology), taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Land Snail
A land snail is any of the numerous species of snail that live on land, as opposed to the sea snails and freshwater snails. ''Land snail'' is the common name for terrestrial gastropod mollusks that have shells (those without shells are known as slugs). However, it is not always easy to say which species are terrestrial, because some are more or less amphibious between land and fresh water, and others are relatively amphibious between land and salt water. Land snails are a polyphyletic group comprising at least ten independent evolutionary transitions to terrestrial life (the last common ancestor of all gastropods was marine). The majority of land snails are pulmonates that have a lung and breathe air. Most of the non-pulmonate land snails belong to lineages in the Caenogastropoda, and tend to have a gill and an operculum. The largest clade of land snails is the Cyclophoroidea, with more than 7,000 species. Many of these operculate land snails live in habitats or microhabitats ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terrestrial Molluscs
Terrestrial molluscs or land molluscs (mollusks) are an ecological group that includes all molluscs that live on land in contrast to freshwater and marine molluscs. They probably first occurred in the Carboniferous, arising from freshwater ones. Characteristics This group includes land snails and land slugs. Loss of the shell has taken place many times in different groups that are not evolutionarily closely related, and land snails and slugs are most often treated together as a single group in specialized malacological literature.Barker G. M. (ed.) The biology of terrestrial molluscs'. CABI Publishing, 2001, 558 pp. .Barker G. M. (ed.) Natural enemies of terrestrial molluscs'. CABI Publishing, 2004, 644 pp. . All terrestrial molluscs belong to the class Gastropoda. However, colonization of the land took place several times during the evolutionary past, and as a result terrestrial molluscs are classified in several different, often not closely related, gastropod taxa. Terrestr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulmonate
Pulmonata or pulmonates, is an informal group (previously an order, and before that a subclass) of snails and slugs characterized by the ability to breathe air, by virtue of having a pallial lung instead of a gill, or gills. The group includes many land and freshwater families, and several marine families. The taxon Pulmonata as traditionally defined was found to be polyphyletic in a molecular study per Jörger ''et al.'', dating from 2010. Pulmonata are known from the Carboniferous Period to the present. Pulmonates have a single atrium and kidney, and a concentrated, symmetrical, nervous system. The mantle cavity is located on the right side of the body, and lacks gills, instead being converted into a vascularised lung. Most species have a shell, but no operculum, although the group does also include several shell-less slugs. Pulmonates are hermaphroditic, and some groups possess love darts. Linnean taxonomy The taxonomy of this group according to the taxonomy of the Ga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastropod
The gastropods (), commonly known as snails and slugs, belong to a large taxonomic class of invertebrates within the phylum Mollusca called Gastropoda (). This class comprises snails and slugs from saltwater, from freshwater, and from land. There are many thousands of species of sea snails and slugs, as well as freshwater snails, freshwater limpets, and land snails and slugs. The class Gastropoda contains a vast total of named species, second only to the insects in overall number. The fossil history of this class goes back to the Late Cambrian. , 721 families of gastropods are known, of which 245 are extinct and appear only in the fossil record, while 476 are currently extant with or without a fossil record. Gastropoda (previously known as univalves and sometimes spelled "Gasteropoda") are a major part of the phylum Mollusca, and are the most highly diversified class in the phylum, with 65,000 to 80,000 living snail and slug species. The anatomy, behavior, feeding, and re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mollusk
Mollusca is the second-largest phylum of invertebrate animals after the Arthropoda, the members of which are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 85,000 extant species of molluscs are recognized. The number of fossil species is estimated between 60,000 and 100,000 additional species. The proportion of undescribed species is very high. Many taxa remain poorly studied. Molluscs are the largest marine phylum, comprising about 23% of all the named marine organisms. Numerous molluscs also live in freshwater and terrestrial habitats. They are highly diverse, not just in size and anatomical structure, but also in behaviour and habitat. The phylum is typically divided into 7 or 8 taxonomic classes, of which two are entirely extinct. Cephalopod molluscs, such as squid, cuttlefish, and octopuses, are among the most neurologically advanced of all invertebrates—and either the giant squid or the colossal squid is the largest known invertebrate species. The gas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |