|
Speri (region)
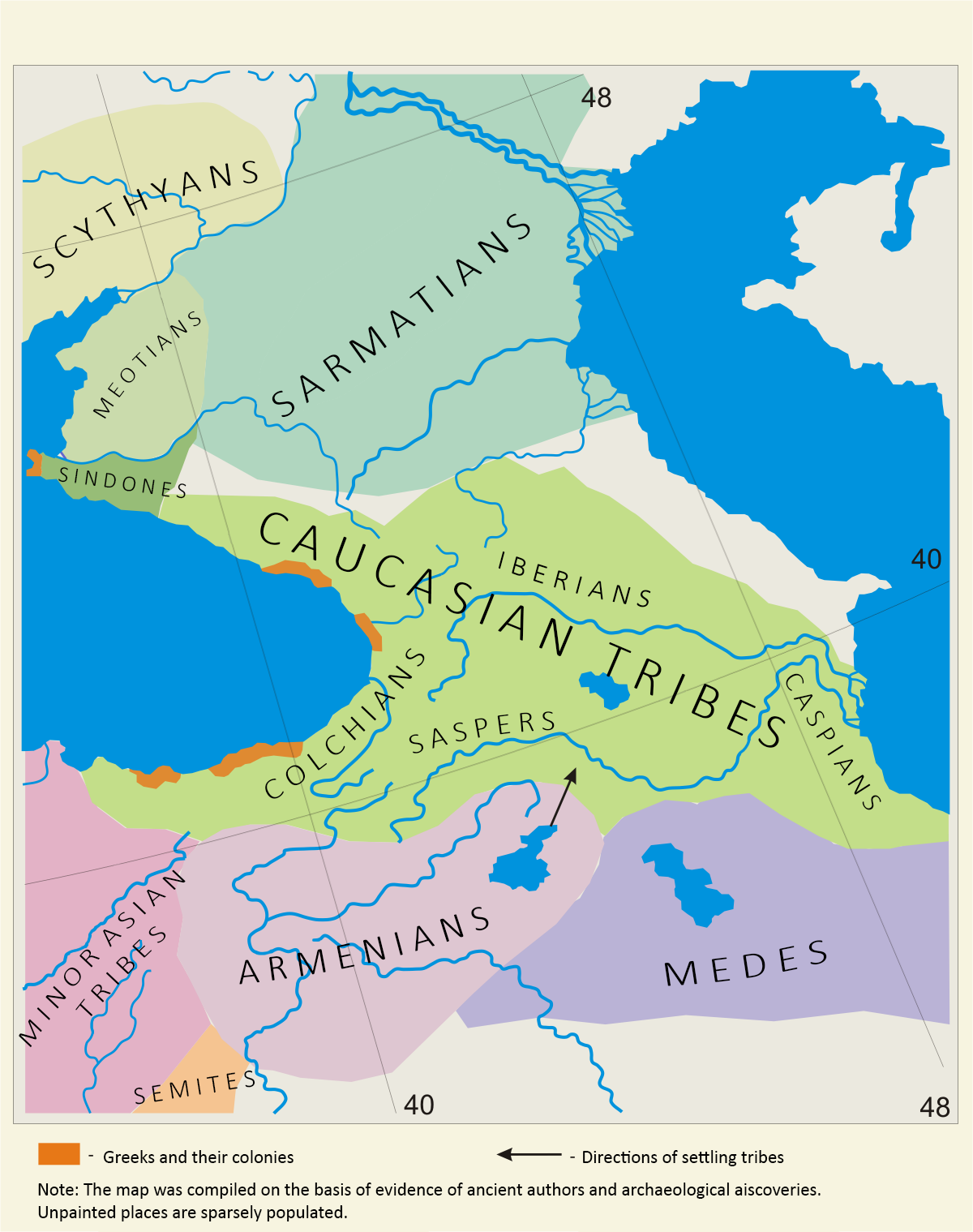
Speri, also known as Sper ( ''Sber'' or ''Sper'', ka, სპერი ''Speri''), is a historical region now part of the Eastern Anatolia region of Turkey. It was centered in the upper reaches of the valley of the Çoruh River, its probable capital was the town of İspir, or Syspiritus as indicated on the map next to the Byzantine-Sassanid border, and it originally extended as far west as the town of Bayburt and the Bayburt plains. Origin Sper was a part of ancient confederation Hayasa-Azzi on lands of Armenian Highland, in 2nd millennium BC.A History Of Georgia. Tbilisi: Artanuji Publ., 2014. The name Speri is thought by some to be derived from Saspers. According to the most widespread theory, they are a Kartvelian tribe.Mikaberidze, Alexander. Historical Dictionary Of Georgia. Lanham, Md.: Scarecrow Press, 2007. However, their origins have also been attributed to Scythian people. History Antiquity In 2nd millennium BC on lands of Sper was an ancient confederation Hayasa- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sultanate Of Rum
fa, سلجوقیان روم () , status = , government_type = Hereditary monarchyTriarchy (1249–1254)Diarchy (1257–1262) , year_start = 1077 , year_end = 1308 , p1 = Byzantine Empire under the Doukas dynastyByzantine Empire , p2 = Seljuk Empire , p3 = Danishmends , p4 = Mengujekids , p5 = Saltukids , p6 = Artuqids , s1 = Anatolian beyliks , s2 = Ilkhanate, , event_pre = Battle of Manzikert , date_pre = 1071 , event_start = Division from the Seljuk Empire , event1 = Battle of Köse Dağ , date_event1 = 1243 , event_end = Karamanid conquest , image_flag = Double-headed eagle of the Sultanate of Rum.svg , flag_size = 100px , flag_type = ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suleiman II (Rûm)
Suleiman II may refer to: * Suleiman II of the Ottoman Empire * Suleiman II of Persia Mir Sayyed Muhammad Marashi (June 1714May 1763), better known by his dynastic name of Suleiman II ( fa, شاه سلیمان), was a Safavid pretender who managed to briefly become ruler of some parts of Iran from 1749 to 1750. He was in charge ... * Suleiman II of Rûm * Suleiman II of Cordoba {{hndis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaldia
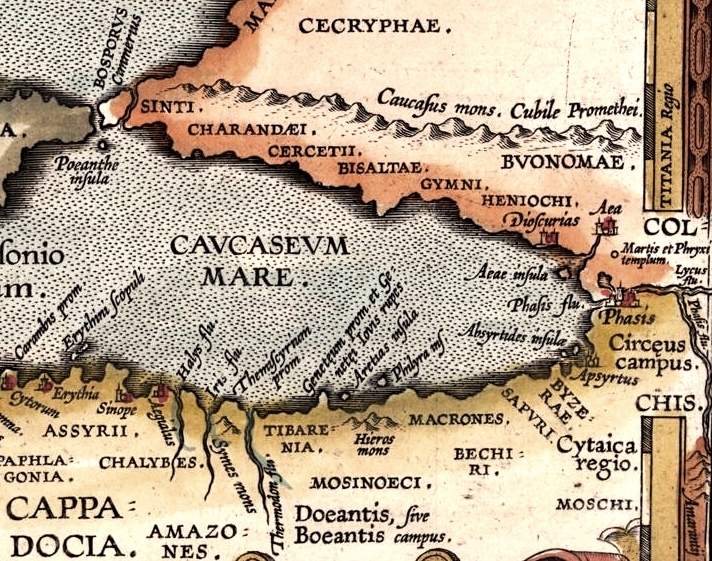
Chaldia ( el, Χαλδία, ''Khaldia'') was a historical region located in the mountainous interior of the eastern Black Sea, northeast Anatolia (modern Turkey). Its name was derived from a people called the ''Chaldoi'' (or ''Chalybes'') that inhabited the region in antiquity. Chaldia was used throughout the Byzantine period and was established as a formal theme, known as the Theme of Chaldia (Greek: θέμα Χαλδίας), by 840. During the Late Middle Ages, it formed the core of the Empire of Trebizond until its fall to the Ottoman Empire in 1461. Anthony Bryer traces the origin of its name not to Chaldea, as Constantine VII had done, but to the Urartian language, for whose speakers Ḫaldi was the Sun God. Bryer notes at the time of his writing that a number of villages in the Of district were still known as "Halt". Other scholars, however, reject the Urartian connection. Χάλυψ, the tribe's name in Greek, means "tempered iron, steel", a term that passed into Lati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theme (Byzantine District)
The themes or ( el, θέματα, , singular: , ) were the main military/administrative divisions of the middle Byzantine Empire. They were established in the mid-7th century in the aftermath of the Slavic invasion of the Balkans and Muslim conquests of parts of Byzantine territory, and replaced the earlier provincial system established by Diocletian and Constantine the Great. In their origin, the first themes were created from the areas of encampment of the field armies of the East Roman army, and their names corresponded to the military units that had existed in those areas. The theme system reached its apogee in the 9th and 10th centuries, as older themes were split up and the conquest of territory resulted in the creation of new ones. The original theme system underwent significant changes in the 11th and 12th centuries, but the term remained in use as a provincial and financial circumscription until the very end of the Empire. History Background During the late 6th and e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yusufeli
Yusufeli ( hy, Բերդագրակ, Berdagrak; ka, ახალთი, Akhalti) is a town and district of Artvin Province in the Black Sea region of Turkey. It is located on the bank of Çoruh River 104 km south-west of the city of Artvin, on the road to Erzurum. The town of Yusufeli (population 5863) sits in a valley where the Çoruh River is joined by the Barhal, the surrounding countryside is a range of mountains running east to west, with villages in other valleys between the mountains. The micro climate allows the cultivation of olives, grapes, and citrus fruits, the driving forces of the economy in addition to tourism. The town can be reached by air via Erzurum Airport, away from Yusufeli or by road from Artvin, Erzurum and Trabzon (via İspir in Erzurum Province). There is a widely criticised plan to dam the Çoruh at Yusufeli, which would submerge 15,000 homes. Climate Yusufeli has an oceanic climate (Köppen: ''Cfb''). History The history of Yusufeli, for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinople. It survived the fragmentation and fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD and continued to exist for an additional thousand years until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. During most of its existence, the empire remained the most powerful economic, cultural, and military force in Europe. The terms "Byzantine Empire" and "Eastern Roman Empire" were coined after the end of the realm; its citizens continued to refer to their empire as the Roman Empire, and to themselves as Romans—a term which Greeks continued to use for themselves into Ottoman times. Although the Roman state continued and its traditions were maintained, modern historians prefer to differentiate the Byzantine Empire from Ancient Rome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upper Armenia
Upper Armenia ( hy, Բարձր Հայք ''Bardzr Hayq'') was the first province of the ancient kingdom of Armenia, located in present-day Turkey, roughly corresponding to the modern province of Erzincan, to the west of the Kura River. Within the borders of the kingdom, it was bounded by the regions of Sophene, Turuberan, Tayk, and Ayrarat. It was called Upper Armenia, as it was higher in elevation than the other provinces. The total area of Upper Armenia was . It consisted of 9 cantons: * Daranaghi * Aghyun * Mzur * Yekeghyats * Mananaghi * Derjan * Sper * Shaghagom * Karin History Upper Armenia was famous for its lakes, rivers (especially the Euphrates), gold mines and fields. In the 2nd millennium BC, Upper Armenia's western parts were conquered by Hittite Empire; from the 15th century BC, it was conquered by Hayasa-Azzi. From 189 BC, it became part of the Kingdom of Armenia. Upper Armenia was famous for its pagan temples. From 62 AD, it became part of the Arsacid Dy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anania Shirakatsi
Anania Shirakatsi ( hy, Անանիա Շիրակացի, ''Anania Širakac’i'', anglicized: Ananias of Shirak) was a 7th-century Armenian polymath and natural philosopher, author of extant works covering mathematics, astronomy, geography, chronology, and other fields. Little is known for certain of his life outside of his own writings, but he is considered the father of the exact and natural sciences in Armenia—the first Armenian mathematician, astronomer, and cosmographer. Seen as a part of the Armenian Hellenizing School, the last lay scholar in Christian Armenia until the 11th century, Anania was educated primarily by Tychicus, in Trebizond. He composed science textbooks and the first known geographic work in classical Armenian (''Ashkharhatsuyts''), which provides detailed information about Greater Armenia, Persia and the Caucasus (Georgia and Caucasian Albania). In mathematics, his accomplishments include the earliest known table of results of the four basic operations, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ashkharatsuyts
''Ashkharatsuyts'' or ''Ašxarhac′oyc′'' (Աշխարհացոյց (traditional); Աշխարհացույց ( reformed)), often translated as ''Geography'' in English sources, is an early Medieval Armenian illustrated book by Anania Shirakatsi. It is about the geography of Armenia, Georgia, Iran, Iraq, etc. ''Ashkharatsuyts'' is the oldest book in Matenadaran on geography. . Matenadaran
The Matenadaran ( hy, Մատենադարան), officially the Mesrop Mashtots Institute of Ancient Manuscripts, is a museum, repository of manuscripts, and a research institute in Yerevan, Armenia. It is the world's largest repository of Armenia ... . Accessed October 28, 2009 ...
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chalybes
The Chalybes ( grc, Χάλυβες/Χάλυβοι, ka, ხალიბები, Khalibebi) and Chaldoi ( grc, Χάλδοι, ) were peoples mentioned by classical authors as living in Pontus and Cappadocia in northern Anatolia during Classical Antiquity. Their territory was known as Chaldia, extending from the Halys River to Pharnakeia and Trabzon in the east and as far south as eastern Anatolia. According to Apollonius of Rhodes, the Chalybes were Scythians. The Chaldoi, Chalybes, '' Mossynoikoi'', and ''Tibareni'', are counted among the first ironsmith nations by classical authors. , the tribe's name in Ancient Greek, means "tempered iron, steel", a term that passed into Latin as , "steel". Sayce derived the Greek name from Hittite , "land of Halys River". More than an identifiable people or tribe, "Chalybes" was a generic Greek term for "peoples of the Black Sea coast who trade in iron" or "a group of specialised metalworkers". The main sources for the history of the Cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |