|
Source-code
In computing, source code, or simply code, is any collection of code, with or without comments, written using a human-readable programming language, usually as plain text. The source code of a program is specially designed to facilitate the work of computer programmers, who specify the actions to be performed by a computer mostly by writing source code. The source code is often transformed by an assembler or compiler into binary machine code that can be executed by the computer. The machine code is then available for execution at a later time. Most application software is distributed in a form that includes only executable files. If the source code were included it would be useful to a user, programmer or a system administrator, any of whom might wish to study or modify the program. Alternatively, depending on the technology being used, source code may be interpreted and executed directly. Definitions Richard Stallman's definition, formulated in his 1989 sem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hello World C
''Hello'' is a salutation or greeting habits, greeting in the English language. It is first attested in writing from 1826. Early uses ''Hello'', with that spelling, was used in publications in the U.S. as early as the 18 October 1826 edition of the ''Norwich Courier'' of Norwich, Connecticut. Another early use was an 1833 American book called ''The Sketches and Eccentricities of Col. David Crockett, of West Tennessee'', which was reprinted that same year in ''Literary Gazette, The London Literary Gazette''. The word was extensively used in literature by the 1860s. Etymology According to the ''Oxford English Dictionary'', ''hello'' is an alteration of ''hallo'', ''hollo'', which came from Old High German "''halâ'', ''holâ'', emphatic imperative of ''halôn'', ''holôn'' to fetch, used especially in hailing a ferryman". It also connects the development of ''hello'' to the influence of an earlier form, ''holla'', whose origin is in the French ''holà'' (roughly, 'whoa there!', f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Stallman
Richard Matthew Stallman (; born March 16, 1953), also known by his initials, rms, is an American free software movement activist and programmer. He campaigns for software to be distributed in such a manner that its users have the freedom to use, study, distribute, and modify that software. Software that ensures these freedoms is termed free software. Stallman launched the GNU Project, founded the Free Software Foundation (FSF) in October 1985, developed the GNU Compiler Collection and GNU Emacs, and wrote the GNU General Public License. Stallman launched the GNU's Not Unix, GNU Project in September 1983 to write a Unix-like computer operating system composed entirely of free software. With this, he also launched the free software movement. He has been the GNU project's lead architect and organizer, and developed a number of pieces of widely used GNU software including, among others, the GNU Compiler Collection, GNU Debugger, and Emacs, GNU Emacs text editor. Stallman pioneere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Randy Thompson
Randy Thompson is a Virginia based americana/ country music singer and songwriter. He is a resident of the Clifton, Virginia area. He has toured in France, Norway, Austria, United Kingdom, Germany, Switzerland and the United States. As of 2018 he has released 6 albums; 4 have reached the top 40 on US charts. *In The Rain – 1988 *Wearin Blue – 1998 (Jackpot Records 1001) *That's Not Me – 2004 (Jackpot Records 1105) *Further On – 2008 (Jackpot Records) *Collected – 2012 (Jackpot Records) *War, Peace, Love, Fear – 2017 (Jackpot Records) Chart success *#6 Freeform Americana Roots (FAR Chart #105, April 2008) *#28 Americana Music Chart (The Nielson Co., April 2008) *#12 Roots Music Report (April 2008) *#26 XM Cross Country Chart (March 30, 2008) *#16 Euro Americama Chart (June 2008) *#5 European Hotdisc Chart (For Single Ol' 97, March 2008) *#3 European Hotdisc Chart (For Single Further On, December 2008) *#1 European Hotdisc Independent Chart (For Single Further On, D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philip Zimmermann
Philip R. Zimmermann (born 1954) is an American computer scientist and cryptographer. He is the creator of Pretty Good Privacy (PGP), the most widely used email encryption software in the world. He is also known for his work in VoIP encryption protocols, notably ZRTP and Zfone. Zimmermann is co-founder and Chief Scientist of the global encrypted communications firm Silent Circle. Background He was born in Camden, New Jersey. Zimmermann received a B.S. degree in computer science from Florida Atlantic University in Boca Raton, Florida in 1978. In the 1980s, Zimmermann worked in Boulder, Colorado as a software engineer on the Nuclear Weapons Freeze Campaign as a military policy analyst. PGP In 1991, he wrote the popular Pretty Good Privacy (PGP) program, and made it available (together with its source code) through public FTP for download, the first widely available program implementing public-key cryptography. Shortly thereafter, it became available overseas via the Internet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
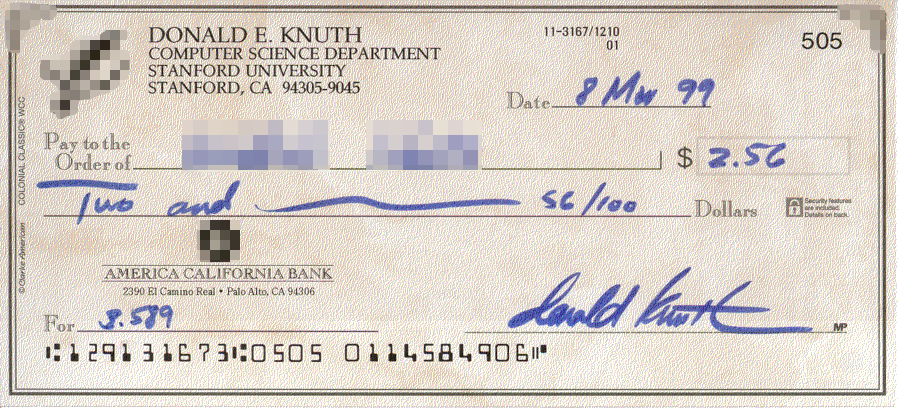
Donald Knuth
Donald Ervin Knuth ( ; born January 10, 1938) is an American computer scientist, mathematician, and professor emeritus at Stanford University. He is the 1974 recipient of the ACM Turing Award, informally considered the Nobel Prize of computer science. Knuth has been called the "father of the analysis of algorithms". He is the author of the multi-volume work '' The Art of Computer Programming'' and contributed to the development of the rigorous analysis of the computational complexity of algorithms and systematized formal mathematical techniques for it. In the process, he also popularized the asymptotic notation. In addition to fundamental contributions in several branches of theoretical computer science, Knuth is the creator of the TeX computer typesetting system, the related METAFONT font definition language and rendering system, and the Computer Modern family of typefaces. As a writer and scholar, Knuth created the WEB and CWEB computer programming systems designed to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type-in Program
A type-in program or type-in listing was computer source code printed in a home computer magazine or book. It was meant to be entered via the Keyboard (computing), keyboard by the reader and then saved to Compact Cassette (data), cassette tape or floppy disk. The result was a usable game, utility, or application program. Type-in programs were common in the home computer era from the late 1970s through the early 1990s, when the Random-access memory, RAM of 8-bit computing, 8-bit systems was measured in kilobytes and most computer owners did not have access to networks such as bulletin board systems. Magazines such as ''Softalk'', ''Compute!'', ''ANALOG Computing'', and ''Ahoy!'' dedicated much of each issue to type-in programs. The magazines could contain multiple games or other programs for a fraction of the cost of purchasing commercial software on removable media, but the user had to spend up to several hours typing each one in. Most listings were either in a system-specific B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computerworld
''Computerworld'' (abbreviated as CW) is an ongoing decades old professional publication which in 2014 "went digital." Its audience is information technology (IT) and business technology professionals, and is available via a publication website and as a digital magazine. As a printed weekly during the 1970s and into the 1980s, ''Computerworld'' was the leading trade publication in the data processing industry. Indeed, based on circulation and revenue it was one of the most successful trade publications in any industry. Later in the 1980s it began to lose its dominant position. It is published in many countries around the world under the same or similar names. Each country's version of ''Computerworld'' includes original content and is managed independently. The parent company of Computerworld US is IDG Communications. History The first issue was published in 1967. Going international The company IDG offers the brand "Computerworld" in 47 countries worldwide, the name and f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First-generation Programming Language
A first-generation programming language (1GL) is a machine-level programming language. A first generation (programming) language (1GL) is a grouping of programming languages that are machine level languages used to program first-generation computers. Originally, no translator was used to compile or assemble the first-generation language. The first-generation programming instructions were entered through the front panel switches of the computer system. The instructions in 1GL are made of binary numbers, represented by 1s and 0s. This makes the language suitable for the understanding of the machine but far more difficult to interpret and learn by the human programmer. The main advantage of programming in 1GL is that the code can run very fast and very efficiently, precisely because the instructions are executed directly by the central processing unit (CPU). One of the main disadvantages of programming in a low level language is that when an error occurs, the code is not as ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Front Panel
A front panel was used on early electronic computers to display and allow the alteration of the state of the machine's internal registers and memory. The front panel usually consisted of arrays of indicator lamps, digit and symbol displays, toggle switches, dials, and push buttons mounted on a sheet metal face plate. In early machines, CRTs might also be present (as an oscilloscope, or, for example, to mirror the contents of Williams–Kilburn tube memory). Prior to the development of CRT system consoles, many computers such as the IBM 1620 had console typewriters. Usually the contents of one or more hardware registers would be represented by a row of lights, allowing the contents to be read directly when the machine was stopped. The switches allowed direct entry of data and address values into registers or memory. Details On some machines, certain lights and switches were reserved for use under program control. These were often referred to as ''sense indicators'', '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stored-program Computer
A stored-program computer is a computer that stores program instructions in electronically or optically accessible memory. This contrasts with systems that stored the program instructions with plugboards or similar mechanisms. The definition is often extended with the requirement that the treatment of programs and data in memory be interchangeable or uniform. Description In principle, stored-program computers have been designed with various architectural characteristics. A computer with a von Neumann architecture stores program data and instruction data in the same memory, while a computer with a Harvard architecture has separate memories for storing program and data. However, the term ''stored-program computer'' is sometimes used as a synonym for the von Neumann architecture. Jack Copeland considers that it is "historically inappropriate, to refer to electronic stored-program digital computers as 'von Neumann machines'". Hennessy and Patterson wrote that the early Harva ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Moldova to the east, and the Black Sea to the southeast. It has a predominantly temperate- continental climate, and an area of , with a population of around 19 million. Romania is the twelfth-largest country in Europe and the sixth-most populous member state of the European Union. Its capital and largest city is Bucharest, followed by Iași, Cluj-Napoca, Timișoara, Constanța, Craiova, Brașov, and Galați. The Danube, Europe's second-longest river, rises in Germany's Black Forest and flows in a southeasterly direction for , before emptying into Romania's Danube Delta. The Carpathian Mountains, which cross Romania from the north to the southwest, include Moldoveanu Peak, at an altitude of . Settlement in what is now Romania began in the Lower Pale ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timișoara
), City of Roses ( ro, Orașul florilor), City of Parks ( ro, Orașul parcurilor) , image_map = Timisoara jud Timis.svg , map_caption = Location in Timiș County , pushpin_map = Romania#Europe , pushpin_relief = 1 , pushpin_label_position = bottom , coordinates = , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = , subdivision_type1 = County , subdivision_name1 = Timiș , subdivision_type2 = Status , subdivision_name2 = County seat A county seat is an administrative center, seat of government, or capital city of a county or civil parish. The term is in use in Canada, China, Hungary, Romania, Taiwan, and the United States. The equivalent term shire town is used in the US ... , established_title = First official record , established_date = 1212 (as ''castrum regium Themes'') , leader_party = USR , leader_title = ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |