|
St Germain's Railway Station
St. Germain's railway station was located on the line between and Watlington (Norfolk) railway station, Watlington. It served the parish of Wiggenhall St. Germans, and closed in 1850. History The Bill for the Lynn and Ely Railway (L&ER) received the Royal Assent on 30 June 1845. Work started on the line in 1846. The first section of the L&ER opened on 27 October 1846 between King's Lynn railway station, Lynn and Downham Market railway station, Downham, and included a station at St Germain's. St Germain's station opened with the line and was situated between Watlington station and King's Lynn. It did not last long, being closed in October 1850, by which time the L&ER had amalgamated with other railways to form the East Anglian Railway. Routes References {{DEFAULTSORT:Saint Germains Railway Station Former Great Eastern Railway stations Railway stations in Great Britain opened in 1846 Railway stations in Great Britain closed in 1850 Disused railway stations in Norf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norfolk
Norfolk () is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in East Anglia in England. It borders Lincolnshire to the north-west, Cambridgeshire to the west and south-west, and Suffolk to the south. Its northern and eastern boundaries are the North Sea, with The Wash to the north-west. The county town is the city of Norwich. With an area of and a population of 859,400, Norfolk is a largely rural county with a population density of 401 per square mile (155 per km2). Of the county's population, 40% live in four major built up areas: Norwich (213,000), Great Yarmouth (63,000), King's Lynn (46,000) and Thetford (25,000). The Broads is a network of rivers and lakes in the east of the county, extending south into Suffolk. The area is protected by the Broads Authority and has similar status to a national park. History The area that was to become Norfolk was settled in pre-Roman times, (there were Palaeolithic settlers as early as 950,000 years ago) with camps along the highe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ordnance Survey National Grid
The Ordnance Survey National Grid reference system (OSGB) (also known as British National Grid (BNG)) is a system of geographic grid references used in Great Britain, distinct from latitude and longitude. The Ordnance Survey (OS) devised the national grid reference system, and it is heavily used in their survey data, and in maps based on those surveys, whether published by the Ordnance Survey or by commercial map producers. Grid references are also commonly quoted in other publications and data sources, such as guide books and government planning documents. A number of different systems exist that can provide grid references for locations within the British Isles: this article describes the system created solely for Great Britain and its outlying islands (including the Isle of Man); the Irish grid reference system was a similar system created by the Ordnance Survey of Ireland and the Ordnance Survey of Northern Ireland for the island of Ireland. The Universal Transverse Merca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
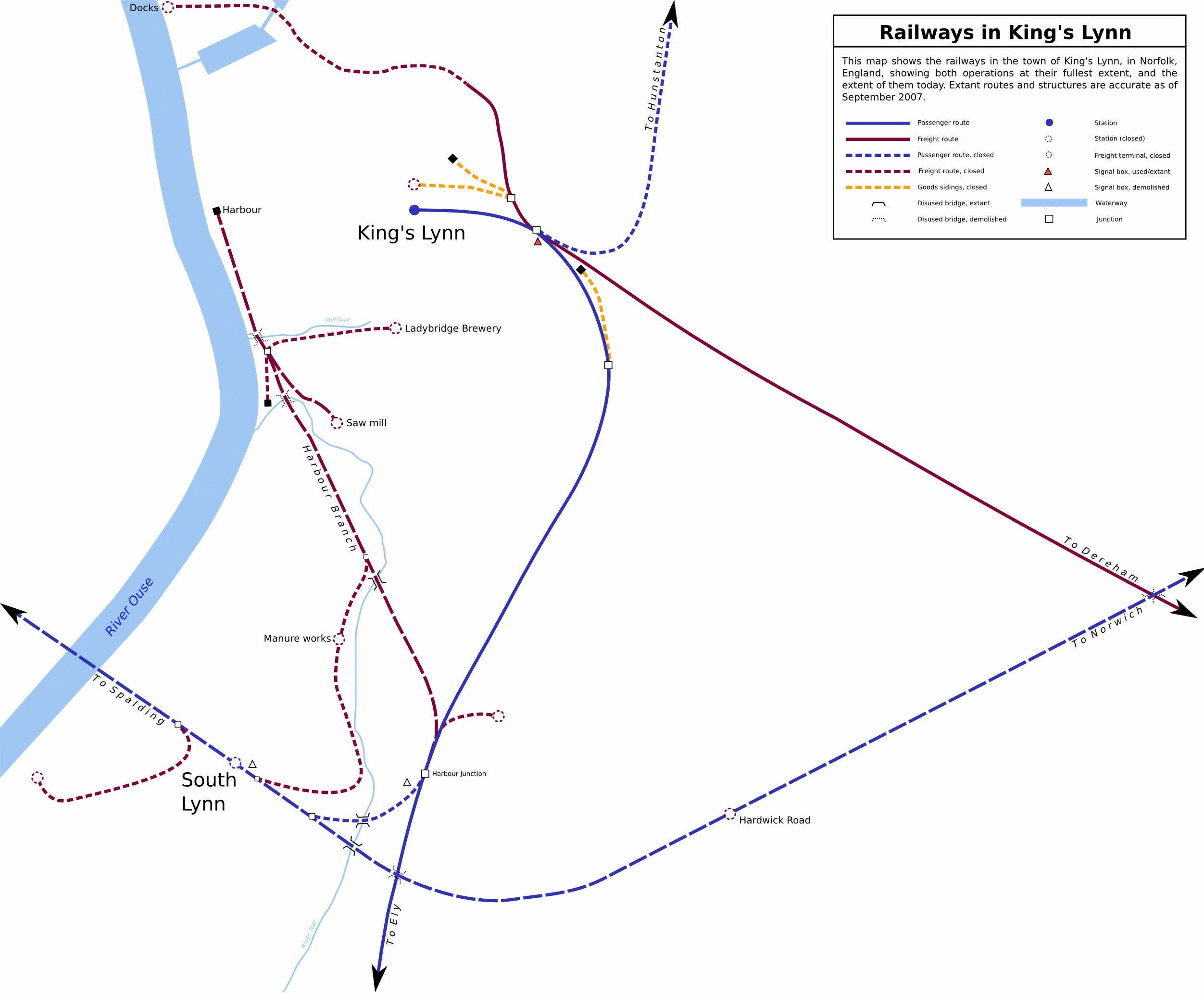
Lynn And Ely Railway
King's Lynn railway station is the northern terminus of the Fen line in the east of England, serving the town of King's Lynn, Norfolk. It is from and measured from London Liverpool Street. The station and most trains calling are operated by Great Northern (with service to and from ), with some additional peak services being operated by Greater Anglia (to and from London Liverpool Street). It has been the only station in the town since the closure of South Lynn railway station in 1959. Early growth The Act for the Lynn and Ely Railway received Royal Assent on 30 June 1845. Work started on the line in 1846 and so the railway arrived at Lynn on 27 October 1846. The original line ran South to Downham with the first station after Lynn being St Germain's. It took another two years to reach Ely. Great Eastern Railway. Lynn, when opened was a Joint station (Lynn & Ely and Lynn & Dereham). However, on 22 July 1847 the Lynn & Ely and Lynn & Dereham were amalgamated to form the E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Watlington (Norfolk) Railway Station
Watlington railway station (formerly known as Magdalen Road) is on the Fen line in the east of England, serving the village of Watlington, Norfolk. It is measured from London Liverpool Street and is situated between and stations. Its three-letter station code is WTG. The station and most trains calling are operated by Great Northern (with service to and from ), with some additional peak services being operated by Abellio Greater Anglia (to and from London Liverpool Street). History The Bill for the Lynn and Ely Railway received Royal Assent on 30 June 1845. Work started on the line in 1846 and the line and its stations were opened on 27 October 1846. Watlington station opened with the line and was, as it is now, situated South of Lynn station (now King's Lynn). The station to the south was St Germain's station. The line ran from Ely to Downham, the eventual destination being Ely. Watlington station, from 1847 part of the East Anglian Railway, became part of the Great E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King's Lynn Railway Station
King's Lynn railway station is the northern terminus of the Fen line in the east of England, serving the town of King's Lynn, Norfolk. It is from and measured from London Liverpool Street. The station and most trains calling are operated by Great Northern (with service to and from ), with some additional peak services being operated by Greater Anglia (to and from London Liverpool Street). It has been the only station in the town since the closure of South Lynn railway station in 1959. Early growth The Act for the Lynn and Ely Railway received Royal Assent on 30 June 1845. Work started on the line in 1846 and so the railway arrived at Lynn on 27 October 1846. The original line ran South to Downham with the first station after Lynn being St Germain's. It took another two years to reach Ely. Great Eastern Railway. Lynn, when opened was a Joint station (Lynn & Ely and Lynn & Dereham). However, on 22 July 1847 the Lynn & Ely and Lynn & Dereham were amalgamated to form the E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Downham Market Railway Station
Downham Market railway station is on the Fen line in the east of England, serving the town of Downham Market, Norfolk. It is measured from London Liverpool Street and is situated between and stations. Its three-letter station code is DOW. The station and most trains calling are operated by Great Northern (with service to and from ), with some additional peak services being operated by Greater Anglia (to and from London Liverpool Street). The station building of 1846, built of carrstone with pale brick dressings, is a Grade II listed building. History The Lynn & Ely Railway Act received the Royal Assent on 30 June 1845. Work started on the line in 1846 and the line and its stations were opened on 27 October 1846. Downham Station opened with the line and was situated south of Stow Station and was a temporary end of the line. The line was completed to Ely in 1847. On New Year's Day, Downham station ceased to be a temporary terminus when the line was opened through to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ian Allan Publishing
Ian Allan Publishing was an English publisher, established in 1942, which specialised in transport books. It was founded by Ian Allan. In 1942 Ian Allan, then working in the public relations department for the Southern Railway at Waterloo station, decided he could deal with many of the requests he received about rolling stock by collecting the information into a book. The result was his first book, ''ABC of Southern Locomotives''. This proved to be a success, contributing to the emergence of trainspotting as a popular hobby in the UK, and leading to the formation of the company.Ian Allan…the man who launched a million locospotters ''The Railway Magazine'' issue 1174 February 1999 pages 20-27 The company grew from a small producer of books for train enthusiasts and spotters to a large transport publisher. Each year it published books covering subjects such as military and civil aviation, naval and maritime topics, buses, trams, trolleybuses and steam railways, including hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Anglian Railway
East or Orient is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from west and is the direction from which the Sun rises on the Earth. Etymology As in other languages, the word is formed from the fact that east is the direction where the Sun rises: ''east'' comes from Middle English ''est'', from Old English ''ēast'', which itself comes from the Proto-Germanic *''aus-to-'' or *''austra-'' "east, toward the sunrise", from Proto-Indo-European *aus- "to shine," or "dawn", cognate with Old High German ''*ōstar'' "to the east", Latin ''aurora'' 'dawn', and Greek ''ēōs'' 'dawn, east'. Examples of the same formation in other languages include Latin oriens 'east, sunrise' from orior 'to rise, to originate', Greek ανατολή anatolé 'east' from ἀνατέλλω 'to rise' and Hebrew מִזְרָח mizraḥ 'east' from זָרַח zaraḥ 'to rise, to shine'. ''Ēostre'', a Germanic goddess of dawn, might have been a personification ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Former Great Eastern Railway Stations
A former is an object, such as a template, gauge or cutting die, which is used to form something such as a boat's hull. Typically, a former gives shape to a structure that may have complex curvature. A former may become an integral part of the finished structure, as in an aircraft fuselage, or it may be removable, being using in the construction process and then discarded or re-used. Aircraft formers Formers are used in the construction of aircraft fuselage, of which a typical fuselage has a series from the nose to the empennage, typically perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the aircraft. The primary purpose of formers is to establish the shape of the fuselage and reduce the column length of stringers to prevent instability. Formers are typically attached to longerons, which support the skin of the aircraft. The "former-and-longeron" technique (also called stations and stringers) was adopted from boat construction, and was typical of light aircraft built until the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railway Stations In Great Britain Opened In 1846
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a prepared flat surface, rail vehicles (rolling stock) are directionally guided by the tracks on which they run. Tracks usually consist of steel rails, installed on sleepers (ties) set in ballast, on which the rolling stock, usually fitted with metal wheels, moves. Other variations are also possible, such as "slab track", in which the rails are fastened to a concrete foundation resting on a prepared subsurface. Rolling stock in a rail transport system generally encounters lower frictional resistance than rubber-tyred road vehicles, so passenger and freight cars (carriages and wagons) can be coupled into longer trains. The operation is carried out by a railway company, providing transport between train stations or freight customer facilit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railway Stations In Great Britain Closed In 1850
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a prepared flat surface, rail vehicles (rolling stock) are directionally guided by the tracks on which they run. Tracks usually consist of steel rails, installed on sleepers (ties) set in ballast, on which the rolling stock, usually fitted with metal wheels, moves. Other variations are also possible, such as "slab track", in which the rails are fastened to a concrete foundation resting on a prepared subsurface. Rolling stock in a rail transport system generally encounters lower frictional resistance than rubber-tyred road vehicles, so passenger and freight cars (carriages and wagons) can be coupled into longer trains. The operation is carried out by a railway company, providing transport between train stations or freight customer facilit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |