|
SraJ RNA
GlmZ (formally known as SraJ) is a small non-coding RNA (ncRNA). It is the functional product of a gene which is not translated into protein. This ncRNA was discovered in the bacteria ''Escherichia coli'' during a large scale computational screen for transcription signals and genomic features of known small RNA-encoding genes. During this screen 14 novel ncRNA genes were identified, including SraB, SraC, SraD and SraG. The expression of SraJ was experimentally confirmed by Northern blotting. This ncRNA is expressed in early logarithmic phase, but its level decreases into stationary phase. Northern blot analysis also indicated this RNA undergoes specific cleavage processing. The GlmZ sRNA has been shown to positively control the synthesis of GlmS mRNA In molecular biology, messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) is a single-stranded molecule of RNA that corresponds to the genetic sequence of a gene, and is read by a ribosome in the process of Protein biosynthesis, synthesizi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secondary Structure
Protein secondary structure is the three dimensional conformational isomerism, form of ''local segments'' of proteins. The two most common Protein structure#Secondary structure, secondary structural elements are alpha helix, alpha helices and beta sheets, though beta turns and omega loops occur as well. Secondary structure elements typically spontaneously form as an intermediate before the protein protein folding, folds into its three dimensional protein tertiary structure, tertiary structure. Secondary structure is formally defined by the pattern of hydrogen bonds between the Amine, amino hydrogen and carboxyl oxygen atoms in the peptide backbone chain, backbone. Secondary structure may alternatively be defined based on the regular pattern of backbone Dihedral angle#Dihedral angles of proteins, dihedral angles in a particular region of the Ramachandran plot regardless of whether it has the correct hydrogen bonds. The concept of secondary structure was first introduced by Kaj Ulrik ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SraC/RyeA RNA
The SraC/RyeA RNA is a non-coding RNA that was discovered in ''E. coli'' during two large scale screens for RNAs. The function of this RNA is currently unknown. This RNA overlaps the SdsR/RyeB RNA The SdsR/RyeB RNA is a non-coding RNA that was identified in a large scale screen of ''E. coli''. The exact 5′ and 3′ ends of this RNA are uncertain. This RNA overlaps the SraC/RyeA RNA on the opposite strand suggesting that the two may act i ... on the opposite strand suggesting that the two RNAs may act in a concerted manner. References External links * Non-coding RNA {{molecular-cell-biology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GlmY RNA
The GlmY RNA (formally known as tke1) family consists of a number of bacterial RNA genes of around 167 bases in length. The GlmY RNA gene is present in ''Escherichia coli'', ''Shigella flexneri'', ''Yersinia pestis'' and ''Salmonella'' species, where it is found between the ''yfhK'' and ''purL'' genes. It was originally predicted in a bioinformatic screen for novel ncRNAs in ''E. coli''. The GlmY sRNA has been shown to activate the synthesis of GlmS. It achieves this by influencing the action of another sRNA called GlmZ in a hierarchical fashion. GlmY functions as an anti-adaptor, it binds to RapZ (RNase adaptor protein for sRNA GlmZ), this binding prevents RapZ from binding to GlmZ and targeting it for cleavage by RNase E. Further studies have shown that GlmY mutants are sensitive to cell envelope The cell envelope comprises the inner cell membrane and the cell wall of a bacterium. In gram-negative bacteria an outer membrane is also included. This envelope is not present in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MRNA
In molecular biology, messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) is a single-stranded molecule of RNA that corresponds to the genetic sequence of a gene, and is read by a ribosome in the process of Protein biosynthesis, synthesizing a protein. mRNA is created during the process of Transcription (biology), transcription, where an enzyme (RNA polymerase) converts the gene into primary transcript mRNA (also known as pre-mRNA). This pre-mRNA usually still contains introns, regions that will not go on to code for the final amino acid sequence. These are removed in the process of RNA splicing, leaving only exons, regions that will encode the protein. This exon sequence constitutes mature mRNA. Mature mRNA is then read by the ribosome, and, utilising amino acids carried by transfer RNA (tRNA), the ribosome creates the protein. This process is known as Translation (biology), translation. All of these processes form part of the central dogma of molecular biology, which describes the flow of genet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glucosamine Synthase
Glucosamine (C6H13NO5) is an amino sugar and a prominent precursor in the biochemical synthesis of glycosylated proteins and lipids. Glucosamine is part of the structure of two polysaccharides, chitosan and chitin. Glucosamine is one of the most abundant monosaccharides. Produced commercially by the hydrolysis of shellfish exoskeletons or, less commonly, by fermentation of a grain such as corn or wheat, glucosamine has many names depending on country. Although a common dietary supplement, there is little evidence that it is effective for relief of arthritis or pain, and is not an approved prescription drug. Dietary supplement Oral glucosamine is a dietary supplement and is not a prescription drug. Glucosamine is marketed as a supplement to support the structure and function of joints, and the marketing is targeted to people with osteoarthritis. Commonly sold forms of glucosamine are glucosamine sulfate, glucosamine chondroitin, glucosamine hydrochloride, and ''N''-acetylglucosa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacterial Growth
250px, Growth is shown as ''L'' = log(numbers) where numbers is the number of colony forming units per ml, versus ''T'' (time.) Bacterial growth is proliferation of bacterium into two daughter cells, in a process called binary fission. Providing no event occurs, the resulting daughter cells are genetically identical to the original cell. Hence, bacterial growth occurs. Both daughter cells from the division do not necessarily survive. However, if the surviving number exceeds unity on average, the bacterial population undergoes exponential growth. The measurement of an exponential bacterial growth curve in batch culture was traditionally a part of the training of all microbiologists; the basic means requires bacterial enumeration (cell counting) by direct and individual (microscopic, flow cytometry), direct and bulk (biomass), indirect and individual (colony counting), or indirect and bulk (most probable number, turbidity, nutrient uptake) methods. Models reconcile theory with th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
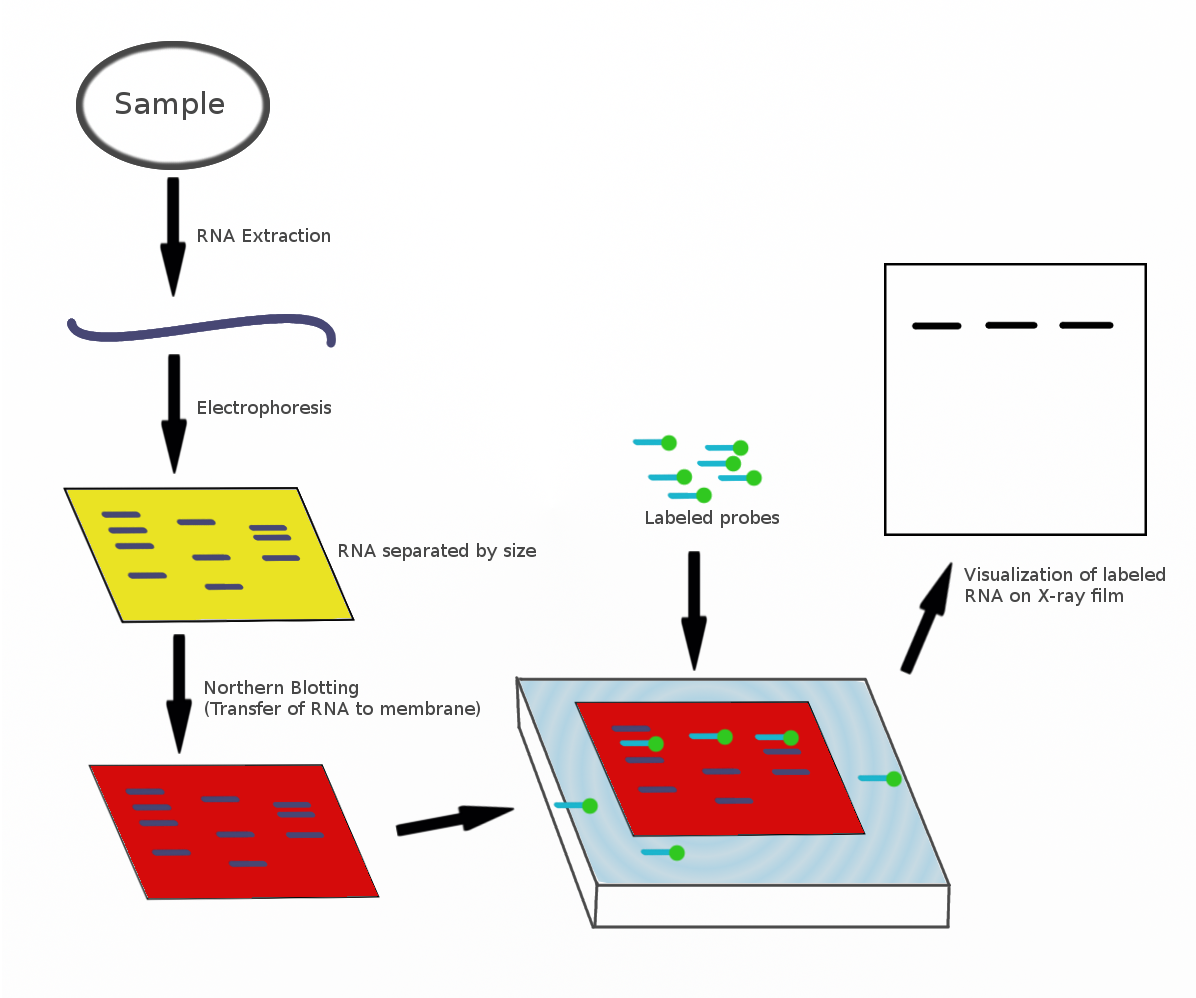
Northern Blotting
The northern blot, or RNA blot,Gilbert, S. F. (2000) Developmental Biology, 6th Ed. Sunderland MA, Sinauer Associates. is a technique used in molecular biology research to study gene expression by detection of RNA (or isolated mRNA) in a sample.Kevil, C. G., Walsh, L., Laroux, F. S., Kalogeris, T., Grisham, M. B., Alexander, J. S. (1997) An Improved, Rapid Northern Protocol. Biochem. and Biophys. Research Comm. 238:277–279. With northern blotting it is possible to observe cellular control over structure and function by determining the particular gene expression rates during differentiation and morphogenesis, as well as in abnormal or diseased conditions. Northern blotting involves the use of electrophoresis to separate RNA samples by size, and detection with a hybridization probe complementary to part of or the entire target sequence. Strictly speaking, the term 'northern blot' refers specifically to the capillary transfer of RNA from the electrophoresis gel to the blotting m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SraG RNA
SraG (small RNA G) is a small non-coding RNA (ncRNA). It is the functional product of a gene which is not translated into protein. This ncRNA was discovered in the bacteria ''Escherichia coli'' during a large scale computational screen for transcription signals and genomic features of known small RNA-encoding genes. During this screen 14 novel ncRNA genes were identified, including GlmZ, SraB, SraC and SraD. The expression of SraG was experimentally confirmed by Northern blotting The northern blot, or RNA blot,Gilbert, S. F. (2000) Developmental Biology, 6th Ed. Sunderland MA, Sinauer Associates. is a technique used in molecular biology research to study gene expression by detection of RNA (or isolated mRNA) in a sample.K ... which also indicated this RNA undergoes specific cleavage processing. The function of this RNA is unknown. References External links * Non-coding RNA {{molecular-cell-biology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SraD RNA
The MicA RNA (also known as SraD) is a small non-coding RNA that was discovered in ''E. coli'' during a large scale screen. Expression of SraD is highly abundant in stationary phase, but low levels could be detected in exponentially growing cells as well. Function This RNA binds the Hfq protein and regulates levels of gene expression by an antisense mechanism. It is known to target the OmpA gene in ''E. coli'' and occludes the ribosome binding site. Under conditions of envelope stress, micA transcription is induced. MicA, RybB RNA and MicL RNA transcription is under the control of the sigma factor sigma(E). In ''E.coli'', SraD also interacts in ''cis'' and ''trans'' with the mRNA species, ''luxS'', ''ompA a''nd ''phoP'', respectively. This observation describes MicA to be the first known sRNA to carry out antisense regulation in both structural configurations. MicA is known to interact with the mRNA encoding the quorum sensing synthase homolog, LuxS in E.coli and both RNAs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SraB RNA
The SraB RNA is a small non-coding RNA discovered in ''E. coli'' during a large scale experimental screen. The 14 novel RNAs discovered were named 'sra' for small RNA, examples include SraC, SraD and SraG. This ncRNA was found to be expressed only in stationary phase. The exact function of this RNA is unknown but it has been shown to affect survival of '' Salmonella enterica'' to antibiotic administration in egg albumin Ovalbumin (abbreviated OVA) is the main protein found in egg white, making up approximately 55% of the total protein. Ovalbumin displays sequence and three-dimensional homology to the serpin superfamily, but unlike most serpins it is not a serine .... The authors suggest this may be due to SraB regulating a response to components in albumin. See also * Escherichia coli sRNA References External links * Non-coding RNA {{molecular-cell-biology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sequence Conservation
In evolutionary biology, conserved sequences are identical or similar sequences in nucleic acids ( DNA and RNA) or proteins across species ( orthologous sequences), or within a genome ( paralogous sequences), or between donor and receptor taxa ( xenologous sequences). Conservation indicates that a sequence has been maintained by natural selection. A highly conserved sequence is one that has remained relatively unchanged far back up the phylogenetic tree, and hence far back in geological time. Examples of highly conserved sequences include the RNA components of ribosomes present in all domains of life, the homeobox sequences widespread amongst Eukaryotes, and the tmRNA in Bacteria. The study of sequence conservation overlaps with the fields of genomics, proteomics, evolutionary biology, phylogenetics, bioinformatics and mathematics. History The discovery of the role of DNA in heredity, and observations by Frederick Sanger of variation between animal insulins in 1949, promp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Escherichia Coli
''Escherichia coli'' (),Wells, J. C. (2000) Longman Pronunciation Dictionary. Harlow ngland Pearson Education Ltd. also known as ''E. coli'' (), is a Gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus ''Escherichia'' that is commonly found in the lower intestine of warm-blooded organisms. Most ''E. coli'' strains are harmless, but some serotypes ( EPEC, ETEC etc.) can cause serious food poisoning in their hosts, and are occasionally responsible for food contamination incidents that prompt product recalls. Most strains do not cause disease in humans and are part of the normal microbiota of the gut; such strains are harmless or even beneficial to humans (although these strains tend to be less studied than the pathogenic ones). For example, some strains of ''E. coli'' benefit their hosts by producing vitamin K2 or by preventing the colonization of the intestine by pathogenic bacteria. These mutually beneficial relationships between ''E. col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |