|
South Persia Rifles
The South Persia Rifles (Persian: تپانچهداران جنوب پارس), also known as SPR, was a Persian military force recruited by the British in 1916 and under British command.Fromkin, p. 209 They participated in the Persian Campaign of World War I. History The British formed the South Persia Rifles in response to German influence in southern Iran in 1915 and early 1916. The German agents influenced tribal groups who were already in rebellion against the British. As a result, the British had to divert troops to Iran rather than Ottoman Iraq. The South Persia Rifles was a measure to use locally raised troops rather than British or Indian units, so that the latter could be sent to the main campaign against the Ottomans in Iraq. With the assent of the Shah’s government, the British were allowed to form a military force of up to 11,000 men to quell the resistive tribes and maintain order. Sir Percy Sykes was selected by the British to command the new force. In March ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmenistan to the north, by Afghanistan and Pakistan to the east, and by the Gulf of Oman and the Persian Gulf to the south. It covers an area of , making it the 17th-largest country. Iran has a population of 86 million, making it the 17th-most populous country in the world, and the second-largest in the Middle East. Its largest cities, in descending order, are the capital Tehran, Mashhad, Isfahan, Karaj, Shiraz, and Tabriz. The country is home to one of the world's oldest civilizations, beginning with the formation of the Elamite kingdoms in the fourth millennium BC. It was first unified by the Medes, an ancient Iranian people, in the seventh century BC, and reached its territorial height in the sixth century BC, when Cyrus the Great fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
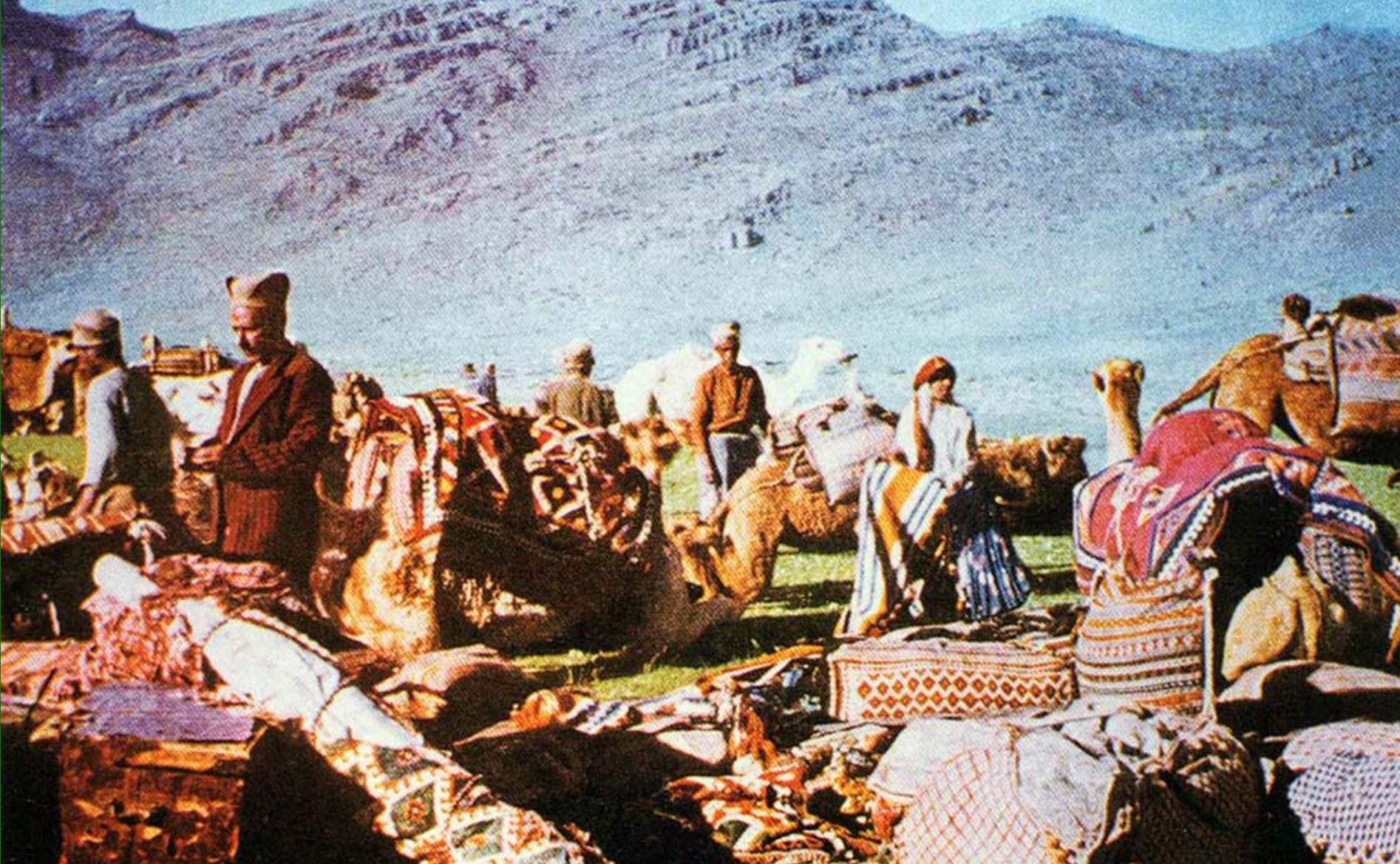
Qashqai People
Qashqai people (pronounced ; fa, قشقایی) are a tribal confederation in Iran mostly of Turkic origin. They are also believed to have incorporated Lurs, Kurds, and Arabs. Almost all of them speak a Western Turkic (Oghuz) language known as the Qashqai language, which they call "Turki", as well as Persian (the national language of Iran) in formal use. The Qashqai mainly live in the provinces of Fars, Khuzestan, Kohgiluyeh and Boyer-Ahmad, Chaharmahal and Bakhtiari, Bushehr and Southern Isfahan, especially around the cities of Shiraz and Firuzabad in Fars. The majority of Qashqai people were originally nomadic pastoralists and some remain so today. The traditional nomadic Qashqai traveled with their flocks twice yearly between the summer highland pastures north of Shiraz roughly 480 km or 300 miles south and the winter pastures on lower (and warmer) lands near the Persian Gulf, to the southwest of Shiraz. The majority, however, have now become partially or wholly s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Units And Formations Established In 1916
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. It is typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with its members identifiable by their distinct military uniform. It may consist of one or more military branches such as an army, navy, air force, space force, marines, or coast guard. The main task of the military is usually defined as defence of the state and its interests against external armed threats. In broad usage, the terms ''armed forces'' and ''military'' are often treated as synonymous, although in technical usage a distinction is sometimes made in which a country's armed forces may include both its military and other paramilitary forces. There are various forms of irregular military forces, not belonging to a recognized state; though they share many attributes with regular military forces, they are less often referred to as simply ''military''. A nation's military may f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infantry Regiments Of The British Army
Infantry is a military specialization which engages in ground combat on foot. Infantry generally consists of light infantry, mountain infantry, motorized infantry & mechanized infantry, airborne infantry, air assault infantry, and marine infantry. Although disused in modern times, heavy infantry also commonly made up the bulk of many historic armies. Infantry, cavalry, and artillery have traditionally made up the core of the combat arms professions of various armies, with the infantry almost always comprising the largest portion of these forces. Etymology and terminology In English, use of the term ''infantry'' began about the 1570s, describing soldiers who march and fight on foot. The word derives from Middle French ''infanterie'', from older Italian (also Spanish) ''infanteria'' (foot soldiers too inexperienced for cavalry), from Latin '' īnfāns'' (without speech, newborn, foolish), from which English also gets ''infant''. The individual-soldier term ''inf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Eastern Theatre Of World War I
The Middle Eastern theatre of World War I saw action between 29 October 1914 and 30 October 1918. The combatants were, on one side, the Ottoman Empire (including the majority of Kurdish tribes, a relative majority of Arabs, and Caucasian ''Tatars''), with some assistance from the other Central Powers; and on the other side, the British (with the help of Jews, Greeks, Assyrians, some Kurdish tribes, and many Arabs, along with Hindu and Muslim colonial troops from India), the Russians (with the help of Armenians, Assyrians, and occasionally some Kurdish tribes) and the French (with its North African and West African Muslim colonial troops) from among the Allied Powers. There were five main campaigns: the Sinai and Palestine Campaign, the Mesopotamian Campaign, the Caucasus Campaign, the Persian Campaign, and the Gallipoli Campaign. There were also several minor campaigns: Arab Campaign, and South Arabia Campaign. Both sides used local asymmetrical forces in the region. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Units And Formations Of Iran
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. It is typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with its members identifiable by their distinct military uniform. It may consist of one or more military branches such as an army, navy, air force, space force, marines, or coast guard. The main task of the military is usually defined as defence of the state and its interests against external armed threats. In broad usage, the terms ''armed forces'' and ''military'' are often treated as synonymous, although in technical usage a distinction is sometimes made in which a country's armed forces may include both its military and other paramilitary forces. There are various forms of irregular military forces, not belonging to a recognized state; though they share many attributes with regular military forces, they are less often referred to as simply ''military''. A nation's military may f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
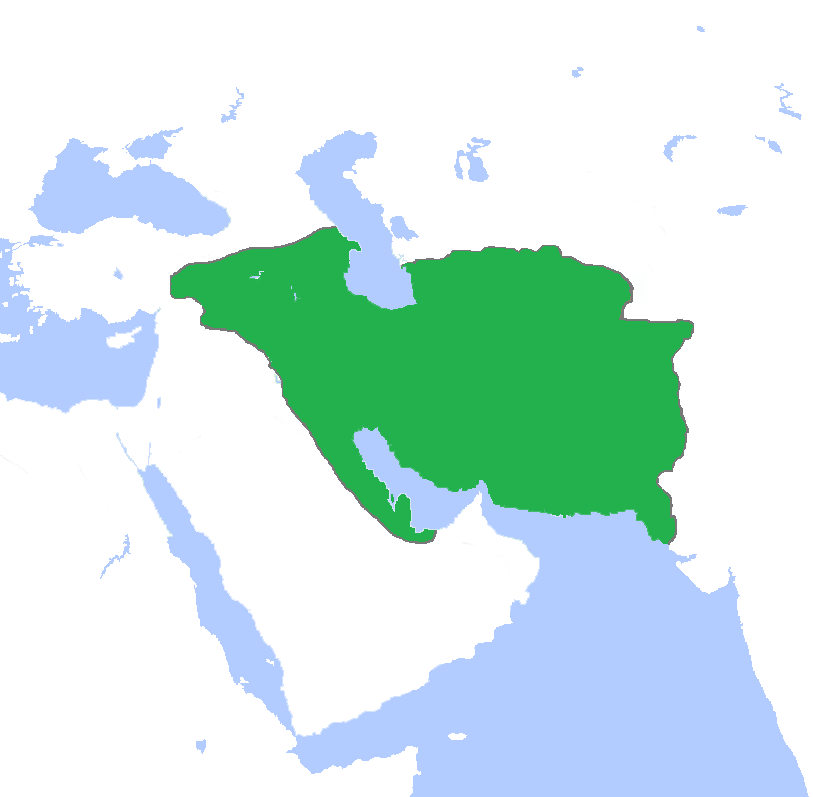
Military History Of Iran
The military history of Iran has been relatively well-documented, with thousands of years' worth of recorded history. Largely credited to its historically unchanged geographical and geopolitical condition, the modern-day Islamic Republic of Iran (historically known as Persia) has had a long and checkered military culture and history; ranging from triumphant and unchallenged ancient military supremacy, affording effective superpower status for its time; to a series of near-catastrophic defeats (beginning with the destruction of Elam) at the hands of previously subdued and conquered peripheral nations, most notably including the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon as well as the Asiatic nomadic tribes at the northeastern boundary of the lands traditionally home to the Iranian peoples. Elam (3500–539 BCE) Medes (678–549 BCE) Achaemenid Empire (550–330 BCE) Oxus chariot model.jpg, A golden chariot made during Achaemenid Empire (550–330 BCE). Achaemenid true exten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military History Of Qajar Iran
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. It is typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with its members identifiable by their distinct military uniform. It may consist of one or more military branches such as an army, navy, air force, space force, marines, or coast guard. The main task of the military is usually defined as defence of the state and its interests against external armed threats. In broad usage, the terms ''armed forces'' and ''military'' are often treated as synonymous, although in technical usage a distinction is sometimes made in which a country's armed forces may include both its military and other paramilitary forces. There are various forms of irregular military forces, not belonging to a recognized state; though they share many attributes with regular military forces, they are less often referred to as simply ''military''. A nation's military may f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Fall Of The Ottoman Empire And The Creation Of The Modern Middle East
''The'' () is a grammatical article in English, denoting persons or things already mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with pronouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a consonant sound, and as (homophone of pronoun ''thee'') when followed by a v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Fromkin
David Henry Fromkin (August 27, 1932 June 11, 2017) was an American historian, best known for his interpretive account of the Middle East, ''A Peace to End All Peace'' (1989), in which he recounts the role European powers played between 1914 and 1922 in creating the modern Middle East. The book was a finalist for both the National Book Critics Circle Award and the Pulitzer Prize for General Nonfiction. Fromkin wrote seven books, ending in 2007 with ''The King and the Cowboy: Theodore Roosevelt and Edward the Seventh, Secret Partners''. Life Fromkin was born in Milwaukee, Wisconsin, on August 27, 1932. He died on June 11, 2017 in New York City due to heart failure; he was 84. Career A graduate of the University of Chicago and the University of Chicago Law School, he was Professor Emeritus of History and International Relations, and Law at the Pardee School of Global Studies at Boston University, where he was also the Director of The Frederick S. Pardee Center for the Study of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iranian Army
The Islamic Republic of Iran Army Ground Forces ( fa, نیروی زمینی ارتش جمهوری اسلامی ایران, ''Niroo-ye Zamini-ye Artesh-e Jomhuri-ye Eslâmi-ye Iran''), acronymed NEZAJA ( fa, نزاجا, NEZEJA) are the ground forces of the Islamic Republic of Iran Army. In Iran, it is also called ''Artesh,'' () which is Persian for "army." In 2007, the regular Iranian Army was estimated to have 357,000 personnel (167,000 conscripts and 190,000 professionals) plus around 350,000 reservists for a total of 700,000 soldiers according to the CSIS. It is the 9th largest ground force in the world, the 9th largest armoured force globally and possesses the biggest Army Aviation fleet in the Middle East. Conscripts serve for 21 months and have professional military training. Iran has two parallel land forces with some integration at the command level: the regular ''Artesh'' (Army), and the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps, also known as the ''Sepâh'' (IRGC). History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shia
Shīʿa Islam or Shīʿīsm is the second-largest Islamic schools and branches, branch of Islam. It holds that the Prophets and messengers in Islam, Islamic prophet Muhammad in Islam, Muhammad designated Ali, ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib as his Succession to Muhammad, successor (''khalīfa'') and the Imamah (Shia doctrine), Imam (spiritual and political leader) after him, most notably at the event of Ghadir Khumm, but was prevented from succeeding Muhammad as the leader of the Muslims as a result of the choice made by some of Companions of the Prophet, Muhammad's other companions (''ṣaḥāba'') at Saqifah. This view primarily contrasts with that of Sunni Islam, Sunnī Islam, whose adherents believe that Muhammad did not appoint a successor before Death of Muhammad, his death and consider Abu Bakr, Abū Bakr, who was appointed caliph by a group of senior Muslims at Saqifah, to be the first Rashidun, rightful (''rāshidūn'') caliph after Muhammad. Adherents of Shīʿa Islam are c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.png)
