|
Type-in Program
A type-in program or type-in listing was computer source code printed in a home computer magazine or book. It was meant to be entered via the keyboard by the reader and then saved to cassette tape or floppy disk. The result was a usable game, utility, or application program. Type-in programs were common in the home computer era from the late 1970s through the early 1990s, when the RAM of 8-bit systems was measured in kilobytes and most computer owners did not have access to networks such as bulletin board systems. Magazines such as ''Softalk'', ''Compute!'', '' ANALOG Computing'', and ''Ahoy!'' dedicated much of each issue to type-in programs. The magazines could contain multiple games or other programs for a fraction of the cost of purchasing commercial software on removable media, but the user had to spend up to several hours typing each one in. Most listings were either in a system-specific BASIC dialect or machine code. Machine code programs were long lists of decimal or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Machine Code
In computer programming, machine code is computer code consisting of machine language instructions, which are used to control a computer's central processing unit (CPU). For conventional binary computers, machine code is the binaryOn nonbinary machines it is, e.g., a decimal representation. representation of a computer program that is actually read and interpreted by the computer. A program in machine code consists of a sequence of machine instructions (possibly interspersed with data). Each machine code instruction causes the CPU to perform a specific task. Examples of such tasks include: # Load a word from memory to a CPU register # Execute an arithmetic logic unit (ALU) operation on one or more registers or memory locations # Jump or skip to an instruction that is not the next one In general, each architecture family (e.g., x86, ARM) has its own instruction set architecture (ISA), and hence its own specific machine code language. There are exceptions, such as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BASIC
Basic or BASIC may refer to: Science and technology * BASIC, a computer programming language * Basic (chemistry), having the properties of a base * Basic access authentication, in HTTP Entertainment * Basic (film), ''Basic'' (film), a 2003 film * Basic, one of the Galactic Basic, languages in ''Star Wars'' Music * Basic (Glen Campbell album), ''Basic'' (Glen Campbell album), 1978 * Basic (Robert Quine and Fred Maher album), ''Basic'' (Robert Quine and Fred Maher album), 1984 * B.A.S.I.C. (Alpinestars album), ''B.A.S.I.C.'' (Alpinestars album), 2000 * Basic (Brown Eyed Girls album), ''Basic'' (Brown Eyed Girls album), 2015 * B.A.S.I.C. (The Basics album), ''B.A.S.I.C.'' (The Basics album), 2019 Places * Basic, Mississippi, a community in the US * BASIC countries, Brazil, South Africa, India and China in climate change negotiations Organizations * BASIC Bank Limited, government owned bank in Bangladesh * Basic Books, an American publisher Other uses * Basic (cigarette), a brand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opcode
In computing, an opcode (abbreviated from operation code) is an enumerated value that specifies the operation to be performed. Opcodes are employed in hardware devices such as arithmetic logic units (ALUs), central processing units (CPUs), and software instruction sets. In ALUs, the opcode is directly applied to circuitry via an input signal bus. In contrast, in CPUs, the opcode is the portion of a machine language instruction that specifies the operation to be performed. CPUs Opcodes are found in the machine language instructions of CPUs as well as in some abstract computing machines. In CPUs, an opcode may be referred to as an instruction machine code, instruction code, instruction syllable, instruction parcel, or opstring. For any particular processor (which may be a general CPU or a more specialized processing unit), the opcodes are defined by the processor's instruction set architecture (ISA). They can be described using an opcode table. The types of operations may in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BASIC Loader
Basic or BASIC may refer to: Science and technology * BASIC, a computer programming language * Basic (chemistry), having the properties of a base * Basic access authentication, in HTTP Entertainment * ''Basic'' (film), a 2003 film * Basic, one of the languages in ''Star Wars'' Music * ''Basic'' (Glen Campbell album), 1978 * ''Basic'' (Robert Quine and Fred Maher album), 1984 * ''B.A.S.I.C.'' (Alpinestars album), 2000 * ''Basic'' (Brown Eyed Girls album), 2015 * ''B.A.S.I.C.'' (The Basics album), 2019 Places * Basic, Mississippi, a community in the US * BASIC countries, Brazil, South Africa, India and China in climate change negotiations Organizations * BASIC Bank Limited, government owned bank in Bangladesh * Basic Books, an American publisher Other uses * Basic (cigarette), a brand of cigarettes manufactured by the Altria Group (Philip Morris Company) * Basic (dance move), the dance move that defines the character of a particular dance * Basic (slang), a pejorativ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
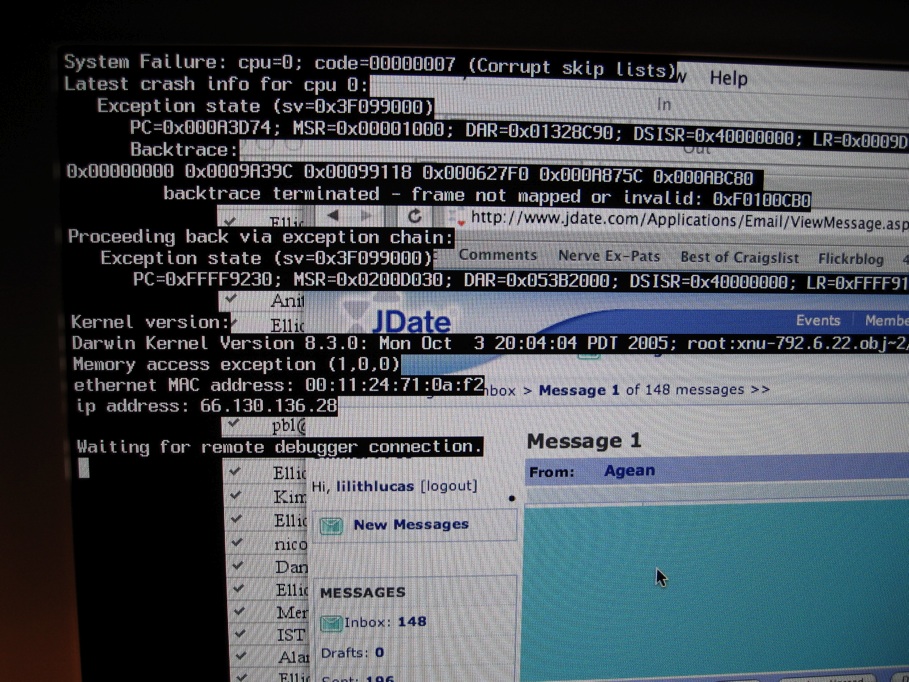
Crash (computing)
In computing, a crash, or system crash, occurs when a computer program such as a software application or an operating system stops functioning properly and exits. On some operating systems or individual applications, a crash reporting service will report the crash and any details relating to it (or give the user the option to do so), usually to the developer(s) of the application. If the program is a critical part of the operating system, the entire system may crash or hang, often resulting in a kernel panic or fatal system error. Most crashes are the result of a software bug. Typical causes include accessing invalid memory addresses, incorrect address values in the program counter, buffer overflow, overwriting a portion of the affected program code due to an earlier bug, executing invalid machine instructions (an illegal or unauthorized opcode), or triggering an unhandled exception. The original software bug that started this chain of events is typically considere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Direct Mode
In computing, direct or immediate mode in an interactive programming system is the immediate execution of commands, statements, or expressions. In many interactive systems, most of these can both be included in programs or executed directly in a read–eval–print loop (REPL). Most interactive systems also offer the possibility of defining programs in the REPL, either with explicit declarations, such as Python's def, or by labelling them with line numbers. Programs can then be run by calling a named or numbered procedure or by running a main program. Many programming systems, from Lisp and JOSS to Python and Perl have interactive REPLs which also allow defining programs. Most integrated development environments offer a direct mode where, during debugging In engineering, debugging is the process of finding the Root cause analysis, root cause, workarounds, and possible fixes for bug (engineering), bugs. For software, debugging tactics can involve interactive debugging, c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Booting
In computing, booting is the process of starting a computer as initiated via Computer hardware, hardware such as a physical button on the computer or by a software command. After it is switched on, a computer's central processing unit (CPU) has no software in its main memory, so some process must load software into memory before it can be executed. This may be done by hardware or firmware in the CPU, or by a separate processor in the computer system. On some systems a power-on reset (POR) does not initiate booting and the operator must initiate booting after POR completes. IBM uses the term Initial Program Load (IPL) on someE.g., System/360 through IBM Z, RS/6000 and System/38 through IBM Power Systems product lines. Restarting a computer also is called Reboot (computing), ''rebooting'', which can be "hard", e.g. after electrical power to the CPU is switched from off to on, or "soft", where the power is not cut. On some systems, a soft boot may optionally clear RAM to zero. Bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CD-ROM
A CD-ROM (, compact disc read-only memory) is a type of read-only memory consisting of a pre-pressed optical compact disc that contains computer data storage, data computers can read, but not write or erase. Some CDs, called enhanced CDs, hold both computer data and audio with the latter capable of being played on a CD player, while data (such as software or digital video) is only usable on a computer (such as ISO 9660 format PC CD-ROMs). During the 1990s and early 2000s, CD-ROMs were popularly used to distribute software and data for computers and fifth generation video game consoles. DVDs as well as downloading started to replace CD-ROMs in these roles starting in the early 2000s, and the use of CD-ROMs for commercial software is now rare. History The earliest theoretical work on optical disc storage was done by independent researchers in the United States including David Paul Gregg (1958) and James Russell (inventor), James Russel (1965–1975). In particular, Gregg's paten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
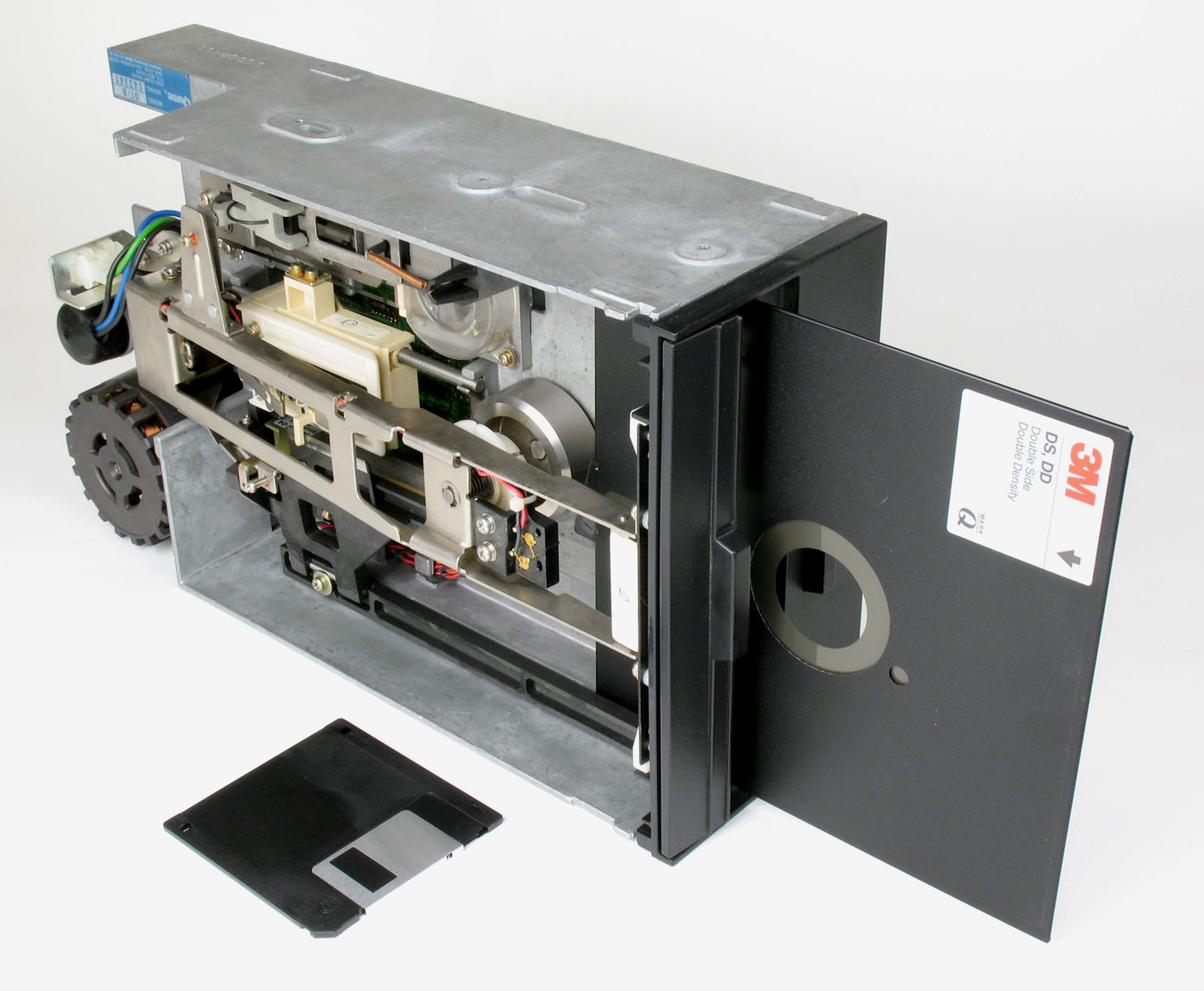
Floppy Disk
A floppy disk or floppy diskette (casually referred to as a floppy, a diskette, or a disk) is a type of disk storage composed of a thin and flexible disk of a magnetic storage medium in a square or nearly square plastic enclosure lined with a fabric that removes dust particles from the spinning disk. The three most popular (and commercially available) floppy disks are the 8-inch, 5¼-inch, and 3½-inch floppy disks. Floppy disks store digital data which can be read and written when the disk is inserted into a floppy disk drive (FDD) connected to or inside a computer or other device. The first floppy disks, invented and made by IBM in 1971, had a disk diameter of . Subsequently, the 5¼-inch (133.35 mm) and then the 3½-inch (88.9 mm) became a ubiquitous form of data storage and transfer into the first years of the 21st century. 3½-inch floppy disks can still be used with an external USB floppy disk drive. USB drives for 5¼-inch, 8-inch, and other-size floppy disks are rare ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Covermount
Covermount (sometimes written cover mount) is the name given to storage media (containing software and or audiovisual media) or other products (ranging from toys to flip-flops) packaged as part of a magazine or newspaper. The name comes from the method of packaging; the media or product is placed in a transparent plastic sleeve and mounted on the cover of the magazine with adhesive tape or glue. History Audio recordings were distributed in the UK by the use of covermounts in the 1960s by the fortnightly satirical magazine '' Private Eye'' though the term "covermount" was not in usage at that time. The Private Eye recordings were pressed onto 7" floppy vinyl (known as "flexi-discs" and "flimsies") and mounted on to the front of the magazine. The weekly pop music paper ''NME'' issued audio recordings of rock music on similar 7" flexi-discs as covermounts in the 1970s. The covermount practice continued with computer magazines in the early era of home computers. In the United King ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |