|
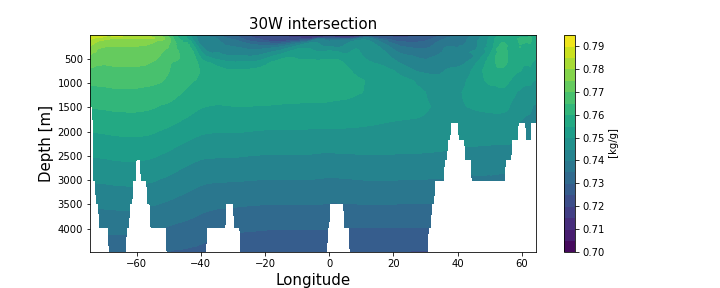
Spiciness (oceanography)
Spiciness (τ) is a term in oceanography that defines the salinity and potential temperature variation, often at constant density. Here, a temperature change offsets a salinity change; an increase in temperature decreases density whereas an increase in salinity increases density. Warmer and more saline water is spicier whereas cooler and less saline water is mintier. Mathematical description Quantifying the sea water density is necessary for describing thermohaline flow in the deep ocean. Changes in the two main parameters for this quantity, potential temperature Θ and salinity S, are multiplied with their thermal expansion \alpha or haline contraction coefficient \beta equal to each other; \alpha d\Theta and \beta dS are both proportional to a change in density and are both terms of the linearized equation of state of the ocean ( TEOS-10). This similarity is supposed to be relevant for understanding the consequences of sea water mixing. \alpha d\Theta=\beta dS The densit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Oceanography
Oceanography (), also known as oceanology and ocean science, is the scientific study of the oceans. It is an Earth science, which covers a wide range of topics, including ecosystem dynamics; ocean currents, Wind wave, waves, and geophysical fluid dynamics; plate tectonics and the geology of the sea floor; and fluxes of various chemical substances and physical properties within the ocean and across its boundaries. These diverse topics reflect multiple disciplines that oceanographers utilize to glean further knowledge of the world ocean, including astronomy, biology, chemistry, climatology, geography, geology, hydrology, meteorology and physics. Paleoceanography studies the history of the oceans in the geologic past. An oceanographer is a person who studies many matters concerned with oceans, including marine geology, physics, chemistry and biology. History Early history Humans first acquired knowledge of the waves and currents of the seas and oceans in pre-historic times. Obser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Salinity
Salinity () is the saltiness or amount of salt dissolved in a body of water, called saline water (see also soil salinity). It is usually measured in g/L or g/kg (grams of salt per liter/kilogram of water; the latter is dimensionless and equal to ‰). Salinity is an important factor in determining many aspects of the chemistry of natural waters and of biological processes within it, and is a thermodynamic state variable that, along with temperature and pressure, governs physical characteristics like the density and heat capacity of the water. A contour line of constant salinity is called an ''isohaline'', or sometimes ''isohale''. Definitions Salinity in rivers, lakes, and the ocean is conceptually simple, but technically challenging to define and measure precisely. Conceptually the salinity is the quantity of dissolved salt content of the water. Salts are compounds like sodium chloride, magnesium sulfate, potassium nitrate, and sodium bicarbonate which dissolve into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Potential Temperature
The potential temperature of a parcel of fluid at pressure P is the temperature that the parcel would attain if adiabatically brought to a standard reference pressure P_, usually . The potential temperature is denoted \theta and, for a gas well-approximated as ideal, is given by : \theta = T \left(\frac\right)^, where T is the current absolute temperature (in K) of the parcel, R is the gas constant of air, and c_p is the specific heat capacity at a constant pressure. R/c_p = 0.286 for air (meteorology). The reference point for potential temperature in the ocean is usually at the ocean's surface which has a water pressure of 0 dbar. The potential temperature in the ocean doesn't account for the varying heat capacities of seawater, therefore it is not a conservative measure of heat content. Graphical representation of potential temperature will always be less than the actual temperature line in a temperature vs depth graph. Contexts The concept of potential temperature applies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Density
Density (volumetric mass density or specific mass) is the substance's mass per unit of volume. The symbol most often used for density is ''ρ'' (the lower case Greek letter rho), although the Latin letter ''D'' can also be used. Mathematically, density is defined as mass divided by volume: : \rho = \frac where ''ρ'' is the density, ''m'' is the mass, and ''V'' is the volume. In some cases (for instance, in the United States oil and gas industry), density is loosely defined as its weight per unit volume, although this is scientifically inaccurate – this quantity is more specifically called specific weight. For a pure substance the density has the same numerical value as its mass concentration. Different materials usually have different densities, and density may be relevant to buoyancy, purity and packaging. Osmium and iridium are the densest known elements at standard conditions for temperature and pressure. To simplify comparisons of density across different syst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Thermohaline Circulation
Thermohaline circulation (THC) is a part of the large-scale ocean circulation that is driven by global density gradients created by surface heat and freshwater fluxes. The adjective ''thermohaline'' derives from '' thermo-'' referring to temperature and ' referring to salt content, factors which together determine the density of sea water. Wind-driven surface currents (such as the Gulf Stream) travel polewards from the equatorial Atlantic Ocean, cooling en route, and eventually sinking at high latitudes (forming North Atlantic Deep Water). This dense water then flows into the ocean basins. While the bulk of it upwells in the Southern Ocean, the oldest waters (with a transit time of about 1000 years) upwell in the North Pacific. Extensive mixing therefore takes place between the ocean basins, reducing differences between them and making the Earth's oceans a global system. The water in these circuits transport both energy (in the form of heat) and mass (dissolved solids an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Thermal Expansion Coefficients Of The Elements (data Page)
Thermal expansion Notes All values refer to 25 °C unless noted. References CRC As quoted from this source in an online version of: David R. Lide (ed), ''CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 84th Edition''. CRC Press. Boca Raton, Florida, 2003; Section 12, Properties of Solids; Thermal and Physical Properties of Pure Metals * Touloukian, Y. S., ''Thermophysical Properties of Matter'', Vol. 12, Thermal Expansion, IFI/Plenum, New York, 1975. CR2 As quoted in an online version of: * David R. Lide (ed), ''CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 84th Edition''. CRC Press. Boca Raton, Florida, 2003; Section 4, Properties of the Elements and Inorganic Compounds; Physical Properties of the Rare Earth Metals which further refers to: * Beaudry, B. J. and Gschneidner, K.A., Jr., in ''Handbook on the Physics and Chemistry of Rare Earths'', Vol. 1, Gschneidner, K.A., Jr. and Eyring, L., Eds., North-Holland Physics, Amsterdam, 1978, 173. * McEwen, K.A., in ''Handbook on the Phys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Haline Contraction Coefficient
The Haline contraction coefficient, abbreviated as β, is a coefficient that describes the change in ocean density due to a salinity change, while the potential temperature and the pressure are kept constant. It is a parameter in the Equation Of State (EOS) of the ocean. β is also described as the saline contraction coefficient and is measured in g in the EOS that describes the ocean. An example is TEOS-10. This is the thermodynamic equation of state. β is the salinity variant of the thermal expansion coefficient α, where the density changes due to a change in temperature instead of salinity. With these two coefficients, the density ratio can be calculated. This determines the contribution of the temperature and salinity to the density of a water parcel. β is called a contraction coefficient, because when salinity increases, water becomes denser, and if the temperature increases, water becomes less dense. Definition Τhe haline contraction coefficient is defined ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Linearization
In mathematics, linearization is finding the linear approximation to a function at a given point. The linear approximation of a function is the first order Taylor expansion around the point of interest. In the study of dynamical systems, linearization is a method for assessing the local stability of an equilibrium point of a system of nonlinear differential equations or discrete dynamical systems. This method is used in fields such as engineering, physics, economics, and ecology. Linearization of a function Linearizations of a function are lines—usually lines that can be used for purposes of calculation. Linearization is an effective method for approximating the output of a function y = f(x) at any x = a based on the value and slope of the function at x = b, given that f(x) is differentiable on , b/math> (or , a/math>) and that a is close to b. In short, linearization approximates the output of a function near x = a. For example, \sqrt = 2. However, what would be a g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
TEOS-10
TEOS-10 (Thermodynamic Equation of Seawater - 2010) is the international standard for the use and calculation of the thermodynamic properties of seawater, humid air and ice. It supersedes the former standard EOS-80 (Equation of State of Seawater 1980). TEOS-10 is used by oceanographers and climate scientists to calculate and model properties of the oceans in an internationally comparable way. History TEOS-10 was developed by thSCOR(Scientific Committee on Oceanic Research)International Association for the Physical Sciences of the Oceans, IAPSO(International Association for the Physical Sciences of the Oceans) Working Group 127 which was chaired by Trevor McDougall. It has been approved as the official description of the thermodynamic properties of seawater, humid air and ice in 2009 by the Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission, Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission (IOC) and in 2011 by the International Union of Geodesy and Geophysics, International Union of Geodesy and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Isopycnal
Isopycnals are layers within the ocean that are stratified based on their densities and can be shown as a line connecting points of a specific density or potential density on a graph. Isopycnals are often displayed graphically to help visualize "layers" of the water in the ocean or gases in the atmosphere in a similar manner to how contour lines are used in topographic maps to help visualize topography. Types Oceanography Water masses in the ocean are characterized by their properties. Factors such as density, temperature, and salinity can all be used to identify these masses and their origins as well as where they are in the water column. Density plays a large role in stratifying the ocean into layers. In a body of water, as the depth increases, so does the density; water masses with the highest density are at the bottom and the lowest densities are at the top. Typically, warm freshwater is less dense than cold salty water, thus the colder water will sink below the warmer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Isopleths
A contour line (also isoline, isopleth, or isarithm) of a function of two variables is a curve along which the function has a constant value, so that the curve joins points of equal value. It is a plane section of the three-dimensional graph of the function f(x,y) parallel to the (x,y)-plane. More generally, a contour line for a function of two variables is a curve connecting points where the function has the same particular value. In cartography, a contour line (often just called a "contour") joins points of equal elevation (height) above a given level, such as mean sea level. A contour map is a map illustrated with contour lines, for example a topographic map, which thus shows valleys and hills, and the steepness or gentleness of slopes. The contour interval of a contour map is the difference in elevation between successive contour lines. The gradient of the function is always perpendicular to the contour lines. When the lines are close together the magnitude of the gra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
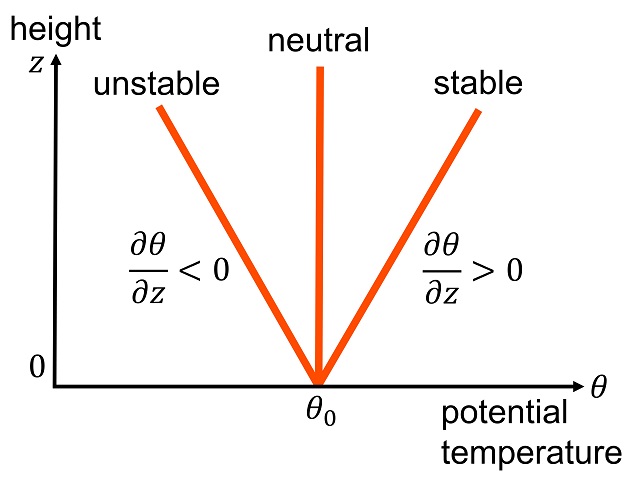
Stability
Stability may refer to: Mathematics * Stability theory, the study of the stability of solutions to differential equations and dynamical systems ** Asymptotic stability ** Linear stability ** Lyapunov stability ** Orbital stability ** Structural stability * Stability (probability), a property of probability distributions * Stability (learning theory), a property of machine learning algorithms *Stability, a property of sorting algorithms * Numerical stability, a property of numerical algorithms which describes how errors in the input data propagate through the algorithm * Stability radius, a property of continuous polynomial functions * Stable theory, concerned with the notion of stability in model theory *Stability, a property of points in geometric invariant theory * K-Stability, a stability condition for algebraic varieties. * Bridgeland stability conditions, a class of stability conditions on elements of a triangulated category. * Stability (algebraic geometry) Engineering *In a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |