|
St Martin's, Dover
The Priory of St. Mary the Virgin and St. Martin of the New Work, or Newark, commonly called Dover Priory, was a priory at Dover in southeast England. It was variously independent in rule, then occupied by canons regular of the Augustinian rule, then finally monks of the Benedictine rule as a cell of Christchurch Monastery, Canterbury. The priory was located just east of what is now Dover Priory railway station, in fact the railway was built on the western part of the site. Housing has been built on the eastern part of the site where the church once stood, between Priory Road and the later Effingham Street in the area of Norman Street and Saxon Street. Dover College, a private boarding school, occupies the land between the station and Effingham Street and has rescued some of the medieval buildings for use by its pupils. The 12th-century Strangers' Refectory on Effingham Street retains its function and is also used for concerts; the gateway to the priory is now a music school ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dover College
, motto_translation = I cannot refuse the task , established = , closed = , type = Public SchoolIndependent day and boarding , religion = Church of England , headmaster = Simon Fisher , r_head_label = , r_head = , chair_label = Chairman of the Governors , chair = Michael Goodridge , founder = Edward Astley , specialist = , address = Effingham Crescent , city = Dover , county = Kent , country = England , postcode = CT17 9RH , local_authority = , urn = 118940 , ofsted = , staff = 50 (approx.) , enrolment = 323 , gender = Co-educational , lower_age = 3 , upper_age = 18 , houses = 6 , colours = Black and Green , fees = £2,575 - £5,350 (Day) £7,000 - £10,500 (Boarding) , publication = , free_label_1 = Former pupils , free_1 = Old Dovorians , free_label_2 = , free_2 = , free_label_3 = , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norman Conquest
The Norman Conquest (or the Conquest) was the 11th-century invasion and occupation of England by an army made up of thousands of Norman, Breton, Flemish, and French troops, all led by the Duke of Normandy, later styled William the Conqueror. William's claim to the English throne derived from his familial relationship with the childless Anglo-Saxon king Edward the Confessor, who may have encouraged William's hopes for the throne. Edward died in January 1066 and was succeeded by his brother-in-law Harold Godwinson. The Norwegian king Harald Hardrada invaded northern England in September 1066 and was victorious at the Battle of Fulford on 20 September, but Godwinson's army defeated and killed Hardrada at the Battle of Stamford Bridge on 25 September. Three days later on 28 September, William's invasion force of thousands of men and hundreds of ships landed at Pevensey in Sussex in southern England. Harold marched south to oppose him, leaving a significant portion of his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
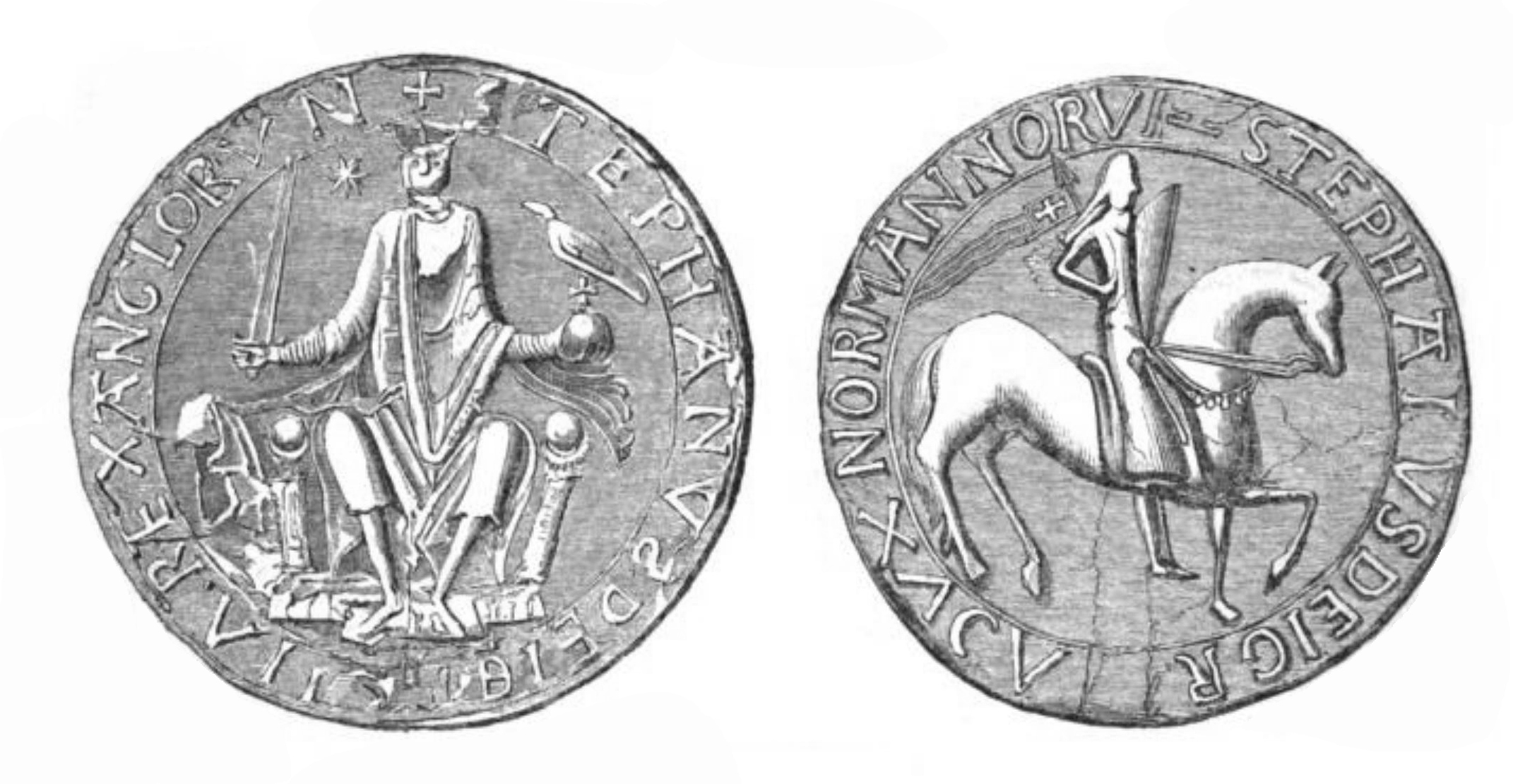
Stephen Of England
Stephen (1092 or 1096 – 25 October 1154), often referred to as Stephen of Blois, was King of England from 22 December 1135 to his death in 1154. He was Count of Boulogne '' jure uxoris'' from 1125 until 1147 and Duke of Normandy from 1135 until 1144. His reign was marked by the Anarchy, a civil war with his cousin and rival, the Empress Matilda, whose son, Henry II, succeeded Stephen as the first of the Angevin kings of England. Stephen was born in the County of Blois in central France as the fourth son of Stephen-Henry, Count of Blois, and Adela, daughter of William the Conqueror. His father died while Stephen was still young, and he was brought up by his mother. Placed into the court of his uncle Henry I of England, Stephen rose in prominence and was granted extensive lands. He married Matilda of Boulogne, inheriting additional estates in Kent and Boulogne that made the couple one of the wealthiest in England. Stephen narrowly escaped drowning with Henry I's son, William ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benedictine Rule
The ''Rule of Saint Benedict'' ( la, Regula Sancti Benedicti) is a book of precepts written in Latin in 516 by St Benedict of Nursia ( AD 480–550) for monks living communally under the authority of an abbot. The spirit of Saint Benedict's Rule is summed up in the motto of the Benedictine Confederation: ''pax'' ("peace") and the traditional ''ora et labora'' ("pray and work"). Compared to other precepts, the Rule provides a moderate path between individual zeal and formulaic institutionalism; because of this middle ground it has been widely popular. Benedict's concerns were the needs of monks in a community environment: namely, to establish due order, to foster an understanding of the relational nature of human beings, and to provide a spiritual father to support and strengthen the individual's ascetic effort and the spiritual growth that is required for the fulfillment of the human vocation, theosis. The ''Rule of Saint Benedict'' has been used by Benedictines for 15 centuri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theobald Of Bec
Theobald of Bec ( c. 1090 – 18 April 1161) was a Norman archbishop of Canterbury from 1139 to 1161. His exact birth date is unknown. Some time in the late 11th or early 12th century Theobald became a monk at the Abbey of Bec, rising to the position of abbot in 1137. King Stephen of England chose him to be Archbishop of Canterbury in 1138. Canterbury's claim to Primacy of Canterbury, primacy over the Welsh ecclesiastics was resolved during Theobald's term of office when Pope Eugene III decided in 1148 in Canterbury's favour. Theobald faced challenges to his authority from a subordinate bishop, Henry of Blois, Bishop of Winchester and King Stephen's younger brother, and his relationship with King Stephen was turbulent. On one occasion Stephen forbade him from attending a Council of Reims (1148), papal council, but Theobald defied the king, which resulted in the confiscation of his property and temporary exile. Theobald's relations with his cathedral clergy and the mona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dover Museum
Dover Museum is a museum in Dover, Kent, in south-east England. History Founded in February 1836 by the town's mayor Edward Pett Thompson, it was initially housed in the old Guildhall and run by the Dover Philosophical Institute. The Town Council (predecessor of Dover District Council) formally took it over 12 years later, constructing a new building to house it and the town's market, in Market Square. Shelled from France in 1942 during the Second World War, the Museum lost much of its collections, including nearly all of its natural history collections. Much of the surviving material was left neglected in caves and other stores until 1946, and it is estimated only 30% of the pre-war collection survived to that date. In 1948 a 'temporary' museum was opened in the Town Hall's undercroft, but this in fact lasted until 1991, when a new museum building on three stories (behind the Museum's original Victorian facade) was opened in Market Square. On 20 July 1999 the Queen open ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parish Church
A parish church (or parochial church) in Christianity is the church which acts as the religious centre of a parish. In many parts of the world, especially in rural areas, the parish church may play a significant role in community activities, often allowing its premises to be used for non-religious community events. The church building reflects this status, and there is considerable variety in the size and style of parish churches. Many villages in Europe have churches that date back to the Middle Ages, but all periods of architecture are represented. Roman Catholic Church Each diocese (administrative unit, headed by a Bishop) is divided into parishes. Normally, a parish comprises all Catholics living within its geographically defined area. Within a diocese, there can also be overlapping parishes for Catholics belonging to a particular rite, language, nationality, or community. Each parish has its own central church called the parish church, where religious services take pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charter
A charter is the grant of authority or rights, stating that the granter formally recognizes the prerogative of the recipient to exercise the rights specified. It is implicit that the granter retains superiority (or sovereignty), and that the recipient admits a limited (or inferior) status within the relationship, and it is within that sense that charters were historically granted, and it is that sense which is retained in modern usage of the term. The word entered the English language from the Old French ''charte'', via Latin ''charta'', and ultimately from Greek χάρτης (''khartes'', meaning "layer of papyrus"). It has come to be synonymous with a document that sets out a grant of rights or privileges. Other usages The term is used for a special case (or as an exception) of an institutional charter. A charter school, for example, is one that has different rules, regulations, and statutes from a state school. Charter can be used as a synonym for "hire" or "lease", as in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry I Of England
Henry I (c. 1068 – 1 December 1135), also known as Henry Beauclerc, was King of England from 1100 to his death in 1135. He was the fourth son of William the Conqueror and was educated in Latin and the liberal arts. On William's death in 1087, Henry's elder brothers Robert Curthose and William Rufus inherited Normandy and England, respectively, but Henry was left landless. He purchased the County of Cotentin in western Normandy from Robert, but his brothers deposed him in 1091. He gradually rebuilt his power base in the Cotentin and allied himself with William Rufus against Robert. Present at the place where his brother William died in a hunting accident in 1100, Henry seized the English throne, promising at his coronation to correct many of William's less popular policies. He married Matilda of Scotland and they had two surviving children, Empress Matilda and William Adelin; he also had many illegitimate children by his many mistresses. Robert, who invaded from Normandy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William De Corbeil
William de Corbeil or William of Corbeil (21 November 1136) was a medieval Archbishop of Canterbury. Very little is known of William's early life or his family, except that he was born at Corbeil, south of Paris, and that he had two brothers. Educated as a theologian, he taught briefly before serving the bishops of Durham and London as a clerk and subsequently becoming an Augustinian canon. William was elected to the See of Canterbury as a compromise candidate in 1123, the first canon to become an English archbishop. He succeeded Ralph d'Escures who had employed him as a chaplain. Throughout his archbishopric, William was embroiled in a dispute with Thurstan, the Archbishop of York, over the primacy of Canterbury. As a temporary solution, Pope Honorius II appointed William the papal legate for England, giving him powers superior to those of York. William concerned himself with the morals of the clergy, and presided over three legatine councils, which among other things condemned ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archbishop Of Canterbury
The archbishop of Canterbury is the senior bishop and a principal leader of the Church of England, the ceremonial head of the worldwide Anglican Communion and the diocesan bishop of the Diocese of Canterbury. The current archbishop is Justin Welby, who was enthroned at Canterbury Cathedral on 21 March 2013. Welby is the 105th in a line which goes back more than 1400 years to Augustine of Canterbury, the "Apostle to the English", sent from Rome in the year 597. Welby succeeded Rowan Williams. From the time of Augustine until the 16th century, the archbishops of Canterbury were in full communion with the See of Rome and usually received the pallium from the pope. During the English Reformation, the Church of England broke away from the authority of the pope. Thomas Cranmer became the first holder of the office following the English Reformation in 1533, while Reginald Pole was the last Roman Catholic in the position, serving from 1556 to 1558 during the Counter-Reformation. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pope
The pope ( la, papa, from el, πάππας, translit=pappas, 'father'), also known as supreme pontiff ( or ), Roman pontiff () or sovereign pontiff, is the bishop of Rome (or historically the patriarch of Rome), head of the worldwide Catholic Church, and has also served as the head of state or sovereign of the Papal States and later the Vatican City State since the eighth century. From a Catholic viewpoint, the primacy of the bishop of Rome is largely derived from his role as the apostolic successor to Saint Peter, to whom primacy was conferred by Jesus, who gave Peter the Keys of Heaven and the powers of "binding and loosing", naming him as the "rock" upon which the Church would be built. The current pope is Francis, who was elected on 13 March 2013. While his office is called the papacy, the jurisdiction of the episcopal see is called the Holy See. It is the Holy See that is the sovereign entity by international law headquartered in the distinctively independent Vatic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)

