Speri (region) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Speri, also known as Sper ( ''Sber'' or ''Sper'', ka, бГ°бГЮбГФбГ†бГШ ''Speri''), is a historical region now part of the
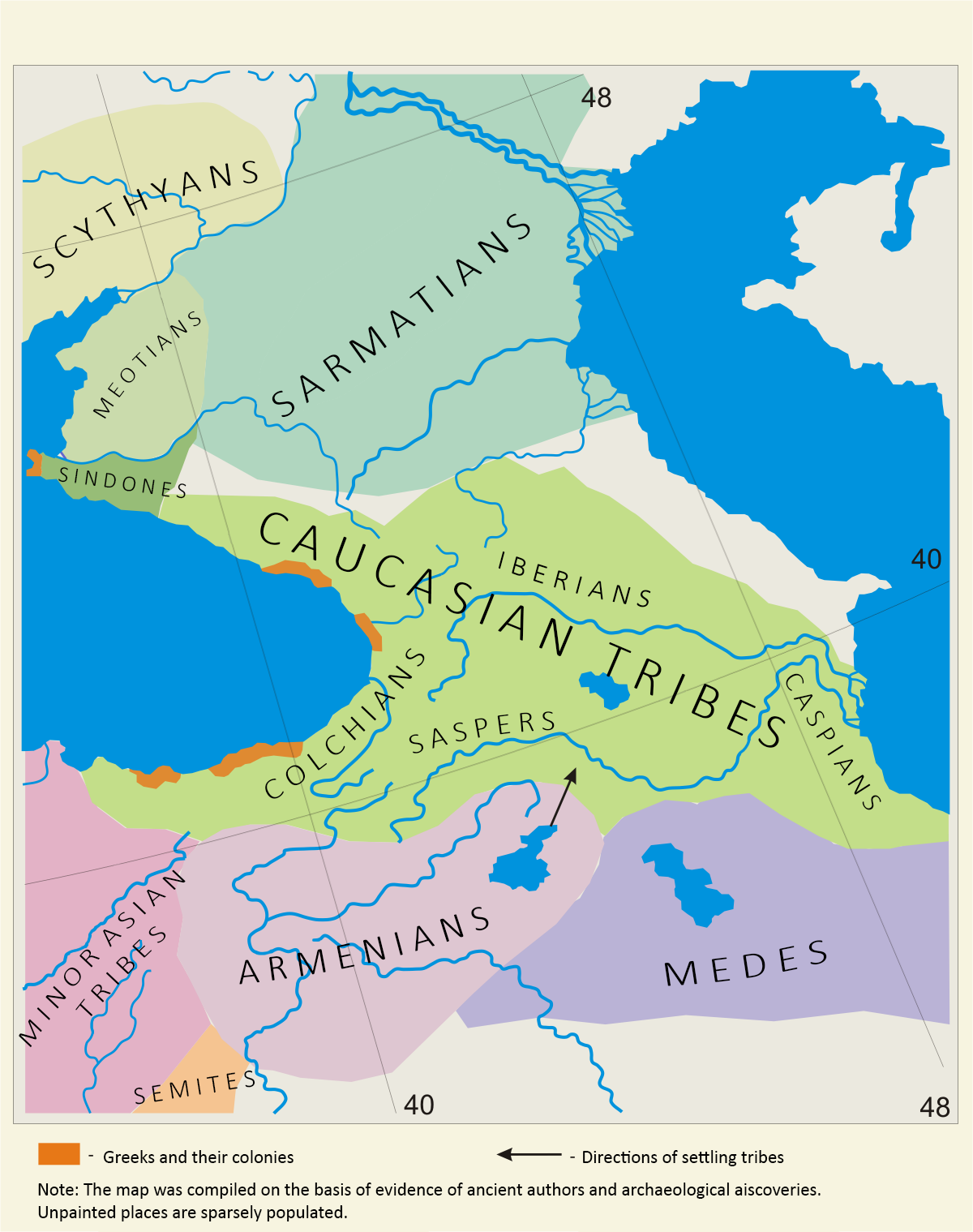 In 2nd millennium BC on lands of Sper was an ancient confederation
In 2nd millennium BC on lands of Sper was an ancient confederation
Eastern Anatolia
The Eastern Anatolia Region ('' tr, DoƒЯu Anadolu B√ґlgesi'') is a geographical region of Turkey. The most populous province in the region is Van Province. Other populous provinces are Malatya, Erzurum and Elazƒ±ƒЯ.
It is bordered by the Black Se ...
region of Turkey
Turkey ( tr, T√Љrkiye ), officially the Republic of T√Љrkiye ( tr, T√Љrkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a list of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolia, Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with ...
. It was centered in the upper reaches of the valley of the √Зoruh River
The Chorokh ( ka, бГ≠бГЭбГ†бГЭбГЃбГШ ''Ch'orokhi'', tr, √Зoruh, hy, ’Й’Є÷А’Є’≠ ''ChвАЩvorokh'', el, ќЖќЇќ±ќЉѕИќєѕВ, ''Akampsis'') is a river that rises in the Mescit Mountains in north-eastern Turkey, flows through the cities of Bayburt, ƒ∞sp ...
, its probable capital was the town of İspir
ƒ∞spir ( hy, ’Н’Ї’•÷А, Sper; ka, бГ°бГЮбГФбГ†бГШ, Speri) is a town and district of Erzurum Province in the Eastern Anatolia region of Turkey, on the √Зoruh River. They also appear as the Sasperi, the name Sper with a Georgian prefix of place Sa-, ...
, or Syspiritus as indicated on the map next to the Byzantine-Sassanid border, and it originally extended as far west as the town of Bayburt
Bayburt () is a city in northeast Turkey lying on the √Зoruh River and is the provincial capital of Bayburt Province. According to the 2021 census the population is determined as around 82,274.
Bayburt was once an important center on the ancient ...
and the Bayburt plains.
Origin
Sper was a part of ancient confederationHayasa-Azzi
Hayasa-Azzi or Azzi-Hayasa ( hit, URUбЄ™aia≈°a-, hy, ’А’°’µ’°’љ’°) was a Late Bronze Age confederation in the Armenian Highlands and/or Pontic region of Asia Minor. The Hayasa-Azzi confederation was in conflict with the Hittite Empire in th ...
on lands of Armenian Highland, in 2nd millennium BC.A History Of Georgia. Tbilisi: Artanuji Publ., 2014.
The name Speri is thought by some to be derived from Saspers
Saspeires ( grc, ќ£ќђѕГѕАќµќєѕБќµѕВ, ka, бГ°бГРбГ°бГЮбГФбГ†бГФбГСбГШ, ''sasp'erebi'', other names include Saspers, Saspines, Sapinians, and Sapirians) are a people of uncertain origin mentioned by Herodotus. According to the most widespread theory ...
. According to the most widespread theory, they are a Kartvelian Kartvelian may refer to:
* Anything coming from or related to Georgia (country)
* Kartvelian languages
* Kartvelian alphabet, see Georgian alphabet
* Kartvelian studies
* Georgians
{{disambig
Language and nationality disambiguation pages ...
tribe.Mikaberidze, Alexander. Historical Dictionary Of Georgia. Lanham, Md.: Scarecrow Press, 2007. However, their origins have also been attributed to Scythian
The Scythians or Scyths, and sometimes also referred to as the Classical Scythians and the Pontic Scythians, were an ancient Eastern
* : "In modern scholarship the name 'Sakas' is reserved for the ancient tribes of northern and eastern Centra ...
people.
History
Antiquity
 In 2nd millennium BC on lands of Sper was an ancient confederation
In 2nd millennium BC on lands of Sper was an ancient confederation Hayasa-Azzi
Hayasa-Azzi or Azzi-Hayasa ( hit, URUбЄ™aia≈°a-, hy, ’А’°’µ’°’љ’°) was a Late Bronze Age confederation in the Armenian Highlands and/or Pontic region of Asia Minor. The Hayasa-Azzi confederation was in conflict with the Hittite Empire in th ...
who were the Armenians.–Ш. –Ф—М—П–Ї–Њ–љ–Њ–≤ ¬Ђ–Ш—Б—В–Њ—А–Є—П –Ь–Є–і–Є–Є¬ї, —Б—В—А. 355, 1956 –°–∞—В—А–∞–њ—Б–Ї–∞—П –і–Є–љ–∞—Б—В–Є—П –Ю—А–Њ–љ—В–Њ–≤ —Б–Є–і–µ–ї–∞ –њ—А–Є –Р—Е–µ–Љ–µ–љ–Є–і–∞—Е –≤ –≤–Њ—Б—В–Њ—З–љ–Њ–є –Р—А–Љ–µ–љ–Є–Є (–≤ XVIII —Б–∞—В—А–∞–њ–Є–Є, –Ј–µ–Љ–ї–µ –Љ–∞—В–Є–µ–љ–Њ–≤-—Е—Г—А—А–Є—В–Њ–≤, —Б–∞—Б–њ–µ–є—А–Њ–≤-–Є–±–µ—А–Њ–≤ –Є –∞–ї–∞—А–Њ–і–Є–µ–≤-—Г—А–∞—А—В–Њ–≤; –Њ–і–љ–∞–Ї–Њ, –Ї–∞–Ї –њ–Њ–Ї–∞–Ј—Л–≤–∞–µ—В —Б–∞–Љ–Њ –љ–∞–Ј–≤–∞–љ–Є–µ, –Ј–і–µ—Б—М –ґ–Є–ї–Є —Г–ґ–µ –Є –∞—А–Љ–µ–љ–Є–Є)вА¶–Ш. –Ф—М—П–Ї–Њ–љ–Њ–≤ ¬Ђ–Ч–∞–Ї–∞–≤–Ї–∞–Ј—М–µ –Є —Б–Њ–њ—А–µ–і–µ–ї—М–љ—Л–µ —Б—В—А–∞–љ—Л –≤ –њ–µ—А–Є–Њ–і —Н–ї–ї–Є–љ–Є–Ј–Љ–∞¬ї, –≥–ї–∞–≤–∞ XXIX –Є–Ј ¬Ђ–Ш—Б—В–Њ—А–Є—П –Т–Њ—Б—В–Њ–Ї–∞: –Ґ. 1. –Т–Њ—Б—В–Њ–Ї –≤ –і—А–µ–≤–љ–Њ—Б—В–Є¬ї. –Ю—В–≤. —А–µ–і. –Т.¬†–Р.¬†–ѓ–Ї–Њ–±—Б–µ–љ.¬†вАФ –Ь.: –Т–Њ—Б—В. –ї–Є—В., 1997.James R. Russell ¬ЂZoroastrianism in Armenia¬ї, chapter 2 ¬ЂArmenia from the Median Conquest to the Rise of the Artaxiads¬ї. Harvard University Department of Near Eastern Languages and Civilizations and National Association for Armenian Studies and Research, 1987. Late antique Sper was part of Armenia and is probably the Syspiritis of classical authors. Syspiritis is mentioned in
Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-sighted that he could see ...
's ''Geographica
The ''Geographica'' (Ancient Greek: ќУќµѕЙќ≥ѕБќ±ѕЖќєќЇќђ ''Ge≈Нgraphik√°''), or ''Geography'', is an encyclopedia of geographical knowledge, consisting of 17 'books', written in Ancient Greek, Greek and attributed to Strabo, an educated citizen ...
'': one of two areas (the other being Acilisene
Acilisene from Greek and Latin works, бГФбГЩбГЪбГФбГ™бГШ бЄ≥lecifrom Georgian sources and also known as Hachdeanq, was a region and family in Armenia c. 400вАУ800. It was a strip of land along the Upper Euphrates or Arsanias (Armenian: ‘±÷А’°’Ѓ’°’ ...
) settled by followers of "Armenus of Armenium
Armenium or Armenion ( grc, бЉИѕБќЉќ≠ќљќєќњќљ) was a town of Pelasgiotis in ancient Thessaly, situated between Pherae and Larissa, near Boebeis Lake, said to have been the birthplace of Armenus, who accompanied Jason to Asia, and gave his name t ...
", the eponymous founder of the Armenian race. Strabo also mentions "mines of gold in the Hyspiratis".
After the 380s partition of Armenia into Roman and Sasanian
The Sasanian () or Sassanid Empire, officially known as the Empire of Iranians (, ) and also referred to by historians as the Neo-Persian Empire, was the last Iranian empire before the early Muslim conquests of the 7th-8th centuries AD. Named ...
client states, Sper was one of nine districts forming the territory of the Armenian kingdom of Arshak III
Arshak III, also known as Arsaces III, Arsak III and Arshak III-Vagharshak ( hy, ‘±÷А’Ј’°’ѓ ‘≥, flourished 4th century вАУ died 387), was a prince who served as a Roman client king of Arsacid Armenia from 378 until 387. Arshak III is often known ...
. Sper at that period was a principality, the ancestral domain of the Bagratuni clan. Their capital was the fortress of Smbatavan or Smbataberd, which may have been located either at Bayburt or Ispir. In the northern part of the principality was a territory lived in by non-Armenian people called Chalybes
The Chalybes ( grc, ќІќђќїѕЕќ≤ќµѕВ/ќІќђќїѕЕќ≤ќњќє, ka, бГЃбГРбГЪбГШбГСбГФбГСбГШ, Khalibebi) and Chaldoi ( grc, ќІќђќїќіќњќє, ) were peoples mentioned by classical authors as living in Pontus and Cappadocia in northern Anatolia during Classical A ...
, whose name was preserved in the alternative Armenian name for the Sper valley: Khaghto Dzor (Chaldian Valley). After Arshak's death, in 390 his kingdom was annexed by Rome and turned into a Roman province called Inner Armenia.
During the time of Justinian this province was incorporated into Armenia Magna ("Greater Armenia"). In the Geography
Geography (from Greek: , ''geographia''. Combination of Greek words вАШGeoвАЩ (The Earth) and вАШGraphienвАЩ (to describe), literally "earth description") is a field of science devoted to the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, and ...
of Anania Shirakatsi
Anania Shirakatsi ( hy, ‘±’ґ’°’ґ’Ђ’° ’З’Ђ÷А’°’ѓ’°÷Б’Ђ, ''Anania ≈†irakacвАЩi'', anglicized: Ananias of Shirak) was a 7th-century Armenian polymath and natural philosopher, author of extant works covering mathematics, astronomy, geography, chronol ...
, a 7th-century text, Sper is listed as being part of Bardzr Hayk ("High Armenia" or "Upper Armenia"). Hewsen speculates that "Bardzr Hayk" may simply be a translation of the Roman/Byzantine name for the province. The border between Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
-ruled and Sasanid Persian-ruled Armenia crossed the Choruh valley somewhere between İspir
ƒ∞spir ( hy, ’Н’Ї’•÷А, Sper; ka, бГ°бГЮбГФбГ†бГШ, Speri) is a town and district of Erzurum Province in the Eastern Anatolia region of Turkey, on the √Зoruh River. They also appear as the Sasperi, the name Sper with a Georgian prefix of place Sa-, ...
and Yusufeli
Yusufeli ( hy, ‘≤’•÷А’§’°’£÷А’°’ѓ, Berdagrak; ka, бГРбГЃбГРбГЪбГЧбГШ, Akhalti) is a town and district of Artvin Province in the Black Sea region of Turkey. It is located on the bank of √Зoruh River 104 km south-west of the city of Artvin, on ...
.
Sper was a Bagratid domain in the fourth to sixth centuries but at some point they lost direct control of Bayburt to the Byzantine empire, possibly soon after 387. Bayburt was refortified by the Byzantines in the period of Justinian and was eventually incorporated into its ''theme
Theme or themes may refer to:
* Theme (arts), the unifying subject or idea of the type of visual work
* Theme (Byzantine district), an administrative district in the Byzantine Empire governed by a Strategos
* Theme (computing), a custom graphical ...
'' of Chaldia
Chaldia ( el, ќІќ±ќїќіќѓќ±, ''Khaldia'') was a historical region located in the mountainous interior of the eastern Black Sea, northeast Anatolia (modern Turkey). Its name was derived from a people called the ''Chaldoi'' (or ''Chalybes'') that i ...
.
Middle Ages
In 1203, Rukn ad-din Suleiman II ofRum
Rum is a liquor made by fermenting and then distilling sugarcane molasses or sugarcane juice. The distillate, a clear liquid, is usually aged in oak barrels. Rum is produced in nearly every sugar-producing region of the world, such as the Phili ...
decided to capture the southern shores of the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Roma ...
and rule over Asia minor
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
. He invaded the Kingdom of Georgia
The Kingdom of Georgia ( ka, бГ°бГРбГ•бГРбГ†бГЧбГХбГФбГЪбГЭбГ° бГ°бГРбГЫбГФбГ§бГЭ, tr), also known as the Georgian Empire, was a medieval Eurasian monarchy that was founded in circa 1008 AD. It reached its Golden Age of political and economic ...
with 400 000 Muslim warriors from the emirates and sultanates of Erzinca, Abulistan, Erzerum and Sham (Syria) and took control over several southern Georgian provinces including Speri. In the same year, by winning in the Battle of Basian
The Battle of Basiani was fought, in the 13th century, between the armies of the Kingdom of Georgia and the Seljuqid Sultanate of Rum in the Basiani valley, 60 km northeast of the city of Erzurum in what is now northeast Republic of Turkey ...
i, Georgia managed to banish the Turks
Turk or Turks may refer to:
Communities and ethnic groups
* Turkic peoples, a collection of ethnic groups who speak Turkic languages
* Turkish people, or the Turks, a Turkic ethnic group and nation
* Turkish citizen, a citizen of the Republic o ...
and liberate the region of Speri again.
In the 15th century Sper was controlled by the Ak Koyunlu
The Aq Qoyunlu ( az, AƒЯqoyunlular , ) was a culturally Persianate,Kaushik Roy, ''Military Transition in Early Modern Asia, 1400вАУ1750'', (Bloomsbury, 2014), 38; "Post-Mongol Persia and Iraq were ruled by two tribal confederations: Akkoyunlu (Wh ...
confederation. In 1502, after the defeat and collapse of the confederation, its territory passed into the hands of Safavid Persia
Safavid Iran or Safavid Persia (), also referred to as the Safavid Empire, '. was one of the greatest Iranian empires after the 7th-century Muslim conquest of Persia, which was ruled from 1501 to 1736 by the Safavid dynasty. It is often conside ...
; however, localised Ak Koyunlu rule continued in Sper until, taking advantage of the dissolution of the Ak Koyunlu state following the death of Yakub, it was taken by Mzechabuk, the Atabeg of Samtskhe. The name of Mzechabuk's lieutenant in charge of Ispir during all or part of this period is known thanks to a colophon added in 1512 to an Armenian manuscript that tells of the "principality over Sper of Baron Kitevan, from the Georgian nation". Mzechabuk pursued a policy of appeasement with the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, –ЮќЄѕЙќЉќ±ќљќєќЇќЃ ќСѕЕѕДќњќЇѕБќ±ѕДќњѕБќѓќ±, Oth≈НmanikƒУ Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
and surrendered Ispir fortress to Sultan Selim in October 1514.Hovann H. Simonian (ed.), ''The Hemshin - History, society and identity in the Highlands of Northeast Turkey'', 2007, page 34. The Ottoman Empire had taken all of Sper from Mzechabuk probably by 1515.
Early modern history
In 1520 Sper became a ''kaza
A kaza (, , , plural: , , ; ota, ўВЎґЎІ, script=Arab, (; meaning 'borough')
* bg, –Њ–Ї–Њ–ї–Є—П (; meaning 'district'); also –Ъ–∞–∞–Ј–∞
* el, ѕЕѕАќњќіќєќњќѓќЇќЈѕГќєѕВ () or (, which means 'borough' or 'municipality'); also ()
* lad, kaza
, ...
'' within the Ottoman Empire; in 1536 speri became a ''sanjak
Sanjaks (liwƒБ Њ) (plural form: alwiyƒБ Њ)
* Armenian language, Armenian: ’ґ’°’∞’°’ґ’£ (''nahang''; meaning "province")
* Bulgarian language, Bulgarian: –Њ–Ї—А—К–≥ (''okr«Фg''; meaning "county", "province", or "region")
* el, ќФќєќњќѓќЇќЈѕГќєѕ ...
''. The Ispir valley was still almost completely Armenian Christian in the early 16th century: the Ottoman census recorded no Muslims. Muslims would increase in later centuries and eventually become the majority.
In 1548, during the OttomanвАУSafavid War (1532вАУ55), the towns of Ispir and Bayburt were taken and destroyed by the Safavid Shah Tahmasp.
During World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, in 1916 the region was taken by Russians forces and retaken by the newly formed Turkish Republic
Turkey ( tr, T√Љrkiye ), officially the Republic of T√Љrkiye ( tr, T√Љrkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula in ...
in 1918.
Notes
References
{{coord, 40.4, 41.0, dim:300km, display=title Former provinces of Georgia (country) Historical regions of Georgia (country) Western Armenia Regions of Asia Geography of the Middle East History of Western Asia Near East