|
Space Launch
Space launch is the earliest part of a flight that reaches space. Space launch involves liftoff, when a rocket or other space launch vehicle leaves the ground, floating ship or midair aircraft at the start of a flight. Liftoff is of two main types: rocket launch (the current conventional method), and non-rocket spacelaunch (where other forms of propulsion are employed, including airbreathing jet engines or other kinds). Issues with reaching space Definition of outer space Energy Therefore, by definition for spaceflight to occur, sufficient altitude is necessary. This implies a minimum gravitational potential energy needs to be overcome: for the Kármán line this is approximately 1 MJ/kg. W=mgh, m=1 kg, g=9.82 m/s2, h=105m. W=1*9.82*105≈106J/kg=1MJ/kg In practice, a higher energy than this is needed to be expended due to losses such as airdrag, propulsive efficiency, cycle efficiency of engines that are employed and gravity drag. In the past fifty years spacefl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SpaceX Crew Dragon (More Cropped)
Dragon 2 is a class of partially reusable spacecraft developed and manufactured by American aerospace manufacturer SpaceX, primarily for flights to the International Space Station (ISS). SpaceX has also launched private missions such as Inspiration4 and Axiom Mission 1. There are two variants: Crew Dragon, a spacecraft capable of ferrying four crew, and Cargo Dragon, an updated replacement for the original Dragon 1. The spacecraft consists of a reuseable space capsule and an expendable trunk module. The spacecraft launches atop a Falcon 9 Block 5 rocket and the capsule returns to Earth via splashdown. Cargo Dragon supplies cargo to the ISS under a Commercial Resupply Services-2 contract with NASA. The first flight of Dragon 2 in a cargo configuration launched in December 2020. It shares this duty with Northrop Grumman Innovation Systems' Cygnus spacecraft, and Sierra Nevada Corporation's Dream Chaser spacecraft is expected to join them . , Crew Dragon is the only U.S. hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
G-force
The gravitational force equivalent, or, more commonly, g-force, is a measurement of the type of force per unit mass – typically acceleration – that causes a perception of weight, with a g-force of 1 g (not gram in mass measurement) equal to the conventional value of gravitational acceleration on Earth, ''g'', of about . Since g-forces indirectly produce weight, any g-force can be described as a "weight per unit mass" (see the synonym specific weight). When the g-force is produced by the surface of one object being pushed by the surface of another object, the reaction force to this push produces an equal and opposite weight for every unit of each object's mass. The types of forces involved are transmitted through objects by interior mechanical stresses. Gravitational acceleration (except certain electromagnetic force influences) is the cause of an object's acceleration in relation to free fall. The g-force experienced by an object is due to the vector sum of all ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rocket Propellant
Rocket propellant is the reaction mass of a rocket. This reaction mass is ejected at the highest achievable velocity from a rocket engine A rocket engine uses stored rocket propellants as the reaction mass for forming a high-speed propulsive jet of fluid, usually high-temperature gas. Rocket engines are reaction engines, producing thrust by ejecting mass rearward, in accordanc ... to produce thrust. The energy required can either come from the propellants themselves, as with a chemical rocket, or from an external source, as with ion engines. Overview Rockets create thrust by expelling mass rear-ward, at high velocity. The thrust produced can be calculated by multiplying the mass flow rate of the propellants by their exhaust velocity relative to the rocket (specific impulse). A rocket can be thought of as being accelerated by the pressure of the combusting gases against the combustion chamber and Rocket engine nozzle, nozzle, not by "pushing" against the air behind or belo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Gun
{{disambiguation ...
Space Gun may refer to: *Space gun, a method of launching an object into space * ''Space Gun'' (album), a 2018 album by Guided by Voices * ''Space Gun'' (video game), a 1990 arcade game *Ljutic Space Gun, a 12 gauge single-shot shotgun See also * Hand-Held Maneuvering Unit, or maneuvering gun or zip gun, a device used in spacewalks * Raygun, a science-fiction directed-energy weapon * TP-82 Cosmonaut survival pistol, carried by cosmonauts on space missions * Space warfare and space weapons Space weapons are weapons used in space warfare. They include weapons that can attack space systems in orbit (i.e. anti-satellite weapons), attack targets on the earth from space or disable missiles travelling through space. In the course of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
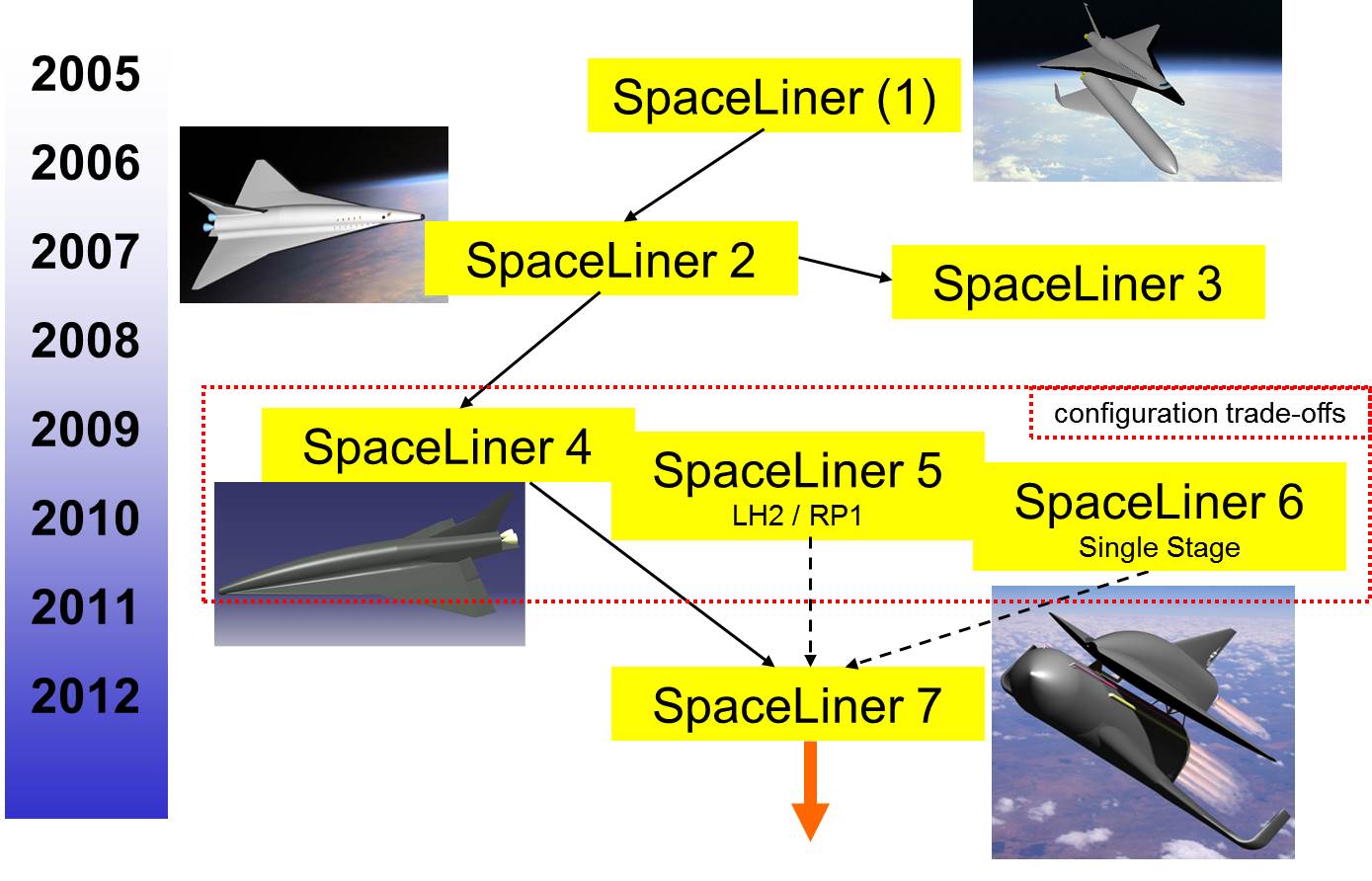
SpaceLiner
SpaceLiner is a concept for a suborbital, hypersonic, winged passenger supersonic transport, conceived at the German Aerospace Center (Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt, or DLR) in 2005. In its second role the SpaceLiner is intended as a reusable launch vehicle (RLV) capable of delivering heavy payloads into orbit. The SpaceLiner is a very long-term project, and does not currently have funding lined up to initiate system development as of 2017. Projections in 2015 were that if adequate funding was eventually secured, the SpaceLiner concept might become an operational spaceplane in the 2040s. Concept The SpaceLiner concept consists of a two-stage, vertical takeoff, horizontal landing configuration with a large uncrewed booster and a crewed stage designed for 50 passengers and 2 crew members. The fully reusable system is accelerated by a total of eleven liquid rocket engines (9 for the booster stage, 2 for the passenger stage), which are to be operated using cryogenic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
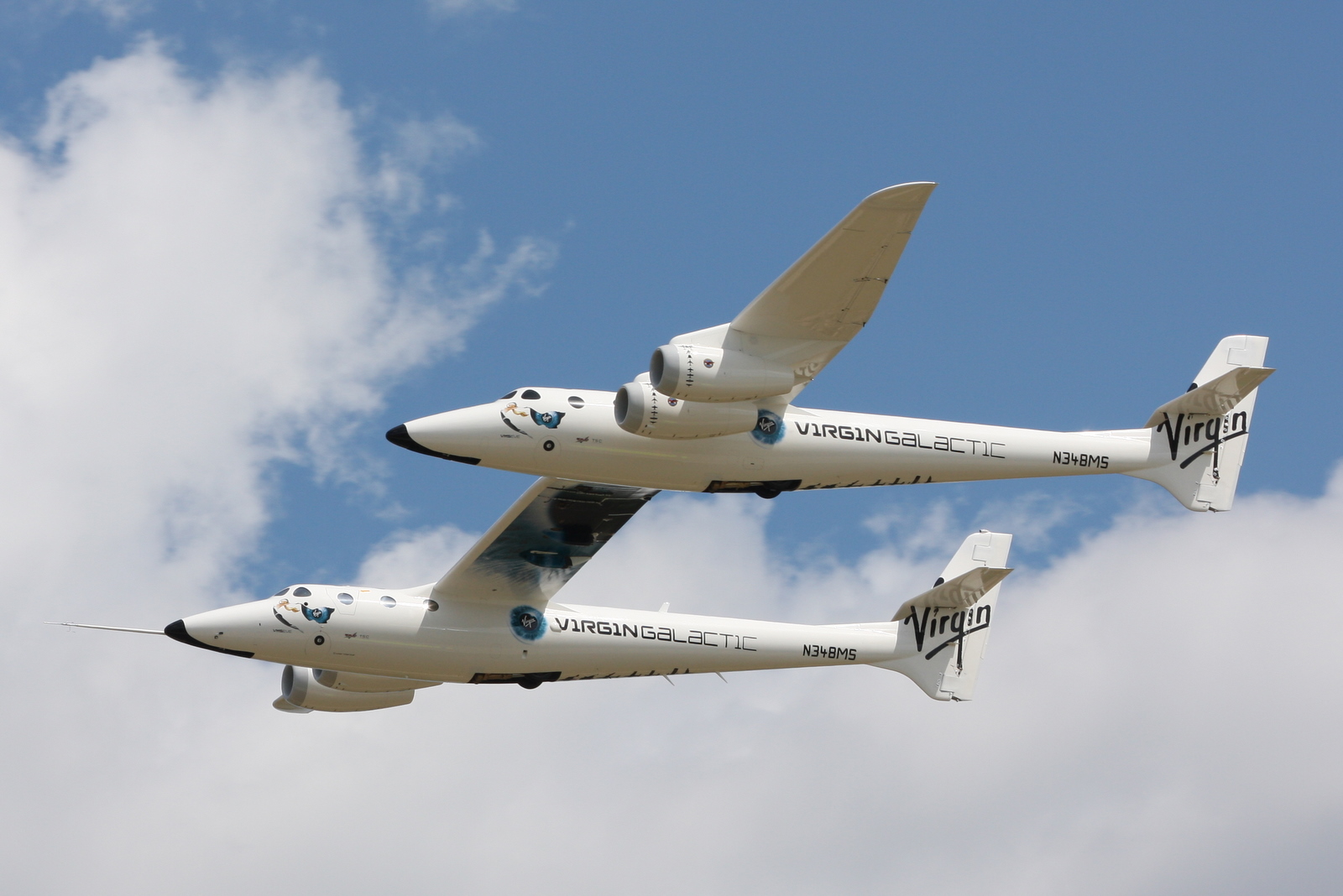
Virgin Galactic
Virgin Galactic is an American spaceflight company founded by Richard Branson and his British Virgin Group retains an 11.9% stake through Virgin Investments Limited. It is headquartered in California, and operates from New Mexico. The company is developing commercial spacecraft and aims to provide suborbital spaceflights to space tourists. Virgin Galactic's suborbital spacecraft are air launched from beneath a carrier airplane known as White Knight Two. Virgin Galactic‘s maiden spaceflight occurred in 2018 with its VSS ''Unity'' spaceship. Branson had originally hoped to see a maiden spaceflight by 2010, but the date was delayed for several years, primarily due to the October 2014 crash of VSS ''Enterprise''. The company did the early work on the satellite launch development of LauncherOne before this was hived off to a separate company, Virgin Orbit, in 2017. The company also has aspirations for suborbital transport and in 2017, Branson has said that Virgin Galactic was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ArianeGroup
ArianeGroup (formerly Airbus Safran Launchers) is an aerospace company based in France. A joint venture between Airbus and Safran, the company was founded in 2015 and is headquartered in Issy-les-Moulineaux. It consists of three core arms: aerospace, defence and security. ArianeGroup is currently developing its next-generation two-stage Ariane 6 launch vehicle, intended to succeed the Ariane 5 rocket, which has been launched more than 110 times. The new vehicle will be offered in two variants that will be capable of carrying between 10,350 and 21,650 Kilogram, kilograms. The first launch of Ariane 6 is expected to occur in 2023. If the company's task is to develop and manufacture the launch vehicles, Arianespace acts as the launch service provider for them. Meanwhile, another subsidiary, ArianeWorks, is tasked with developing next-generation technologies like the reusable Themis rocket booster. ArianeGroup also notably manufactures France's M51 (missile), M51 thermonuclear weap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbex
Orbital Express Launch Ltd., or Orbex, is a United Kingdom-based aerospace company that is developing a small commercial orbital rocket called Prime. Orbex is headquartered in Forres, Moray, in Scotland and has subsidiaries in Denmark and Germany. Its future launch complex is proposed to be built on the A' Mhòine peninsula in the county of Sutherland, northern Scotland. Overview The company was founded in 2015 as Moonspike Ltd., with the goal of crowdfunding a private spacecraft mission to the moon. A Kickstarter campaign running from 1 October to 1 November 2015 raised less than £79,000 ($122,000) out of a goal of £600,000 ($925,000), rendering Moonspike ineligible for the funds. Moonspike was renamed Orbital Express Launch Ltd. in 2016, with the company now aiming to provide commercial launch services of nano- and microsatellites, especially CubeSats, to polar and sun-synchronous low Earth orbits. In July 2018, Orbex secured £30 million ($39.6 million) in public and private ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gravity Drag
In astrodynamics and rocketry, gravity loss is a measure of the loss in the net performance of a rocket while it is thrusting in a gravitational field. In other words, it is the cost of having to hold the rocket up in a gravity field. Gravity losses depend on the time over which thrust is applied as well the direction the thrust is applied in. Gravity losses as a proportion of delta-v are minimised if maximum thrust is applied for a short time, or if thrust is applied in a direction perpendicular to the local gravitational field. During the launch and ascent phase, however, thrust must be applied over a long period with a major component of thrust in the opposite direction to gravity, so gravity losses become significant. For example, to reach a speed of 7.8 km/s in low Earth orbit requires a delta-v of between 9 and 10 km/s. The additional 1.5 to 2 km/s delta-v is due to gravity losses, steering losses and atmospheric drag. Example Consider the simplified case of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flight
Flight or flying is the process by which an object moves through a space without contacting any planetary surface, either within an atmosphere (i.e. air flight or aviation) or through the vacuum of outer space (i.e. spaceflight). This can be achieved by generating lift (force), aerodynamic lift associated with gliding flight, gliding or air propulsion, propulsive thrust, aerostatically using buoyancy, or by ballistics, ballistic movement. Many things can fly, from Flying and gliding animals, animal aviators such as birds, bats and insects, to natural gliders/parachuters such as patagium, patagial animals, anemochorous seeds and ballistospores, to human inventions like aircraft (airplanes, helicopters, airships, balloons, etc.) and rockets which may propel spacecraft and spaceplanes. The engineering aspects of flight are the purview of aerospace engineering which is subdivided into aeronautics, the study of vehicles that travel through the atmosphere, and astronautics, the stud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gravitational Energy
Gravitational energy or gravitational potential energy is the potential energy a massive object has in relation to another massive object due to gravity. It is the potential energy associated with the gravitational field, which is released (converted into kinetic energy) when the objects fall towards each other. Gravitational potential energy increases when two objects are brought further apart. For two pairwise interacting point particles, the gravitational potential energy U is given by U = -\frac, where M and m are the masses of the two particles, R is the distance between them, and G is the gravitational constant. Close to the Earth's surface, the gravitational field is approximately constant, and the gravitational potential energy of an object reduces to U = mgh where m is the object's mass, g = / is the gravity of Earth, and h is the height of the object's center of mass above a chosen reference level. Newtonian mechanics In classical mechanics, two or more masses alw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)