Infantry regiments of the British Army on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Infantry is a military specialization which engages in ground combat on foot. Infantry generally consists of
 In English, use of the term ''infantry'' began about the 1570s, describing soldiers who march and fight on foot. The word derives from Middle French ''infanterie'', from older Italian (also Spanish) ''infanteria'' (foot soldiers too inexperienced for cavalry), from Latin '' īnfāns'' (without speech, newborn, foolish), from which English also gets ''
In English, use of the term ''infantry'' began about the 1570s, describing soldiers who march and fight on foot. The word derives from Middle French ''infanterie'', from older Italian (also Spanish) ''infanteria'' (foot soldiers too inexperienced for cavalry), from Latin '' īnfāns'' (without speech, newborn, foolish), from which English also gets ''
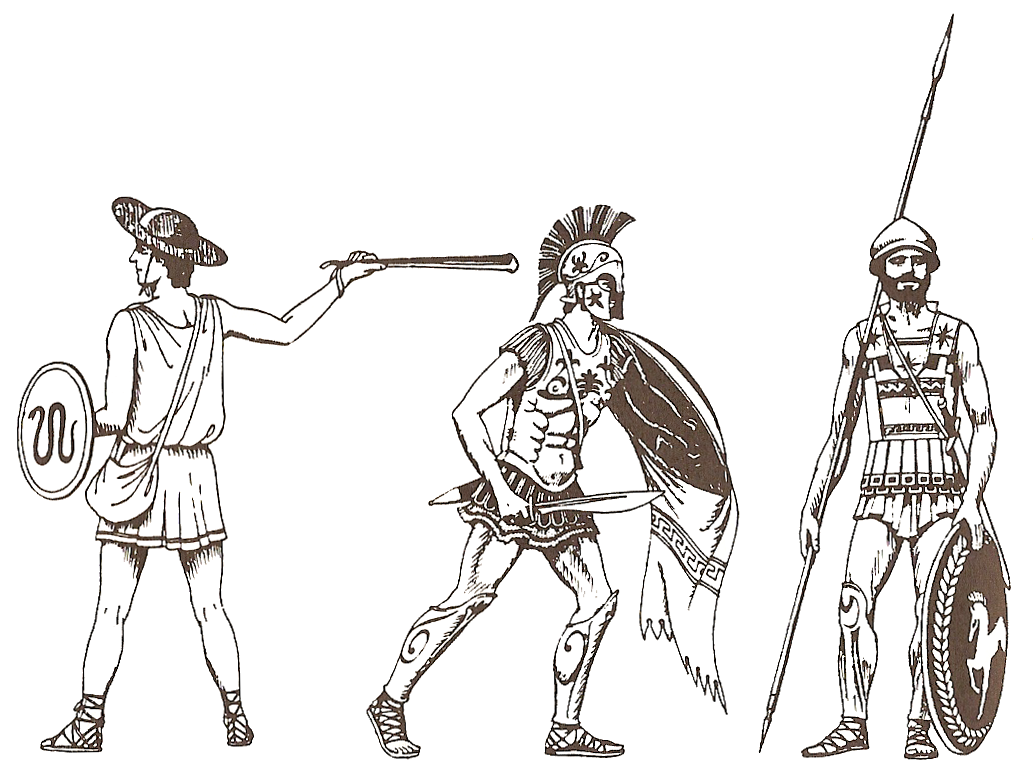
 The first warriors, adopting hunting weapons or improvised melee weapons, before the existence of any organised military, likely started essentially as loose groups without any organisation or formation. But this changed sometime before recorded history; the first
The first warriors, adopting hunting weapons or improvised melee weapons, before the existence of any organised military, likely started essentially as loose groups without any organisation or formation. But this changed sometime before recorded history; the first
 Beginning with the development the first regular military forces, close-combat regular infantry fought less as unorganised groups of individuals and more in coordinated units, maintaining a defined tactical formation during combat, for increased battlefield effectiveness; such infantry formations and the arms they used developed together, starting with the spear and the shield.
A spear has decent attack abilities with the additional advantage keeping opponents at distance; this advantage can be increased by using longer spears, but this could allow the opponent to side-step the point of the spear and close for
Beginning with the development the first regular military forces, close-combat regular infantry fought less as unorganised groups of individuals and more in coordinated units, maintaining a defined tactical formation during combat, for increased battlefield effectiveness; such infantry formations and the arms they used developed together, starting with the spear and the shield.
A spear has decent attack abilities with the additional advantage keeping opponents at distance; this advantage can be increased by using longer spears, but this could allow the opponent to side-step the point of the spear and close for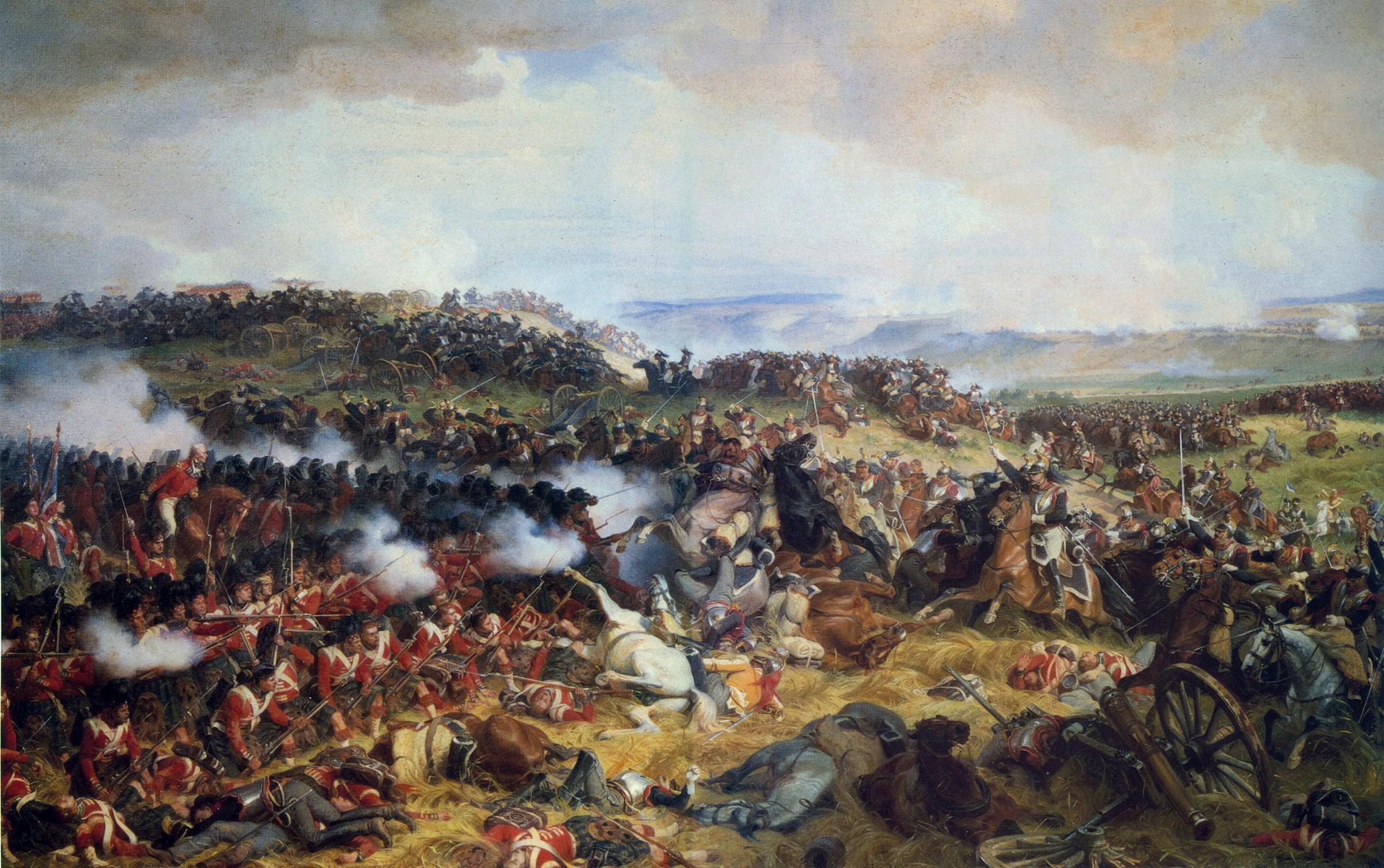  The opponents for these first formations, the close-combat infantry of more tribal societies, or any military without regular infantry (so called "
The opponents for these first formations, the close-combat infantry of more tribal societies, or any military without regular infantry (so called "
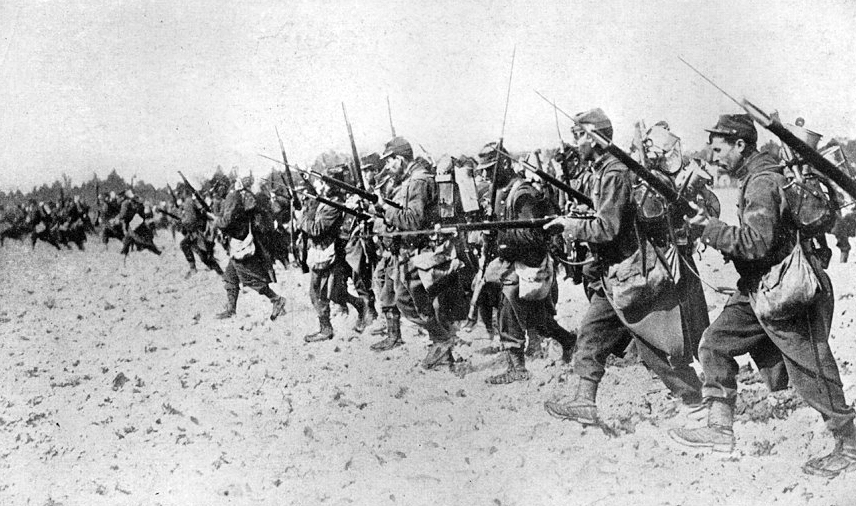
 The training of the infantry has differed drastically over time and from place to place. The cost of maintaining an army in fighting order and the seasonal nature of warfare precluded large permanent armies.
The antiquity saw everything from the well-trained and motivated citizen armies of Greece and Rome, the tribal host assembled from farmers and hunters with only passing acquaintance with warfare and masses of lightly armed and ill-trained militia put up as a last ditch effort. Kushite king Taharqa enjoyed military success in the
The training of the infantry has differed drastically over time and from place to place. The cost of maintaining an army in fighting order and the seasonal nature of warfare precluded large permanent armies.
The antiquity saw everything from the well-trained and motivated citizen armies of Greece and Rome, the tribal host assembled from farmers and hunters with only passing acquaintance with warfare and masses of lightly armed and ill-trained militia put up as a last ditch effort. Kushite king Taharqa enjoyed military success in the
In Praise of Infantry
* Tobin, James, ''Ernie Pyle's War: America's Eyewitness to World War II'', Free Press, 1997. * Mauldin, Bill, Ambrose, Stephen E., ''Up Front'', W. W. Norton, 2000. * Trogdon, Robert W., ''Ernest Hemingway: A Literary Reference'', Da Capo Press, 2002. * ''The New York Times'', Maj Gen C T Shortis, British Director of Infantry, 4 February 1985. * Heinl, Robert Debs, ''Dictionary of Military and Naval Quotations'', Plautus in ''The Braggart Captain'' (3rd century AD), Naval Institute Press, Annapolis, 1978. * Nafziger, George, ''Napoleon's Invasion of Russia'', Presidio Press, 1998. * McManus, John C. ''Grunts: inside the American infantry combat experience, World War II through Iraq'' New York, NY: NAL Caliber. 2010 plu
Webcast Author Lecture
at the Pritzker Military Library on 29 September 2010.
europeanfilmgateway.eu
by Field-Marshal Earl Wavell; First published in "The Times," Thursday, 19 April 1945.
KFOR: KFOR Chronicle.
Web Version of U.S. Army Field Manual 3–21.8
– The Infantry Rifle Platoon and Squad. * — includes several drawings {{Authority control Combat occupations
light infantry
Light infantry refers to certain types of lightly equipped infantry throughout history. They have a more mobile or fluid function than other types of infantry, such as heavy infantry or line infantry. Historically, light infantry often fought ...
, mountain infantry, motorized infantry & mechanized infantry, airborne infantry, air assault infantry, and marine infantry. Although disused in modern times, heavy infantry also commonly made up the bulk of many historic armies. Infantry, cavalry
Historically, cavalry (from the French word ''cavalerie'', itself derived from "cheval" meaning "horse") are soldiers or warriors who fight mounted on horseback. Cavalry were the most mobile of the combat arms, operating as light cavalry ...
, and artillery have traditionally made up the core of the combat arms professions of various armies, with the infantry almost always comprising the largest portion of these forces.
Etymology and terminology
 In English, use of the term ''infantry'' began about the 1570s, describing soldiers who march and fight on foot. The word derives from Middle French ''infanterie'', from older Italian (also Spanish) ''infanteria'' (foot soldiers too inexperienced for cavalry), from Latin '' īnfāns'' (without speech, newborn, foolish), from which English also gets ''
In English, use of the term ''infantry'' began about the 1570s, describing soldiers who march and fight on foot. The word derives from Middle French ''infanterie'', from older Italian (also Spanish) ''infanteria'' (foot soldiers too inexperienced for cavalry), from Latin '' īnfāns'' (without speech, newborn, foolish), from which English also gets ''infant
An infant or baby is the very young offspring of human beings. ''Infant'' (from the Latin word ''infans'', meaning 'unable to speak' or 'speechless') is a formal or specialised synonym for the common term ''baby''. The terms may also be used to ...
''. The individual-soldier term ''infantryman'' was not coined until 1837. In modern usage, foot soldiers of any era are now considered infantry and infantrymen.
From the mid-18th century until 1881 the British Army named its infantry as numbered regiments "of Foot" to distinguish them from cavalry
Historically, cavalry (from the French word ''cavalerie'', itself derived from "cheval" meaning "horse") are soldiers or warriors who fight mounted on horseback. Cavalry were the most mobile of the combat arms, operating as light cavalry ...
and dragoon
Dragoons were originally a class of mounted infantry, who used horses for mobility, but dismounted to fight on foot. From the early 17th century onward, dragoons were increasingly also employed as conventional cavalry and trained for combat w ...
regiments (see List of Regiments of Foot).
Infantry equipped with special weapons were often named after that weapon, such as grenadier
A grenadier ( , ; derived from the word '' grenade'') was originally a specialist soldier who threw hand grenades in battle. The distinct combat function of the grenadier was established in the mid-17th century, when grenadiers were recruited fr ...
s for their grenade
A grenade is an explosive weapon typically thrown by hand (also called hand grenade), but can also refer to a shell (explosive projectile) shot from the muzzle of a rifle (as a rifle grenade) or a grenade launcher. A modern hand grenade genera ...
s, or fusilier
Fusilier is a name given to various kinds of soldiers; its meaning depends on the historical context. While fusilier is derived from the 17th-century French language, French word ''fusil'' – meaning a type of flintlock musket – the term has ...
s for their ''fusils''.These names can persist long after the weapon speciality; examples of infantry units that retained such names are the Royal Irish Fusiliers
The Royal Irish Fusiliers (Princess Victoria's) was an Irish line infantry regiment of the British Army, formed by the amalgamation of the 87th (Prince of Wales's Irish) Regiment of Foot and the 89th (Princess Victoria's) Regiment of Foot in ...
and the Grenadier Guards.
Dragoon
Dragoons were originally a class of mounted infantry, who used horses for mobility, but dismounted to fight on foot. From the early 17th century onward, dragoons were increasingly also employed as conventional cavalry and trained for combat w ...
s were created as mounted infantry, with horses for travel between battles; they were still considered infantry since they dismounted before combat. However, if light cavalry
Light cavalry comprised lightly armed and armored cavalry troops mounted on fast horses, as opposed to heavy cavalry, where the mounted riders (and sometimes the warhorses) were heavily armored. The purpose of light cavalry was primarily rai ...
was lacking in an army, any available dragoons might be assigned their duties; this practise increased over time, and dragoons eventually received all the weapons and training as both infantry and cavalry, and could be classified as both. Conversely, starting about the mid-19th century, regular cavalry have been forced to spend more of their time dismounted in combat due to the ever-increasing effectiveness of enemy infantry firearms. Thus most cavalry transitioned to mounted infantry. As with grenadiers, the ''dragoon'' and ''cavalry'' designations can be retained long after their horses, such as in the Royal Dragoon Guards, Royal Lancers, and King's Royal Hussars.
Similarly, motorised infantry have trucks and other unarmed vehicles for non-combat movement, but are still infantry since they leave their vehicles for any combat. Most modern infantry have vehicle transport, to the point where infantry being motorised is generally assumed, and the few exceptions might be identified as modern ''light infantry''. Mechanised infantry
Mechanized infantry are infantry units equipped with armored personnel carriers (APCs) or infantry fighting vehicles (IFVs) for transport and combat (see also mechanized force).
As defined by the United States Army, mechanized infantry is di ...
go beyond motorised, having transport vehicles with combat abilities, armoured personnel carrier
An armoured personnel carrier (APC) is a broad type of armoured military vehicle designed to transport personnel and equipment in combat zones. Since World War I, APCs have become a very common piece of military equipment around the world.
Acc ...
s (APCs), providing at least some options for combat without leaving their vehicles. In modern infantry, some APCs have evolved to be infantry fighting vehicle
An infantry fighting vehicle (IFV), also known as a mechanized infantry combat vehicle (MICV), is a type of armoured fighting vehicle used to carry infantry into battle and provide direct-fire support. The 1990 Treaty on Conventional Armed Forc ...
s (IFVs), which are transport vehicles with more substantial combat abilities, approaching those of light tank
A light tank is a tank variant initially designed for rapid movements in and out of combat, to outmaneuver heavier tanks. It is smaller in size with thinner armor and a less powerful main gun, tailored for better tactical mobility and ease of ...
s. Some well-equipped mechanised infantry can be designated as ''armoured infantry''. Given that infantry forces typically also have some tanks, and given that most armoured forces have more mechanised infantry units than tank units in their organisation, the distinction between mechanised infantry and armour forces has blurred.
History
The first military forces in history were infantry. Inantiquity
Antiquity or Antiquities may refer to:
Historical objects or periods Artifacts
*Antiquities, objects or artifacts surviving from ancient cultures
Eras
Any period before the European Middle Ages (5th to 15th centuries) but still within the histo ...
, infantry were armed with early melee weapons such as a spear, axe, or sword
A sword is an edged, bladed weapon intended for manual cutting or thrusting. Its blade, longer than a knife or dagger, is attached to a hilt and can be straight or curved. A thrusting sword tends to have a straighter blade with a pointed ti ...
, or an early ranged weapon
A ranged weapon is any weapon that can engage targets beyond hand-to-hand distance, i.e. at distances greater than the physical reach of the user holding the weapon itself. The act of using such a weapon is also known as shooting. It is someti ...
like a javelin
A javelin is a light spear designed primarily to be thrown, historically as a ranged weapon, but today predominantly for sport. The javelin is almost always thrown by hand, unlike the sling, bow, and crossbow, which launch projectiles with th ...
, sling
sling may refer to:
Places
*Sling, Anglesey, Wales
*Sling, Gloucestershire, England, a small village in the Forest of Dean
People with the name
* Otto Šling (1912–1952), repressed Czech communist functionary
Arts, entertainment, and media
* ...
, or bow, with a few infantry men being expected to use both a melee and a ranged weapon. With the development of gunpowder, infantry began converting to primarily firearm
A firearm is any type of gun designed to be readily carried and used by an individual. The term is legally defined further in different countries (see Legal definitions).
The first firearms originated in 10th-century China, when bamboo tubes ...
s. By the time of Napoleonic warfare
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of Fren ...
, infantry, cavalry and artillery formed a basic triad of ground forces, though infantry usually remained the most numerous. With armoured warfare, armoured fighting vehicles have replaced the horses of cavalry, and airpower has added a new dimension to ground combat, but infantry remains pivotal to all modern combined arms operations.

 The first warriors, adopting hunting weapons or improvised melee weapons, before the existence of any organised military, likely started essentially as loose groups without any organisation or formation. But this changed sometime before recorded history; the first
The first warriors, adopting hunting weapons or improvised melee weapons, before the existence of any organised military, likely started essentially as loose groups without any organisation or formation. But this changed sometime before recorded history; the first ancient empires
An empire is a "political unit" made up of several territories and peoples, "usually created by conquest, and divided between a dominant center and subordinate peripheries". The center of the empire (sometimes referred to as the metropole) ex ...
(2500–1500 BC) are shown to have some soldiers with standardised military equipment, and the training and discipline required for battlefield formations and manoeuvres: regular infantry. Though the main force of the army, these forces were usually kept small due to their cost of training and upkeep, and might be supplemented by local short-term mass-conscript forces using the older irregular infantry
Irregular military is any non-standard military component that is distinct from a country's national armed forces. Being defined by exclusion, there is significant variance in what comes under the term. It can refer to the type of military orga ...
weapons and tactics; this remained a common practice almost up to modern times.
Before the adoption of the chariot
A chariot is a type of cart driven by a charioteer, usually using horses to provide rapid motive power. The oldest known chariots have been found in burials of the Sintashta culture in modern-day Chelyabinsk Oblast, Russia, dated to c. 2000&nbs ...
to create the first mobile fighting forces , all armies were pure infantry. Even after, with a few exceptions like the Mongol Empire
The Mongol Empire of the 13th and 14th centuries was the largest contiguous land empire in history. Originating in present-day Mongolia in East Asia, the Mongol Empire at its height stretched from the Sea of Japan to parts of Eastern Europe, ...
, infantry has been the largest component of most armies in history.
In the Western world, from Classical Antiquity through the Middle Ages ( 8th century BC to 15th century AD), infantry are categorised as either heavy infantry or light infantry
Light infantry refers to certain types of lightly equipped infantry throughout history. They have a more mobile or fluid function than other types of infantry, such as heavy infantry or line infantry. Historically, light infantry often fought ...
. Heavy infantry, such as Greek hoplite
Hoplites ( ) ( grc, ὁπλίτης : hoplítēs) were citizen-soldiers of Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek Polis, city-states who were primarily armed with spears and shields. Hoplite soldiers used the phalanx formation to be effective in war with ...
s, Macedonian phalangites, and Roman legionaries, specialised in dense, solid formations driving into the main enemy lines, using weight of numbers to achieve a decisive victory, and were usually equipped with heavier weapons and armour
Armour (British English) or armor (American English; see spelling differences) is a covering used to protect an object, individual, or vehicle from physical injury or damage, especially direct contact weapons or projectiles during combat, or fr ...
to fit their role. Light infantry, such as Greek peltasts, Balearic slingers, and Roman velites, using open formations and greater manoeuvrability, took on most other combat roles: scouting
Scouting, also known as the Scout Movement, is a worldwide youth movement employing the Scout method, a program of informal education with an emphasis on practical outdoor activities, including camping, woodcraft, aquatics, hiking, backpacking ...
, screening the army on the march, skirmishing to delay, disrupt, or weaken the enemy to prepare for the main forces' battlefield attack, protecting them from flanking manoeuvers, and then afterwards either pursuing the fleeing enemy or covering their army's retreat.
After the fall of Rome, the quality of heavy infantry declined, and warfare was dominated by heavy cavalry, such as knights, forming small elite units for decisive shock combat
Shock tactics, shock tactic or shock attack is the name of an offensive maneuver which attempts to place the enemy under psychological pressure by a rapid and fully-committed advance with the aim of causing their combatants to retreat. The accep ...
, supported by peasant infantry militias and assorted light infantry from the lower classes. Towards the end of Middle Ages, this began to change, where more professional and better trained light infantry could be effective against knights, such as the English longbow
The English longbow was a powerful medieval type of bow, about long. While it is debated whether it originated in England or in Wales from the Welsh bow, by the 14th century the longbow was being used by both the English and the Welsh as a ...
men in the Hundred Years' War
The Hundred Years' War (; 1337–1453) was a series of armed conflicts between the kingdoms of Kingdom of England, England and Kingdom of France, France during the Late Middle Ages. It originated from disputed claims to the French Crown, ...
. By the start of the Renaissance, the infantry began to return
Return may refer to:
In business, economics, and finance
* Return on investment (ROI), the financial gain after an expense.
* Rate of return, the financial term for the profit or loss derived from an investment
* Tax return, a blank document o ...
to a larger role, with Swiss pikemen and German Landsknechts filling the role of heavy infantry again, using dense formations of pikes to drive off any cavalry.
Dense formations are vulnerable to ranged weapons. Technological developments allowed the raising of large numbers of light infantry units armed with ranged weapons, without the years of training expected for traditional high-skilled archers and slingers. This started slowly, first with crossbowmen, then hand cannoneers and arquebusiers, each with increasing effectiveness, marking the beginning of early modern warfare
Early modern warfare is the era of warfare following medieval warfare. It is associated with the start of the widespread use of gunpowder and the development of suitable weapons to use the explosive, including artillery and firearms; for this ...
, when firearm
A firearm is any type of gun designed to be readily carried and used by an individual. The term is legally defined further in different countries (see Legal definitions).
The first firearms originated in 10th-century China, when bamboo tubes ...
s rendered the use of heavy infantry obsolete. The introduction of musketeer
A musketeer (french: mousquetaire) was a type of soldier equipped with a musket. Musketeers were an important part of early modern warfare particularly in Europe as they normally comprised the majority of their infantry. The musketeer was a pre ...
s using bayonet
A bayonet (from French ) is a knife, dagger, sword, or spike-shaped weapon designed to fit on the end of the muzzle of a rifle, musket or similar firearm, allowing it to be used as a spear-like weapon.Brayley, Martin, ''Bayonets: An Illustr ...
s in the mid 17th century began replacement of the pike with the infantry square replacing the pike square.
To maximise their firepower, musketeer infantry were trained to fight in wide lines facing the enemy, creating line infantry
Line infantry was the type of infantry that composed the basis of European land armies from the late 17th century to the mid-19th century. Maurice of Nassau and Gustavus Adolphus are generally regarded as its pioneers, while Turenne and Monte ...
. These fulfilled the central battlefield role of earlier heavy infantry, using ranged weapons instead of melee weapons. To support these lines, smaller infantry formations using dispersed skirmish lines were created, called light infantry, fulfilling the same multiple roles as earlier light infantry. Their arms were no lighter than line infantry; they were distinguished by their skirmish formation and flexible tactics.
The modern rifleman infantry became the primary force for taking and holding ground on battlefields as a element of combined arms. As firepower continued to increase, use of infantry lines diminished, until all infantry became light infantry in practice.
Modern classifications of infantry have expanded to reflect modern equipment and tactics, such as motorised infantry, mechanised or armoured infantry, mountain infantry, marine infantry, and airborne infantry.
Equipment
Beyond main arms and armour, a infantryman's "military kit" generally includes combat boots, battledress or combat uniform, camping gear, heavy weather gear, survival gear, secondary weapons andammunition
Ammunition (informally ammo) is the material fired, scattered, dropped, or detonated from any weapon or weapon system. Ammunition is both expendable weapons (e.g., bombs, missiles, grenades, land mines) and the component parts of other weap ...
, weapon service and repair kits, health and hygiene items, mess kit, rations
Rationing is the controlled distribution of scarce resources, goods, services, or an artificial restriction of demand. Rationing controls the size of the ration, which is one's allowed portion of the resources being distributed on a particular ...
, filled water canteen, and all other consumables each infantryman needs for the expected duration of time operating away from their unit's base, plus any special mission-specific equipment. One of the most valuable pieces of gear is the entrenching tool—basically a folding spade—which can be employed not only to dig important defences, but also in a variety of other daily tasks, and even sometimes as a weapon. Infantry typically have shared equipment on top of this, like tents or heavy weapons, where the carrying burden is spread across several infantrymen. In all, this can reach for each soldier on the march. Such heavy infantry burdens have changed little over centuries of warfare; in the late Roman Republic, legionaries were nicknamed '' Marius' mules'' as their main activity seemed to be carrying the weight of their legion around on their backs.Marius' reforms of the Roman army included making each man responsible for carrying his own supplies, weapons and several days' worth of ration. This made the legions less dependent on the baggage train and therefore more mobile.
When combat is expected, infantry typically switch to "packing light", meaning reducing their equipment to weapons, ammo, and bare essentials, and leaving the rest with their transport or baggage train, at camp or rally point, in temporary hidden caches, or even (in emergencies) discarding whatever may slow them down. Additional specialised equipment may be required, depending on the mission or to the particular terrain or environment, including satchel charges, demolition
Demolition (also known as razing, cartage, and wrecking) is the science and engineering in safely and efficiently tearing down of buildings and other artificial structures. Demolition contrasts with deconstruction, which involves taking a ...
tools, mines, barbed wire
A close-up view of a barbed wire
Roll of modern agricultural barbed wire
Barbed wire, also known as barb wire, is a type of steel fencing wire constructed with sharp edges or points arranged at intervals along the strands. Its primary use is t ...
, carried by the infantry or attached specialists.
Historically, infantry have suffered high casualty rates from disease, exposure, exhaustion and privation — often in excess of the casualties suffered from enemy attacks. Better infantry equipment to support their health, energy, and protect from environmental factors greatly reduces these rates of loss, and increase their level of effective action. Health, energy, and morale are greatly influenced by how the soldier is fed, so militaries often standardised field rations, starting from hardtack, to US K-rations, to modern MREs.
Communications gear has become a necessity, as it allows effective command of infantry units over greater distances, and communication with artillery and other support units. Modern infantry can have GPS
The Global Positioning System (GPS), originally Navstar GPS, is a Radionavigation-satellite service, satellite-based radionavigation system owned by the United States government and operated by the United States Space Force. It is one of t ...
, encrypted individual communications equipment, surveillance and night vision equipment, advanced intelligence and other high-tech mission-unique aids.
Armies have sought to improve and standardise infantry gear to reduce fatigue for extended carrying, increase freedom of movement, accessibility, and compatibility with other carried gear, such as the US All-purpose Lightweight Individual Carrying Equipment (ALICE).
Weapons
Infantrymen are defined by their primary arms – the personal weapons and body armour for their own individual use. The available technology, resources, history, and society can produce quite different weapons for each military and era, but common infantry weapons can be distinguished in a few basic categories. * Ranged combat weapons:javelin
A javelin is a light spear designed primarily to be thrown, historically as a ranged weapon, but today predominantly for sport. The javelin is almost always thrown by hand, unlike the sling, bow, and crossbow, which launch projectiles with th ...
s, slings, blowguns, bows, crossbows, hand cannons, arquebuses, muskets, grenades, flamethrower
A flamethrower is a ranged incendiary device designed to project a controllable jet of fire. First deployed by the Byzantine Empire in the 7th century AD, flamethrowers saw use in modern times during World War I, and more widely in World ...
s.
* Close combat weapons: bludgeoning weapons like clubs, flails and maces
Mace may refer to:
Spices
* Mace (spice), a spice derived from the aril of nutmeg
* '' Achillea ageratum'', known as English mace, a flowering plant once used as a herb
Weapons
* Mace (bludgeon), a weapon with a heavy head on a solid shaft used ...
; bladed weapons
An edged weapon, or bladed weapon, is a melee weapon with a cutting edge. Bladed weapons include swords, daggers, knives, and bayonets. Edged weapons are used to cut, hack, or slash; some edged weapons (such as many kinds of swords) may also permit ...
like swords, daggers, and axes; pole weapons like spears, halberds, naginata, and pikes.
* Both ranged and close weapons: the bayonet fixed to a firearm allows infantrymen to use the same weapon for both ranged combat and close combat. This started with muskets and continued with rifle
A rifle is a long-barreled firearm designed for accurate shooting, with a barrel that has a helical pattern of grooves ( rifling) cut into the bore wall. In keeping with their focus on accuracy, rifles are typically designed to be held with ...
s to automatic firearm
An automatic firearm is an auto-loading firearm that continuously chambers and fires rounds when the trigger mechanism is actuated. The action of an automatic firearm is capable of harvesting the excess energy released from a previous discharg ...
s. Use of the bayonet has declined with modern automatic firearms, but still generally kept as a weapon of last resort.
Infantrymen often carry secondary or back-up weapons, sometimes called a sidearm or ancillary weapons. Infantry with ranged or pole weapons often carried a sword or dagger for possible hand-to-hand combat. The ''pilum
The ''pilum'' (; plural ''pila'') was a javelin commonly used by the Roman army in ancient times. It was generally about long overall, consisting of an iron shank about in diameter and long with a pyramidal head, attached to a wooden shaft ...
'' was a javelin the Roman legionaries threw just before drawing their primary weapon, the '' gladius'' (short sword), and closing with the enemy line.
Modern infantrymen now treat the bayonet as a backup weapon, but may also have handgun
A handgun is a short- barrelled gun, typically a firearm, that is designed to be usable with only one hand. It is distinguished from a long gun (i.e. rifle, shotgun or machine gun, etc.), which needs to be held by both hands and also braced ...
s or pistol
A pistol is a handgun, more specifically one with the chamber integral to its gun barrel, though in common usage the two terms are often used interchangeably. The English word was introduced in , when early handguns were produced in Europe, an ...
s. They may also deploy anti-personnel mines, booby traps, incendiary or explosive devices defensively before combat.
Protection
Infantry have employed many different methods of protection from enemy attacks, including various kinds of armour and other gear, and tactical procedures. The most basic is personal armour. This includesshield
A shield is a piece of personal armour held in the hand, which may or may not be strapped to the wrist or forearm. Shields are used to intercept specific attacks, whether from close-ranged weaponry or projectiles such as arrows, by means of a ...
s, helmets and many types of armour – padded linen, leather, lamellar, mail, plate, and kevlar. Initially, armour was used to defend both from ranged and close combat; even a fairly light shield could help defend against most slings and javelins, though high-strength bows and crossbows might penetrate common armour at very close range. Infantry armour had to compromise between protection and coverage, as a full suit of attack-proof armour would be too heavy to wear in combat.
As firearms improved, armour for ranged defence had to be thicker and stronger. With the introduction of the heavy arquebus designed to pierce standard steel armour, it was proven easier to make heavier firearms than heavier armour; armour transitioned to be only for close combat purposes. Pikemen armour tended to be just steel helmets and breastplates, and gunners little or no armour. By the time of the musket, the dominance of firepower shifted militaries away from any close combat, and use of armour decreased, until infantry typically went without any armour.
Helmets were added back during World War I as artillery began to dominate the battlefield, to protect against their fragmentation
Fragmentation or fragmented may refer to:
Computers
* Fragmentation (computing), a phenomenon of computer storage
* File system fragmentation, the tendency of a file system to lay out the contents of files non-continuously
* Fragmented distributi ...
and other blast effects beyond a direct hit. Modern developments in bullet-proof composite materials like kevlar have started a return to body armour for infantry, though the extra weight is a notable burden.
In modern times, infantrymen must also often carry protective measures against chemical and biological
Biology is the scientific study of life. It is a natural science with a broad scope but has several unifying themes that tie it together as a single, coherent field. For instance, all organisms are made up of cells that process hereditary in ...
attack, including military gas mask
A gas mask is a mask used to protect the wearer from inhaling airborne pollutants and toxic gases. The mask forms a sealed cover over the nose and mouth, but may also cover the eyes and other vulnerable soft tissues of the face. Most gas mask ...
s, counter-agents, and protective suits. All of these protective measures add to the weight an infantryman must carry, and may decrease combat efficiency.
Infantry-served weapons
Early crew-served weapons were siege weapons, like the ballista, trebuchet, and battering ram. Modern versions includemachine guns
A machine gun is a fully automatic, rifled autoloading firearm designed for sustained direct fire with rifle cartridges. Other automatic firearms such as automatic shotguns and automatic rifles (including assault rifles and battle rifles) a ...
, anti-tank missiles, and infantry mortars.
Formations
 Beginning with the development the first regular military forces, close-combat regular infantry fought less as unorganised groups of individuals and more in coordinated units, maintaining a defined tactical formation during combat, for increased battlefield effectiveness; such infantry formations and the arms they used developed together, starting with the spear and the shield.
A spear has decent attack abilities with the additional advantage keeping opponents at distance; this advantage can be increased by using longer spears, but this could allow the opponent to side-step the point of the spear and close for
Beginning with the development the first regular military forces, close-combat regular infantry fought less as unorganised groups of individuals and more in coordinated units, maintaining a defined tactical formation during combat, for increased battlefield effectiveness; such infantry formations and the arms they used developed together, starting with the spear and the shield.
A spear has decent attack abilities with the additional advantage keeping opponents at distance; this advantage can be increased by using longer spears, but this could allow the opponent to side-step the point of the spear and close for hand-to-hand combat
Hand-to-hand combat (sometimes abbreviated as HTH or H2H) is a physical confrontation between two or more persons at short range (grappling distance or within the physical reach of a handheld weapon) that does not involve the use of weapons.Huns ...
where the longer spear is near useless. This can be avoided when each spearman stays side by side with the others in close formation, each covering the ones next to him, presenting a solid wall of spears to the enemy that they cannot get around.
Similarly, a shield has decent defence abilities, but is literally hit-or-miss; an attack from an unexpected angle can bypass it completely. Larger shields can cover more, but are also heavier and less manoeuvrable, making unexpected attacks even more of a problem. This can be avoided by having shield-armed soldiers stand close together, side-by-side, each protecting both themselves and their immediate comrades, presenting a solid shield wall
A shield wall ( or in Old English, in Old Norse) is a military formation that was common in ancient and medieval warfare. There were many slight variations of this formation,
but the common factor was soldiers standing shoulder to shoulder ...
to the enemy.
 The opponents for these first formations, the close-combat infantry of more tribal societies, or any military without regular infantry (so called "
The opponents for these first formations, the close-combat infantry of more tribal societies, or any military without regular infantry (so called "barbarian
A barbarian (or savage) is someone who is perceived to be either Civilization, uncivilized or primitive. The designation is usually applied as a generalization based on a popular stereotype; barbarians can be members of any nation judged by som ...
s") used arms that focused on the individual – weapons using personal strength and force, such as larger swinging swords, axes, and clubs. These take more room and individual freedom to swing and wield, necessitating a more loose organisation. While this may allow for a fierce running attack (an initial shock advantage) the tighter formation of the heavy spear and shield infantry gave them a local manpower advantage where several might be able to fight each opponent.
Thus tight formations heightened advantages of heavy arms, and gave greater local numbers in melee. To also increase their staying power, multiple rows of heavy infantrymen were added. This also increased their shock combat effect; individual opponents saw themselves literally lined-up against several heavy infantryman each, with seemingly no chance of defeating all of them. ''Heavy infantry'' developed into huge solid block formations, up to a hundred meters wide and a dozen rows deep.
Maintaining the advantages of heavy infantry meant maintaining formation; this became even more important when two forces with heavy infantry met in battle; the solidity of the formation became the deciding factor. Intense discipline and training became paramount. Empires formed around their military.
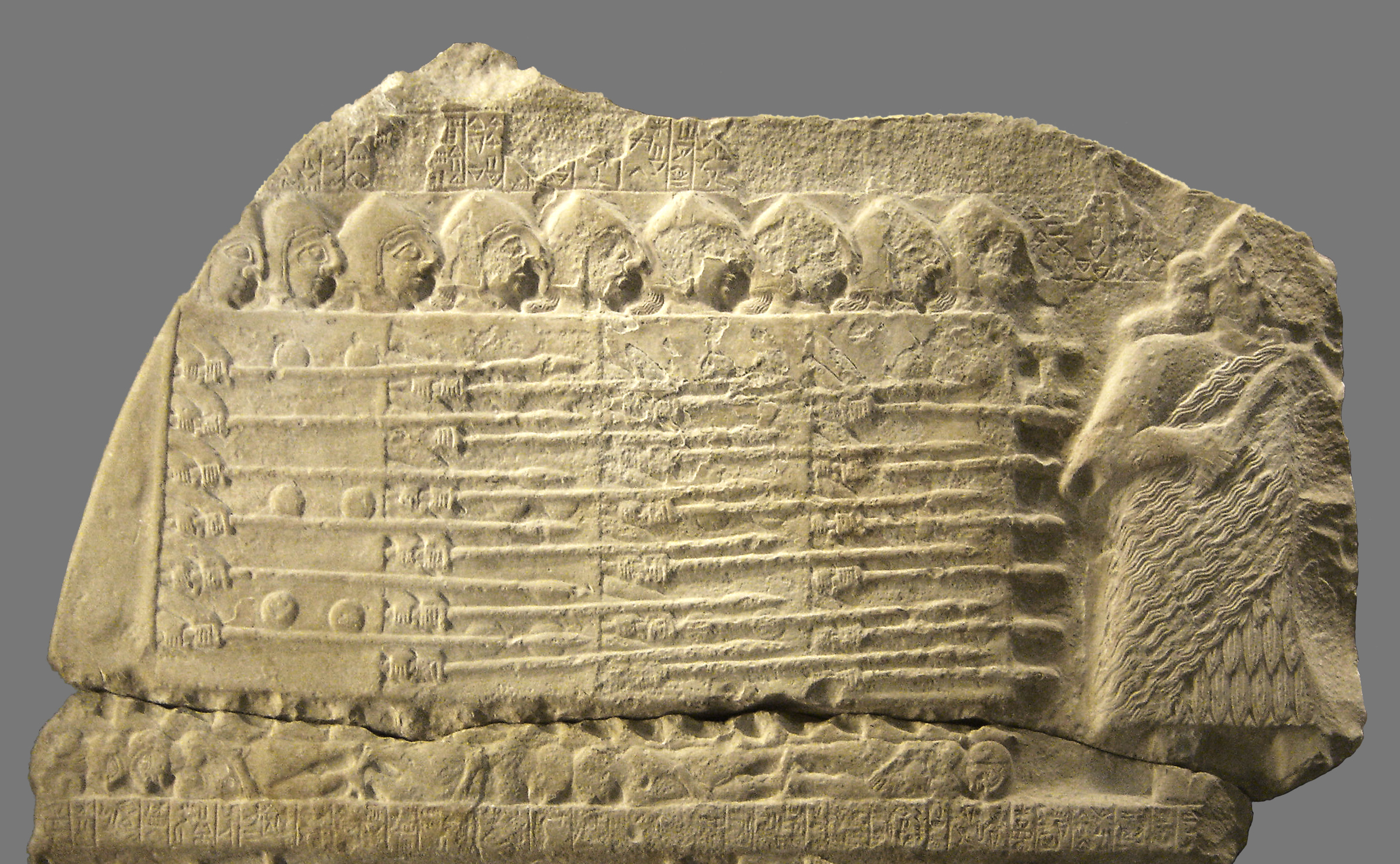
Organization
The organization of military forces into regular military units is first noted in Egyptian records of the Battle of Kadesh (). Soldiers were grouped into units of 50, which were in turn grouped into larger units of 250, then 1,000, and finally into units of up to 5,000 – the largest independent command. Several of these Egyptian "divisions" made up an army, but operated independently, both on the march and tactically, demonstrating sufficient military command and control organisation for basic battlefield manoeuvres. Similar hierarchical organizations have been noted in other ancient armies, typically with approximately 10 to 100 to 1,000 ratios (even where base 10 was not common), similar to modern sections (squads), companies, and regiments.Training
 The training of the infantry has differed drastically over time and from place to place. The cost of maintaining an army in fighting order and the seasonal nature of warfare precluded large permanent armies.
The antiquity saw everything from the well-trained and motivated citizen armies of Greece and Rome, the tribal host assembled from farmers and hunters with only passing acquaintance with warfare and masses of lightly armed and ill-trained militia put up as a last ditch effort. Kushite king Taharqa enjoyed military success in the
The training of the infantry has differed drastically over time and from place to place. The cost of maintaining an army in fighting order and the seasonal nature of warfare precluded large permanent armies.
The antiquity saw everything from the well-trained and motivated citizen armies of Greece and Rome, the tribal host assembled from farmers and hunters with only passing acquaintance with warfare and masses of lightly armed and ill-trained militia put up as a last ditch effort. Kushite king Taharqa enjoyed military success in the Near East
The ''Near East''; he, המזרח הקרוב; arc, ܕܢܚܐ ܩܪܒ; fa, خاور نزدیک, Xāvar-e nazdik; tr, Yakın Doğu is a geographical term which roughly encompasses a transcontinental region in Western Asia, that was once the hist ...
as a result of his efforts to strengthen the army through daily training in long distance running.
In medieval times the foot soldiers varied from peasant levies to semi-permanent companies of mercenaries, foremost among them the Swiss, English, Aragon
Aragon ( , ; Spanish and an, Aragón ; ca, Aragó ) is an autonomous community in Spain, coextensive with the medieval Kingdom of Aragon. In northeastern Spain, the Aragonese autonomous community comprises three provinces (from north to sou ...
ese and German, to men-at-arms who went into battle as well-armoured as knights, the latter of which at times also fought on foot.
The creation of standing armies
A standing army is a permanent, often professional, army. It is composed of full-time soldiers who may be either career soldiers or conscripts. It differs from army reserves, who are enrolled for the long term, but activated only during wars or na ...
—permanently assembled for war or defence—saw increase in training and experience. The increased use of firearms and the need for drill to handle them efficiently.
The introduction of national and mass armies saw an establishment of minimum requirements and the introduction of special troops (first of them the engineers going back to medieval times, but also different kinds of infantry adopted to specific terrain, bicycle, motorcycle, motorised and mechanised troops) culminating with the introduction of highly trained special forces during the first and second World War.
Air force and naval infantry
Naval infantry, commonly known as marines, are primarily a category of infantry that form part of the naval forces of states and perform roles on land and at sea, including amphibious operations, as well as other, naval roles. They also perform other tasks, including land warfare, separate from naval operations. Air force infantry and base defense forces, such as the Royal Air Force Regiment, Royal Australian Air Force Airfield Defence Guards, and Indonesian Air Force Paskhas Corps are used primarily for ground-based defense of air bases and other air force facilities. They also have a number of other, specialist roles. These include, among others, Chemical, Biological, Radiological and Nuclear (CBRN) defence and training other airmen in basic ground defense tactics.See also
*Air assault
Air assault is the movement of ground-based military forces by vertical take-off and landing (VTOL) aircraft—such as the helicopter—to seize and hold key terrain which has not been fully secured, and to directly engage enemy forces behind e ...
* Combined arms
* Foot guards
* Fusilier
Fusilier is a name given to various kinds of soldiers; its meaning depends on the historical context. While fusilier is derived from the 17th-century French language, French word ''fusil'' – meaning a type of flintlock musket – the term has ...
s
* Glider infantry / Paratrooper
* Grenadier
A grenadier ( , ; derived from the word '' grenade'') was originally a specialist soldier who threw hand grenades in battle. The distinct combat function of the grenadier was established in the mid-17th century, when grenadiers were recruited fr ...
s
* Indonesian Army infantry battalions
* Infantry Branch (United States)
The Infantry Branch (also known as the "Queen of Battle") is a branch of the United States Army first established in 1775.
History
Ten companies of riflemen were authorized by a resolution of the Continental Congress on 14 June 1775. However, t ...
* Infantry of the British Army
* Infantry tactics
* Line infantry
Line infantry was the type of infantry that composed the basis of European land armies from the late 17th century to the mid-19th century. Maurice of Nassau and Gustavus Adolphus are generally regarded as its pioneers, while Turenne and Monte ...
* Marines
* United States Army Rangers
* Riflemen
* Royal Canadian Infantry Corps
* School of Infantry
* Special forces
Special forces and special operations forces (SOF) are military units trained to conduct special operations. NATO has defined special operations as "military activities conducted by specially designated, organized, selected, trained and equip ...
* Pathfinder (military)
Notes
References
Citations
Sources
* English, John A., Gudmundsson, Bruce I., ''On Infantry'', (Revised edition), The Military Profession series, Praeger Publishers, London, 1994. . * ''The Times'', Earl Wavell, Thursday, 19 April 194In Praise of Infantry
* Tobin, James, ''Ernie Pyle's War: America's Eyewitness to World War II'', Free Press, 1997. * Mauldin, Bill, Ambrose, Stephen E., ''Up Front'', W. W. Norton, 2000. * Trogdon, Robert W., ''Ernest Hemingway: A Literary Reference'', Da Capo Press, 2002. * ''The New York Times'', Maj Gen C T Shortis, British Director of Infantry, 4 February 1985. * Heinl, Robert Debs, ''Dictionary of Military and Naval Quotations'', Plautus in ''The Braggart Captain'' (3rd century AD), Naval Institute Press, Annapolis, 1978. * Nafziger, George, ''Napoleon's Invasion of Russia'', Presidio Press, 1998. * McManus, John C. ''Grunts: inside the American infantry combat experience, World War II through Iraq'' New York, NY: NAL Caliber. 2010 plu
Webcast Author Lecture
at the Pritzker Military Library on 29 September 2010.
External links
* Historic films and photos showing Infantries in World War I aeuropeanfilmgateway.eu
by Field-Marshal Earl Wavell; First published in "The Times," Thursday, 19 April 1945.
KFOR: KFOR Chronicle.
Web Version of U.S. Army Field Manual 3–21.8
– The Infantry Rifle Platoon and Squad. * — includes several drawings {{Authority control Combat occupations