|
South Brother Island (Andaman And Nicobar Islands)
South Brother Island is an uninhabited island in the Indian Ocean, part of the Andaman Archipelago. It is located in the Duncan Passage, about 9.5 kilometre northeast of Little Andaman Island. It is part of the South Andaman district of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, a Union Territory of India. The island is roughly bean-shaped, about 1800 m by 630 m, with a broad bay on the north side. It is almost flat, thickly wooded, fringed by a narrow beach and surrounded by a reefs. The central part is depressed and becomes a lake in the rainy season. The island hosts a 1.24 km2 wildlife sanctuary, established 1987.Government of India, Directory of Wildlife Protected Areas in India''. Accessed on 2012-07-03. By the end of the 19th century, the island was occasionally visited by the Onge of Little Andaman to catch sea turtles; one explorer reports finding huts "with neat charpoys of bamboos" capable of holding 30 people. The island seemed to be their limit in disputes with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Island
An island (or isle) is an isolated piece of habitat that is surrounded by a dramatically different habitat, such as water. Very small islands such as emergent land features on atolls can be called islets, skerries, cays or keys. An island in a river or a lake island may be called an eyot or ait, and a small island off the coast may be called a holm. Sedimentary islands in the Ganges delta are called chars. A grouping of geographically or geologically related islands, such as the Philippines, is referred to as an archipelago. There are two main types of islands in the sea: continental and oceanic. There are also artificial islands, which are man-made. Etymology The word ''island'' derives from Middle English ''iland'', from Old English ''igland'' (from ''ig'' or ''ieg'', similarly meaning 'island' when used independently, and -land carrying its contemporary meaning; cf. Dutch ''eiland'' ("island"), German ''Eiland'' ("small island")). However, the spelling of the word ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wildlife Sanctuary
A nature reserve (also known as a wildlife refuge, wildlife sanctuary, biosphere reserve or bioreserve, natural or nature preserve, or nature conservation area) is a protected area of importance for flora, fauna, or features of geological or other special interest, which is reserved and managed for purposes of conservation and to provide special opportunities for study or research. They may be designated by government institutions in some countries, or by private landowners, such as charities and research institutions. Nature reserves fall into different IUCN categories depending on the level of protection afforded by local laws. Normally it is more strictly protected than a nature park. Various jurisdictions may use other terminology, such as ecological protection area or private protected area in legislation and in official titles of the reserves. History Cultural practices that roughly equate to the establishment and maintenance of reserved areas for animals date back t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Brother Island, India
North Brother Island is an uninhabited island in the Indian Ocean, part of the Andaman Archipelago. It is located in the Duncan Passage, about 19 kilometre northeast of Little Andaman Island. It is part of the South Andaman district of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, a Union Territory of India. The island is nearly round, about 1.1 km across. It is almost flat, thickly wooded except in its central part, fringed by a narrow beach and surrounded by a reef all around. The central part is depressed and becomes a lake in the rainy season. A lighthouse tower was erected during 1992-93 and commissioned on 17 April 1993.Indian Directorate General of Lighthouses and Lightships, Welcome to NORTH BROTHER ISLAND LIGHT HOUSE'. Accessed on 2012-07-03. The island hosts a 0.75 km2 wildlife sanctuary, established 1987.Government of India, Directory of Wildlife Protected Areas in India''. Accessed on 2012-07-03. By the end of the 19th century, the island was occasionally visited by the O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Andaman Island
Great Andaman is the main archipelago of the Andaman Islands of India. It comprises seven major islands. From north to south, these are North Andaman, Interview Island, Middle Andaman, Long Island, Baratang Island, South Andaman, and Rutland Island. Geography South, Middle and North islands are the largest of the entire island group. The islands' capital, Port Blair, is located on South Andaman. Great Andaman group is often considered the counterpart to Little Andaman Group, another group of islands in the Andaman's. The Andaman islands consist of five groups: * Great Andaman * Little Andaman * Ritchie's Archipelago * East Volcano Islands Narrow creeks split Great Andaman into North Andaman, Middle Andaman, South Andaman and the other major islands. All of these islands are in the form of peaks of a submerged mountain chain. Each island has a central highland surrounded by bordering flat lands sloping in all directions and finally merged into coastal tracts. Demographics A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Andamanese People
The Great Andamanese are an indigenous people of the Great Andaman archipelago in the Andaman Islands. Historically, the Great Andamanese lived throughout the archipelago, and were divided into ten major tribes. Their distinct but closely related languages comprised the Great Andamanese languages, one of the two identified Andamanese language families. The Great Andamanese were clearly related to the other Andamanese peoples, but were well separated from them by culture and geography. The languages of those other four groups were only distantly related to those of the Great Andamanese and mutually unintelligible; they are classified in a separate family, the Ongan languages. They were once the most numerous of the five major groups in the Andaman Islands with an estimated population between 2,000 and 6,600, the Great Andamanese were heavily decimated by diseases, alcohol, colonial warfare and loss of hunting territory. Only 52 remained as of February 2010; by August 2020 there ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bamboo
Bamboos are a diverse group of evergreen perennial flowering plants making up the subfamily Bambusoideae of the grass family Poaceae. Giant bamboos are the largest members of the grass family. The origin of the word "bamboo" is uncertain, but it probably comes from the Dutch or Portuguese language, which originally borrowed it from Malay or Kannada. In bamboo, as in other grasses, the internodal regions of the stem are usually hollow and the vascular bundles in the cross-section are scattered throughout the stem instead of in a cylindrical arrangement. The dicotyledonous woody xylem is also absent. The absence of secondary growth wood causes the stems of monocots, including the palms and large bamboos, to be columnar rather than tapering. Bamboos include some of the fastest-growing plants in the world, due to a unique rhizome-dependent system. Certain species of bamboo can grow within a 24-hour period, at a rate of almost an hour (equivalent to 1 mm every 90 seco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charpoy
Charpai, Charpaya, Charpoy, Khat or Manji (Tamil :கட்டில் Hindi : चारपाई, Bengali: চারপায়া, Urdu: چارپائی, Saraiki, Punjabi; ''char'' "four" + ''paya'' "footed") is a traditional woven bed used across South Asia. Regional variations are found in Afghanistan and Pakistan, North and Central India, Bihar and Myanmar. It is also known as khaat, khatia, or manji, and as manjaa in Punjab. The charpai is a simple design that is easy to construct. It was traditionally made out of a wooden frame and natural-fiber ropes, but modern charpais may have metal frames and plastic tapes. The frame is four strong vertical posts connected by four horizontal members; the design makes the construction self-leveling. Webbing can be made out of cotton, date leaves, and other natural fibers. There are many interpretations of the traditional design, and over the years craftspeople have innovated with the weave patterns and materials used. The weaving i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
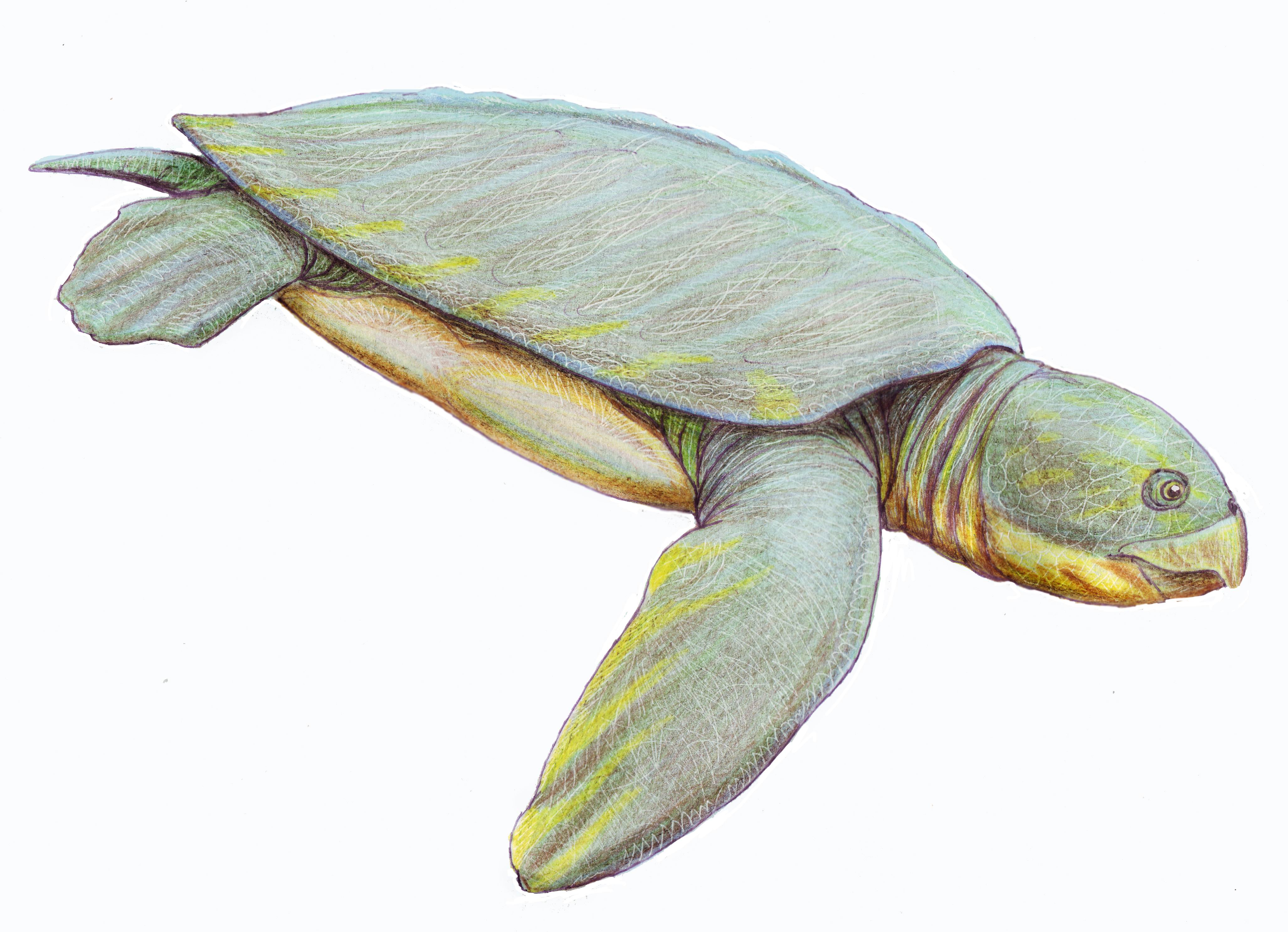
Sea Turtle
Sea turtles (superfamily Chelonioidea), sometimes called marine turtles, are reptiles of the order Testudines and of the suborder Cryptodira. The seven existing species of sea turtles are the flatback, green, hawksbill, leatherback, loggerhead, Kemp's ridley, and olive ridley sea turtles. All six of the sea turtle species present in US waters (all of those listed above except the flatback) are listed as endangered and/or threatened under the Endangered Species Act. The seventh sea turtle species is the flatback, which exists in the waters of Australia, Papua New Guinea and Indonesia. Sea turtles can be separated into the categories of hard-shelled (cheloniid) and leathery-shelled ( dermochelyid).Wyneken, J. 2001. The Anatomy of Sea Turtles. U.S Department of Commerce NOAA Technical Memorandum NMFS-SEFSC-470, 1-172 pp. There is only one dermochelyid species which is the leatherback sea turtle. Description For each of the seven types of sea turtles, females and males are the sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Onge People
The Onge (also Önge, Ongee, and Öñge) are an Andamanese ethnic group, indigenous to the Andaman Islands in Southeast Asia at the Bay of Bengal, currently administered by India. They are traditionally hunter-gatherers and fishers, but also practice plant cultivation. They are designated as a Scheduled Tribe of India. History In the 18th century the Onge, or Madhumitha, were distributed across Little Andaman Island and the nearby islands, with some territory and camps established on Rutland Island and the southern tip of South Andaman Island. After they encountered British colonial officers, friendly relations were established with the British Empire in the 1800s through Lieutenant Archibald Blair. British naval officer M. V. Portman described them as the "mildest, most timid, and inoffensive" group of Andamanese people he had encountered. By the end of the 19th century they sometimes visited the South and North Brother Islands to catch sea turtles; at the time, those ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Square Kilometre
Square kilometre ( International spelling as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures) or square kilometer (American spelling), symbol km2, is a multiple of the square metre, the SI unit of area or surface area. 1 km2 is equal to: * 1,000,000 square metres (m2) * 100 hectares (ha) It is also approximately equal to: * 0.3861 square miles * 247.1 acres Conversely: *1 m2 = 0.000001 (10−6) km2 *1 hectare = 0.01 (10−2) km2 *1 square mile = *1 acre = about The symbol "km2" means (km)2, square kilometre or kilometre squared and not k(m2), kilo–square metre. For example, 3 km2 is equal to = 3,000,000 m2, not 3,000 m2. Examples of areas of 1 square kilometre Topographical Map grids Topographical map grids are worked out in metres, with the grid lines being 1,000 metres apart. * 1:100,000 maps are divided into squares representing 1 km2, each square on the map being one square centimetre in area and representing 1 km2 on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or ~19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by the Southern Ocean or Antarctica, depending on the definition in use. Along its core, the Indian Ocean has some large marginal or regional seas such as the Arabian Sea, Laccadive Sea, Bay of Bengal, and Andaman Sea. Etymology The Indian Ocean has been known by its present name since at least 1515 when the Latin form ''Oceanus Orientalis Indicus'' ("Indian Eastern Ocean") is attested, named after Indian subcontinent, India, which projects into it. It was earlier known as the ''Eastern Ocean'', a term that was still in use during the mid-18th century (see map), as opposed to the ''Western Ocean'' (Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic) before the Pacific Ocean, Pacific was surmised. Conversely, Ming treasure voyages, Chinese explorers in the Indian Oce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metre
The metre (British spelling) or meter (American spelling; see spelling differences) (from the French unit , from the Greek noun , "measure"), symbol m, is the primary unit of length in the International System of Units (SI), though its prefixed forms are also used relatively frequently. The metre was originally defined in 1793 as one ten-millionth of the distance from the equator to the North Pole along a great circle, so the Earth's circumference is approximately km. In 1799, the metre was redefined in terms of a prototype metre bar (the actual bar used was changed in 1889). In 1960, the metre was redefined in terms of a certain number of wavelengths of a certain emission line of krypton-86. The current definition was adopted in 1983 and modified slightly in 2002 to clarify that the metre is a measure of proper length. From 1983 until 2019, the metre was formally defined as the length of the path travelled by light in a vacuum in of a second. After the 2019 redefi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |