|
St. Nicholas Church, Leipzig
The St. Nicholas Church (german: Nikolaikirche) is one of the major churches of central Leipzig, Germany (in Leipzig`s district Mitte). Construction started in Romanesque style in 1165, but in the 16th century, the church was turned into a Gothic hall church. Baroque elements like the tower were added in the 18th century. In the 18th century, several works by Johann Sebastian Bach, who was as Thomaskantor the music director of Thomaskirche and Nikolaikirche from 1723 to 1750, premiered here. The Neoclassical interior dates to the late 18th century. The church rose to national fame in 1989 with the Monday Demonstrations when it became the centre of peaceful revolt against communist rule. By capacity, it is one of the largest churches in Saxony. History Construction of the church began about 1165. It is named after St. Nicholas, patron of travelers and merchants. It was built originally in the Romanesque style (with twin towers) but was extended and enlarged in the early 16t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leipzig
Leipzig ( , ; Upper Saxon: ) is the most populous city in the German state of Saxony. Leipzig's population of 605,407 inhabitants (1.1 million in the larger urban zone) as of 2021 places the city as Germany's eighth most populous, as well as the second most populous city in the area of the former East Germany after ( East) Berlin. Together with Halle (Saale), the city forms the polycentric Leipzig-Halle Conurbation. Between the two cities (in Schkeuditz) lies Leipzig/Halle Airport. Leipzig is located about southwest of Berlin, in the southernmost part of the North German Plain (known as Leipzig Bay), at the confluence of the White Elster River (progression: ) and two of its tributaries: the Pleiße and the Parthe. The name of the city and those of many of its boroughs are of Slavic origin. Leipzig has been a trade city since at least the time of the Holy Roman Empire. The city sits at the intersection of the Via Regia and the Via Imperii, two important medie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz
Gottfried Wilhelm (von) Leibniz . ( – 14 November 1716) was a German polymath active as a mathematician, philosopher, scientist and diplomat. He is one of the most prominent figures in both the history of philosophy and the history of mathematics. He wrote works on philosophy, theology, ethics, politics, law, history and philology. Leibniz also made major contributions to physics and technology, and anticipated notions that surfaced much later in probability theory, biology, medicine, geology, psychology, linguistics and computer science. In addition, he contributed to the field of library science: while serving as overseer of the Wolfenbüttel library in Germany, he devised a cataloging system that would have served as a guide for many of Europe's largest libraries. Leibniz's contributions to this vast array of subjects were scattered in various learned journals, in tens of thousands of letters and in unpublished manuscripts. He wrote in several languages, primaril ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lutheran Churches In Leipzig
Lutheranism is one of the largest branches of Protestantism, identifying primarily with the theology of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German monk and reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practice of the Catholic Church launched the Protestant Reformation. The reaction of the government and church authorities to the international spread of his writings, beginning with the ''Ninety-five Theses'', divided Western Christianity. During the Reformation, Lutheranism became the state religion of numerous states of northern Europe, especially in northern Germany, Scandinavia and the then-Livonian Order. Lutheran clergy became civil servants and the Lutheran churches became part of the state. The split between the Lutherans and the Roman Catholics was made public and clear with the 1521 Edict of Worms: the edicts of the Diet condemned Luther and officially banned citizens of the Holy Roman Empire from defending or propagating his ideas, subjecting advocates of Lutheranism t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
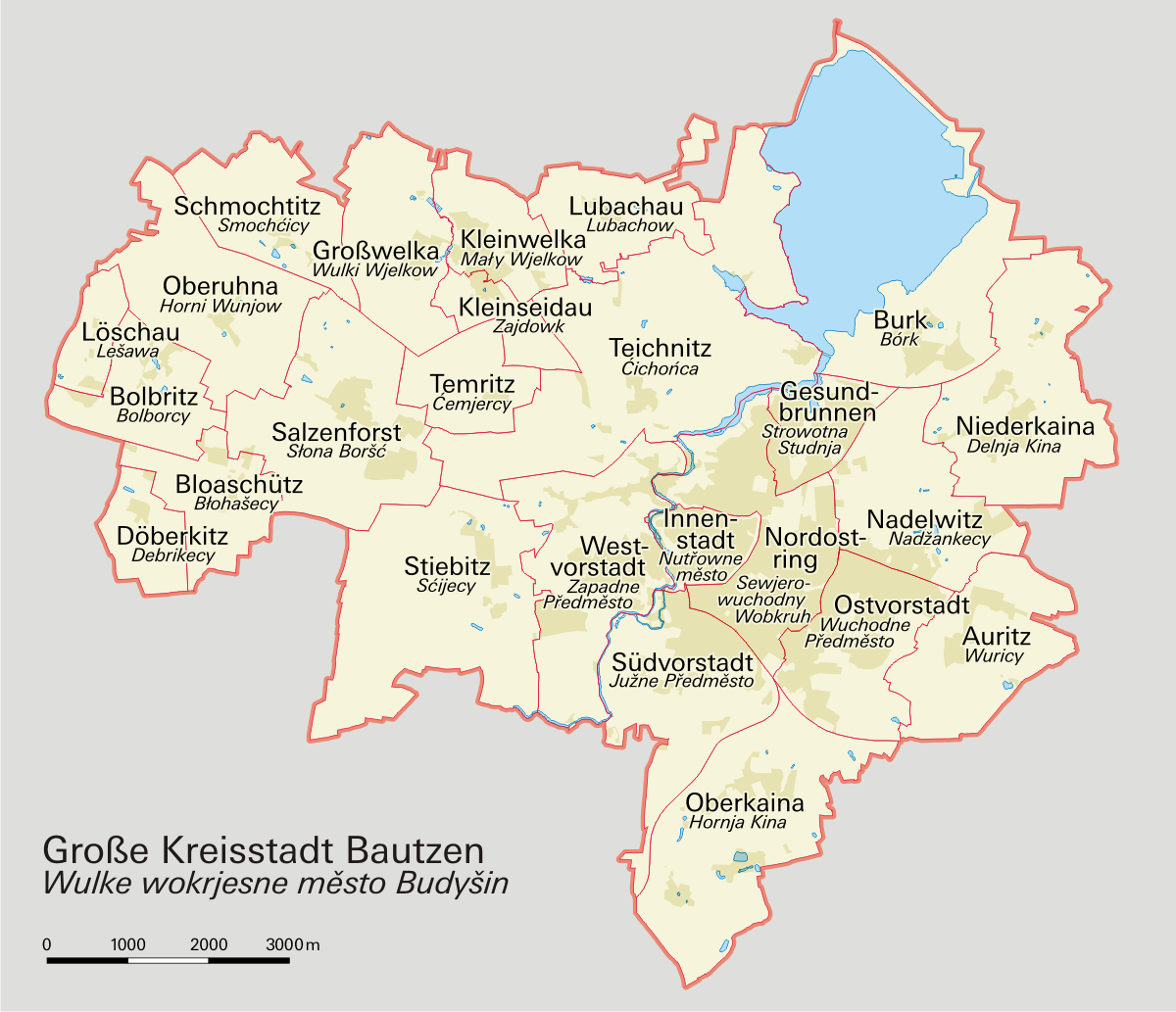
Bautzen
Bautzen () or Budyšin () is a hill-top town in eastern Saxony, Germany, and the administrative centre of the district of Bautzen. It is located on the Spree river. In 2018 the town's population was 39,087. Until 1868, its German name was ''Budissin''. In 1945 the Battle of Bautzen was Hitler’s last victory against the Soviet Union during the Battle of Berlin . Bautzen is often regarded as the unofficial, but historical capital of Upper Lusatia. The town is also the most important cultural centre of the Sorbian minority, which constitutes about 10 percent of Bautzen's population. Asteroid '' 11580 Bautzen'' is named in honour of the city. Names Like other cities and places in Lusatia, Bautzen has several different names across languages. Its German name was also officially changed in 1868. As well as ''Bautzen'' (German) and ''Budyšin'' (Upper Sorbian), the town has had the following names: * German: ''Budissin'' (variants used from c. 11th century onwards; Saxon gov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilhelm Sauer
Wilhelm Carl Friedrich Sauer (23 March 1831 – 9 April 1916) was a German pipe organ builder. One of the famous organ builders of the Romantic period, Sauer and his company W. Sauer Orgelbau built over 1,100 organs during his lifetime, amongst them the organs at Bremen Cathedral, Leipzig's St. Thomas Church, and Berlin Cathedral, which is considered to be "his final great masterpiece". Early years Wilhelm Sauer was born in Schönbeck, in the Grand Duchy of Mecklenburg-Strelitz, the son of blacksmith and self-educated organ builder Ernst Sauer (1799–1873) from Karlsburg in Pomerania, and his wife Johanna Christine, née Sumke (1800–1882). His parents married in 1822. He was the brother of Johann Ernst Sauer (1823–1842). When Wilhelm was seven years old, the family moved to the neighboring town of Friedland, where his father built a factory and started the commercial organ business. Wilhelm spent his youth there, attending school, with the idea that he would transfer to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
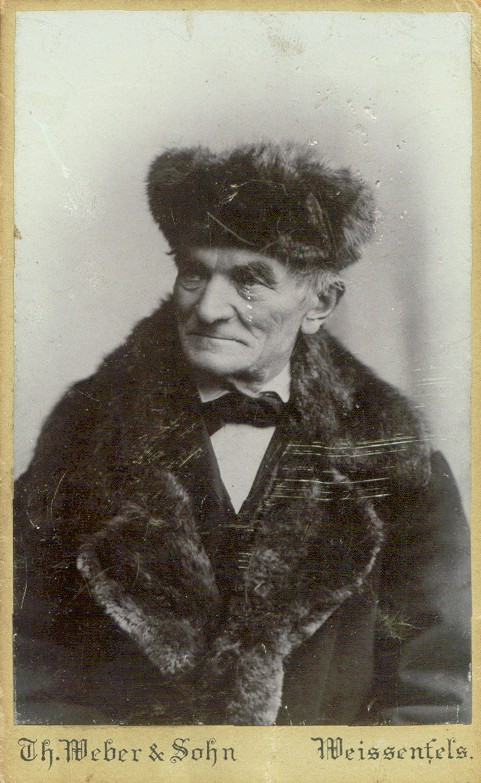
Friedrich Ladegast
Friedrich Ladegast (August 30, 1818 – June 30, 1905) was a famous German organ builder. Ladegast was born in Hochhermsdorf (now Hermsdorf), Saxony, to a carpenter and cabinet-maker. He worked first for his brother Christlieb, an organ builder at Geringswalde, and built his first two organs at the age of twenty. He then traveled as a journeyman to various workshops, including those of Johann Gottlob Mende in Leipzig, Urban Kreutzbach in Borna, Adolf Zuberbier in Dessau, Martin Wetzel in Strasbourg, and Aristide Cavaillé-Coll in Paris. His work with Cavaillé-Coll was especially influential on his own designs; the two developed a friendship, and Ladegast introduced many technical innovations learned from Cavaillé-Coll's workshop to Germany, such as swell pedals and Barker levers. He set up his own workshop at Weißenfels in 1846, with his first commission being for a small organ in Geusa. He went on to build over 200 organs, with notable works including the reconstructi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organ (music)
Carol Williams performing at the West_Point_Cadet_Chapel.html" ;"title="United States Military Academy West Point Cadet Chapel">United States Military Academy West Point Cadet Chapel. In music, the organ is a keyboard instrument of one or more Pipe organ, pipe divisions or other means for producing tones, each played from its own Manual (music), manual, with the hands, or pedalboard, with the feet. Overview Overview includes: * Pipe organs, which use air moving through pipes to produce sounds. Since the 16th century, pipe organs have used various materials for pipes, which can vary widely in timbre and volume. Increasingly hybrid organs are appearing in which pipes are augmented with electric additions. Great economies of space and cost are possible especially when the lowest (and largest) of the pipes can be replaced; * Non-piped organs, which include: ** pump organs, also known as reed organs or harmoniums, which like the accordion and mouth organs (both Eastern and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomanerchor
The Thomanerchor (English: St. Thomas Choir of Leipzig) is a boys' choir in Leipzig, Germany. The choir was founded in 1212. The choir comprises about 90 boys from 9 to 18 years of age. The members, called ''Thomaner'', reside in a boarding school, the ''Thomasalumnat'' and attend the St. Thomas School, Leipzig, a Gymnasium school with a linguistic profile and a focus on musical education. The younger members attend the primary school ''Grundschule Forum Thomanum'' or ''Anna-Magdalena-Bach-Schule''. Johann Sebastian Bach served as Thomaskantor, director of the choir and church music in Leipzig, from 1723 to 1750. The choir Although the choir's main musical field traditionally consists of the vocal works of Johann Sebastian Bach, the repertoire comprises pieces from different eras, from the Renaissance to contemporary music. Andreas Reize is the 18th Thomaskantor since Bach. The Forum Thomanum is the campus of the choir in the Bach quarter of Leipzig. It was inaugurated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oratorio
An oratorio () is a large musical composition for orchestra, choir, and soloists. Like most operas, an oratorio includes the use of a choir, soloists, an instrumental ensemble, various distinguishable characters, and arias. However, opera is musical theatre, while oratorio is strictly a concert piece – though oratorios are sometimes staged as operas, and operas are sometimes presented in concert form. In an oratorio, the choir often plays a central role, and there is generally little or no interaction between the characters, and no props or elaborate costumes. A particularly important difference is in the typical subject matter of the text. Opera tends to deal with history and mythology, including age-old devices of romance, deception, and murder, whereas the plot of an oratorio often deals with sacred topics, making it appropriate for performance in the church. Protestant composers took their stories from the Bible, while Catholic composers looked to the lives of saints, as we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bach Cantata
The cantatas composed by Johann Sebastian Bach, known as Bach cantatas ( German: ), are a body of work consisting of over 200 surviving independent works, and at least several dozen that are considered lost. As far as known, Bach's earliest cantatas date from 1707, the year he moved to Mühlhausen, although he may have begun composing them at his previous post in Arnstadt. Most of Bach's church cantatas date from his first years as and director of church music in Leipzig, a position which he took up in 1723. Working for Leipzig's and , it was part of Bach's job to perform a church cantata every Sunday and holiday, conducting soloists, the Thomanerchor and orchestra as part of the church service. In his first years in Leipzig, starting after Trinity of 1723, Bach regularly composed a new cantata every week, although some of these cantatas were adapted (at least in part) from work he had composed before his Leipzig era. Works from three annual cycles of cantatas for the l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
St John Passion
The ''Passio secundum Joannem'' or ''St John Passion'' (german: Johannes-Passion, link=no), BWV 245, is a Passion or oratorio by Johann Sebastian Bach, the older of the surviving Passions by Bach. It was written during his first year as director of church music in Leipzig and was first performed on April 7, 1724, at Good Friday Vespers at the St. Nicholas Church. The structure of the work falls in two halves, intended to flank a sermon. The anonymous libretto draws on existing works (notably by Barthold Heinrich Brockes) and is compiled from recitatives and choruses narrating the Passion of Christ as told in the Gospel of John, ariosos and arias reflecting on the action, and chorales using hymn tunes and texts familiar to a congregation of Bach's contemporaries. Compared with the '' St Matthew Passion'', the ''St John Passion'' has been described as more extravagant, with an expressive immediacy, at times more unbridled and less "finished". The work is most often hear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protestant Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and in particular to papal authority, arising from what were perceived to be Criticism of the Catholic Church, errors, abuses, and discrepancies by the Catholic Church. The Reformation was the start of Protestantism and the split of the Western Church into Protestantism and what is now the Roman Catholic Church. It is also considered to be one of the events that signified the end of the Middle Ages and the beginning of the early modern period in Europe.Davies ''Europe'' pp. 291–293 Prior to Martin Luther, there were many Proto-Protestantism, earlier reform movements. Although the Reformation is usually considered to have started with the publication of the ''Ninety-five Theses'' by Martin Luther in 1517, he was not excommunicated by Pope Leo X ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)