|
Sphecomyrminae
Sphecomyrminae is an extinct subfamily of ants in family Formicidae known from a series of Cretaceous fossils found in North America, Europe, and Asia. Sphecomyrminae contains eight genera, divided into two tribes Sphecomyrmini and Zigrasimeciini. The tribe Sphecomyrmini contains the six genera '' Armania'', '' Cretomyrma'', '' Gerontoformica'', '' Orapia'', '' Pseudarmania'' and '' Sphecomyrma''; while Zigrasimeciini contains '' Boltonimecia'' and '' Zigrasimecia''. A number of taxa have been removed from the subfamily and placed either in other subfamilies or are now treated as ''incertae sedis'' in Formicidae. Sphecomyrminae is the most basal of the Formicidae subfamilies, but has not been included in several phylogenetic studies of the family. Symplesiomorphies of the subfamily include the structure of the antenna, which has a short basal segment and a flexible group of segments below the antenna tip. The petiole is low and rounded, with an unrestricted gaster and the pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zigrasimecia
''Zigrasimecia'' is an extinct genus of ants which existed in the Cretaceous period approximately 98 million years ago. The first specimens were collected from Burmese amber in Kachin State, west of Myitkyina town in Myanmar. In 2013, palaeoentomologists Phillip Barden and David Grimaldi published a paper describing and naming ''Zigrasimecia tonsora''. They described a dealate female with unusual features, notably the highly specialized mandibles. Other features include large ocelli, short scapes, 12 antennomeres, small eyes, and a clypeal margin that has a row of peg-like denticles. The genus ''Zigrasimecia'' was originally ''incertae sedis'' (uncertain placement) within Formicidae until a second species, ''Zigrasimecia ferox'', was described in 2014, leading to its placement in the subfamily Sphecomyrminae. Later, it was considered to belong to the distinct subfamily Zigrasimeciinae. Due to the highly specialized mandibles, scientists believe that the ants exhibited habi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
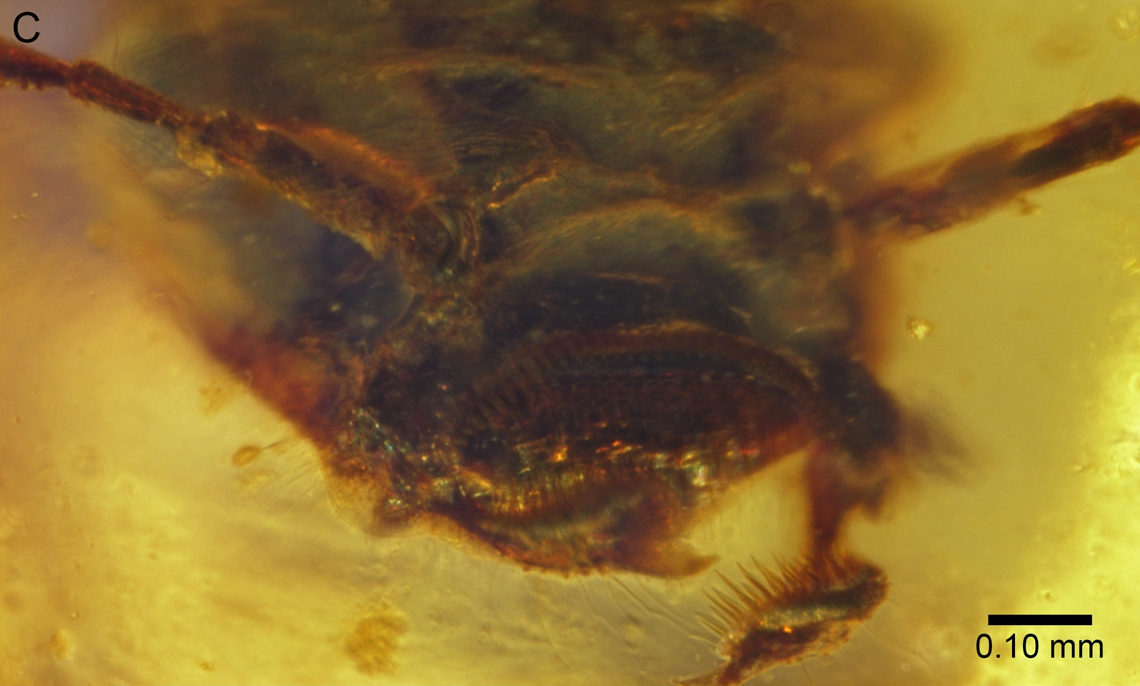
Sphecomyrma Freyi
''Sphecomyrma'' is an extinct genus of ants which existed in the Cretaceous approximately 79 to 92 million years ago. The first specimens were collected in 1966, found embedded in amber which had been exposed in the cliffs of Cliffwood, New Jersey, by Edmund Frey and his wife. In 1967, zoologists E. O. Wilson, Frank Carpenter and William L. Brown, Jr. published a paper describing and naming ''Sphecomyrma freyi''. They described an ant with a mosaic of features—a mix of characteristics from modern ants and aculeate wasps. It possessed a metapleural gland, a feature unique to ants. Furthermore, it was wingless and had a petiole which was ant-like in form. The mandibles were short and wasp-like with only two teeth, the gaster was constricted, and the middle and hind legs had double tibial spurs. The antennae were, in form, midway between the wasps and ants, having a short first segment but a long flexible funiculus. Two additional species, ''S. canadensis'' and ''S. mes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphecomyrma
''Sphecomyrma'' is an extinct genus of ants which existed in the Cretaceous approximately 79 to 92 million years ago. The first specimens were collected in 1966, found embedded in amber which had been exposed in the cliffs of Cliffwood, New Jersey, by Edmund Frey and his wife. In 1967, zoologists E. O. Wilson, Frank Carpenter and William L. Brown, Jr. published a paper describing and naming ''Sphecomyrma freyi''. They described an ant with a mosaic of features—a mix of characteristics from modern ants and aculeate wasps. It possessed a metapleural gland, a feature unique to ants. Furthermore, it was wingless and had a petiole which was ant-like in form. The mandibles were short and wasp-like with only two teeth, the gaster was constricted, and the middle and hind legs had double tibial spurs. The antennae were, in form, midway between the wasps and ants, having a short first segment but a long flexible funiculus. Two additional species, ''S. canadensis'' and ''S. mes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gerontoformica
''Gerontoformica'' is an extinct genus of stem-group ants. The genus contains thirteen described species known from Late Cretaceous fossils found in Asia and Europe. The species were described between 2004 and 2016, with a number of the species formerly being placed into the junior synonym genus ''Sphecomyrmodes''. History and classification ''Gerontoformica'' is known from over thirty adult fossil specimens which are composed of complete adult female workers and queens. The first fossil was discovered preserved as an inclusion in a transparent chunk of Charentese amber. The amber is thought to have been formed from resins of the extinct Pinales tree family Cheirolepidiaceae and possibly from the living family Araucariaceae. Paleoecology of the ambers indicates the shore to mangrove type forests were of a subtropical to warm temperate climate, with occasional dry periods The ambers are recovered from deposits exposed in quarries, road constructions, and beach exposures ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boltonimecia
''Boltonimecia'' is an extinct genus of ant in the formicid subfamily Zigrasimeciinae. The genus contains a single described species, ''Boltonimecia canadensis'', and is known from a single Late Cretaceous fossil which was found in Canada. The type species was originally described as a species of the extinct genus ''Sphecomyrma'' under the combination ''Sphecomyrma canadensis''. History and classification ''Boltonimecia'' is known from a single adult fossil, the holotype, specimen number "CAS 330" entombed in an amber chunk. At the time of the genus description, the specimen was residing in the Canadian National Collection of Insects, Arachnids and Nematodes, in Ottawa, Canada. The described specimen is of a worker caste adult which has been preserved as an inclusion in a transparent orange chunk of Canadian amber. The amber specimen was recovered ''in situ'' from the Taber coal zone near the top of Foremost Formation around Grassy Lake which is near Medicine Hat, Albe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oswald Heer
Oswald Heer (or Oswald von Heer) (31 August 1809 – 27 September 1883), Swiss geologist and naturalist, was born at Niederuzwil in Canton of St. Gallen and died in Lausanne. Biography Oswald Heer was educated as a clergyman at Halle and took holy orders, and he also graduated as Doctor of Philosophy and medicine. Early in life his interest was aroused in entomology, on which subject he acquired special knowledge, and later he took up the study of plants and became one of the pioneers in paleobotany, distinguished for his researches on the Miocene flora. In 1837, Carl Daniel Friedrich Meissner (1800–1874) a Swiss botanist named a genus of flowering plants (in the family of Anacardiaceae) from South Africa after him, '' Heeria''. In 1851, Heer became professor of botany in the university of Zürich, and for some time he was the director of what is now the Old Botanical Garden in that city. He directed his attention to the Tertiary plants and insects of Switzerland. In 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synonym (taxonomy)
The Botanical and Zoological Codes of nomenclature treat the concept of synonymy differently. * In botanical nomenclature, a synonym is a scientific name that applies to a taxon that (now) goes by a different scientific name. For example, Linnaeus was the first to give a scientific name (under the currently used system of scientific nomenclature) to the Norway spruce, which he called ''Pinus abies''. This name is no longer in use, so it is now a synonym of the current scientific name, '' Picea abies''. * In zoology, moving a species from one genus to another results in a different binomen, but the name is considered an alternative combination rather than a synonym. The concept of synonymy in zoology is reserved for two names at the same rank that refers to a taxon at that rank - for example, the name ''Papilio prorsa'' Linnaeus, 1758 is a junior synonym of ''Papilio levana'' Linnaeus, 1758, being names for different seasonal forms of the species now referred to as ''Araschnia l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taymyr Amber
{{Disambiguation, geo, ship ...
Taymyr or Taimyr may refer to: Places *Taymyr Peninsula, a peninsula in Siberia * Taymyr Gulf * Taymyra, a river in the Taymyr Peninsula * Lake Taymyr * Taymyr Island, an island in the Kara Sea *Taymyr Autonomous Okrug, a former federal subject of Russia Transportation *Taymyr (icebreaker), "Taymyr" ship name used for icebreakers ** ''Taymyr'' (1909 icebreaker), a steam-powered icebreaker ** ''Taymyr'' class nuclear icebreaker *** ''Taymyr'' (1987 icebreaker), a nuclear-powered shallow draft icebreaker See also * Maly Taymyr Island, an island in the Laptev Sea *Taymyrsky Dolgano-Nenetsky District Taymyrsky Dolgano-Nenetsky District (russian: Таймы́рский Долга́но-Не́нецкий райо́н) is an administrativeLaw #10-4765 and municipalLaw #2-54 district (raion), one of the forty-three in Krasnoyarsk Krai, Russia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the younger of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''creta'', the Latin word for the white limestone known as chalk. The chalk of northern France and the white cliffs of south-eastern England date from the Cretaceous Period. Climate During the Late Cretaceous, the climate was warmer than present, although throughout the period a cooling trend is evident. The tropics became restricted to equatorial regions and northern latitudes experienced markedly more seasonal climatic conditions. Geography Due to plate tectonics, the Americas were gradually moving westward, causing the Atlantic Ocean to expand. The Western Interior Seaway divided North America into eastern and western halves; Appalachia and Laramidia. India maintained a northward course towards Asia. In the Southern Hemisphere, Australia a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synapomorphy
In phylogenetics, an apomorphy (or derived trait) is a novel character or character state that has evolved from its ancestral form (or plesiomorphy). A synapomorphy is an apomorphy shared by two or more taxa and is therefore hypothesized to have evolved in their most recent common ancestor. ) In cladistics, synapomorphy implies homology. Examples of apomorphy are the presence of erect gait, fur, the evolution of three middle ear bones, and mammary glands in mammals but not in other vertebrate animals such as amphibians or reptiles, which have retained their ancestral traits of a sprawling gait and lack of fur. Thus, these derived traits are also synapomorphies of mammals in general as they are not shared by other vertebrate animals. Etymology The word —coined by German entomologist Willi Hennig—is derived from the Ancient Greek words (''sún''), meaning "with, together"; (''apó''), meaning "away from"; and (''morphḗ''), meaning "shape, form". Clade ana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural History Museum, London
The Natural History Museum in London is a museum that exhibits a vast range of specimens from various segments of natural history. It is one of three major museums on Exhibition Road in South Kensington, the others being the Science Museum and the Victoria and Albert Museum. The Natural History Museum's main frontage, however, is on Cromwell Road. The museum is home to life and earth science specimens comprising some 80 million items within five main collections: botany, entomology, mineralogy, palaeontology and zoology. The museum is a centre of research specialising in taxonomy, identification and conservation. Given the age of the institution, many of the collections have great historical as well as scientific value, such as specimens collected by Charles Darwin. The museum is particularly famous for its exhibition of dinosaur skeletons and ornate architecture—sometimes dubbed a ''cathedral of nature''—both exemplified by the large ''Diplodocus'' cast that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |