|
Sound Of Raasay
The Sound of Raasay ( gd, Linne Ratharsair) is the sound between the islands of Raasay and Skye. See also * Inner Sound, Scotland * Isle of Skye * Loch Kishorn * Mealt Waterfall * Quiraing References External links and references One link, mentions Raasay's depth Landforms of the Inner Hebrides Raasay Raasay (; gd, Ratharsair) or the Isle of Raasay is an island between the Isle of Skye and the mainland of Scotland. It is separated from Skye by the Sound of Raasay and from Applecross by the Inner Sound. It is famous for being the birt ... Landforms of Highland (council area) {{Highland-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inner Sound, Scotland
The Inner Sound ( gd, An Lighe Rathairseach) is a strait separating the Inner Hebridean islands of Skye, Raasay and South Rona from the Applecross peninsula on the Scottish mainland. The Inner Sound is the location of BUTEC, a Royal Navy submarine sensor and emissions range. Deepest Point in the UK The Inner Sound includes the deepest section of the UK's territorial waters, with a maximum depth of . An area, over long and up to wide, exists below a depth of , with a relatively flat bottom. There is another cleft deep, separated from the deeper bowl by an area of shallower water. A dive to examine the deeper trench found the bottom to be made up of bioturbated mud, with a steep slope towards the west of up to 60°. Islands in the Strait * South Rona * Raasay * Scalpay * Pabay * Longay * Crowlin Wildlife In 2020, over a hundred eggs belonging to the critically endangered flapper skate were discovered in the strait. This led to calls for the government to prote ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Applecross
Applecross ( gd, A' Chomraich) is a peninsula north-west of Kyle of Lochalsh in the council area of Highland, Scotland. The name Applecross is at least 1,300 years old and is ''not'' used locally to refer to the 19th century village (which is correctly called 'Shore Street', or simply 'The Street') with the Applecross Inn, lying on the Applecross Bay, facing the Inner Sound, on the opposite side of which lies the Inner Hebridean island of Raasay. The monastery of Applecross was established by St Maelrubha, in the 7th century. A sculptured stone is the only remaining relic of Maelrubha, who built a chapel there. The Applecross peninsula ( gd, A' Chomraich, 'The Sanctuary') is a peninsula in Wester Ross, Highland, on the north west coast of Scotland. Geography This row of houses which is often referred to as 'Applecross', and is marked as Applecross on some maps, is actually called 'Shore Street' and is referred to locally just as 'The Street'. The name Applecross applies to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
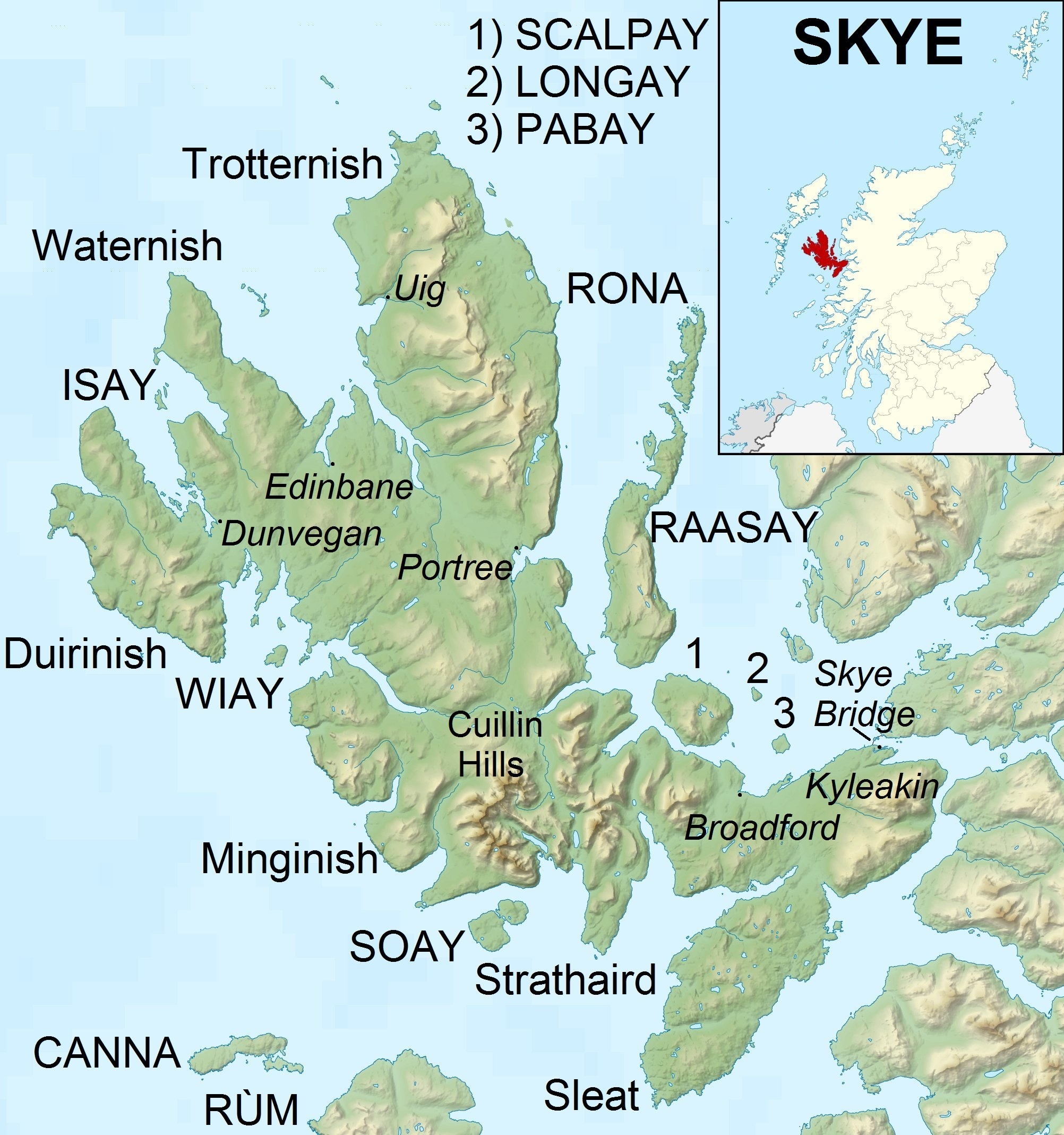
Skye Landsat
The Isle of Skye, or simply Skye (; gd, An t-Eilean Sgitheanach or ; sco, Isle o Skye), is the largest and northernmost of the major islands in the Inner Hebrides of Scotland. The island's peninsulas radiate from a mountainous hub dominated by the Cuillin, the rocky slopes of which provide some of the most dramatic mountain scenery in the country. Slesser (1981) p. 19. Although has been suggested to describe a winged shape, no definitive agreement exists as to the name's origins. The island has been occupied since the Mesolithic period, and over its history has been occupied at various times by Celtic tribes including the Picts and the Gaels, Scandinavian Vikings, and most notably the powerful integrated Norse-Gaels clans of MacLeod and MacDonald. The island was considered to be under Norwegian suzerainty until the 1266 Treaty of Perth, which transferred control over to Scotland. The 18th-century Jacobite risings led to the breaking-up of the clan system and later clearanc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sound (geography)
In geography, a sound is a smaller body of water typically connected to a larger sea or ocean. There is little consistency in the use of "sound" in English-language place names. It can refer to an inlet, deeper than a bight and wider than a fjord, or a narrow sea or ocean channel between two bodies of land (similar to a strait), or it can refer to the lagoon located between a barrier island and the mainland. Overview A sound is often formed by the seas flooding a river valley. This produces a long inlet where the sloping valley hillsides descend to sea-level and continue beneath the water to form a sloping sea floor. The Marlborough Sounds in New Zealand are good examples of this type of formation. Sometimes a sound is produced by a glacier carving out a valley on a coast then receding, or the sea invading a glacier valley. The glacier produces a sound that often has steep, near vertical sides that extend deep underwater. The sea floor is often flat and deeper at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raasay
Raasay (; gd, Ratharsair) or the Isle of Raasay is an island between the Isle of Skye and the mainland of Scotland. It is separated from Skye by the Sound of Raasay and from Applecross by the Inner Sound. It is famous for being the birthplace of Gaelic poet Sorley MacLean, an important figure in the Scottish Renaissance. Traditionally the home of Clan MacSween, the island was ruled by the MacLeods from the 15th to the 19th century. Subsequently, a series of private landlords held title to the island, which is now largely in public ownership. Raasay House, which was visited by James Boswell and Samuel Johnson in 1773, is now a hotel, restaurant, bar and outdoor activity centre. Raasay means "Isle of the Roe Deer" and is home to an endemic subspecies of bank vole. The current Chief of the Island is Roderick John Macleod of Raasay. Geology and geography About north to south and east to west (at its widest), Raasay's terrain is varied. The highest point, at , is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skye
The Isle of Skye, or simply Skye (; gd, An t-Eilean Sgitheanach or ; sco, Isle o Skye), is the largest and northernmost of the major islands in the Inner Hebrides of Scotland. The island's peninsulas radiate from a mountainous hub dominated by the Cuillin, the rocky slopes of which provide some of the most dramatic mountain scenery in the country. Slesser (1981) p. 19. Although has been suggested to describe a winged shape, no definitive agreement exists as to the name's origins. The island has been occupied since the Mesolithic period, and over its history has been occupied at various times by Celtic tribes including the Picts and the Gaels, Scandinavian Vikings, and most notably the powerful integrated Norse-Gaels clans of MacLeod and MacDonald. The island was considered to be under Norwegian suzerainty until the 1266 Treaty of Perth, which transferred control over to Scotland. The 18th-century Jacobite risings led to the breaking-up of the clan system and later clearanc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isle Of Skye
The Isle of Skye, or simply Skye (; gd, An t-Eilean Sgitheanach or ; sco, Isle o Skye), is the largest and northernmost of the major islands in the Inner Hebrides of Scotland. The island's peninsulas radiate from a mountainous hub dominated by the Cuillin, the rocky slopes of which provide some of the most dramatic mountain scenery in the country. Slesser (1981) p. 19. Although has been suggested to describe a winged shape, no definitive agreement exists as to the name's origins. The island has been occupied since the Mesolithic period, and over its history has been occupied at various times by Celtic tribes including the Picts and the Gaels, Scandinavian Vikings, and most notably the powerful integrated Norse-Gaels clans of MacLeod and MacDonald. The island was considered to be under Norwegian suzerainty until the 1266 Treaty of Perth, which transferred control over to Scotland. The 18th-century Jacobite risings led to the breaking-up of the clan system and later cleara ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loch Kishorn
Loch Kishorn ( gd, Ciseòrn) is a sea loch in the north-west Highlands of Scotland. Kishorn is a collective name used to refer to a group of populated settlements located next to the loch. Topography Loch Kishorn is a northern branch of Loch Carron about wide and long, with a maximum recorded depth of around . It is fed by the river and the River Kishorn which flows from the north and enters through a small estuary. To the north and west of the loch is the Applecross peninsula; to the east is a headland that separates it from upper Loch Carron. The mouth of the loch is marked by the Garra Islands, the largest of which is Kishorn Island. There are several small settlements located in the vicinity of the loch: Sanachan, Tornapress, Courthill, Achintraid, Ardarroch and Rhunasoul. It is common to refer to these populated settlements collectively as Kishorn. Sanachan is a little inland at the head of the loch. It contains a small gift shop, "Patterns of Light", the award-winning ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mealt Waterfall
Loch Mealt is an inland fresh-water loch on the Isle of Skye in Scotland. It lies close to Ellishadder and south of Staffin, on the eastern side of the Trotternish peninsula. Geography This roughly square-shaped loch is about 1 km in length. It is located close to the sea and its eastern side comprises the spectacular tall sea-cliffs of Kilt Rock, made of dolerite rock strata in many different colours. ukclimbing.com. Retrieved 25 July 2010. Kilt Rock boasts a dramatic waterfall created from the outflow of Loch Mealt. Ecology There are a number of bird species in this roadside loch.Its waters are favoured by s. The Orkney charr (''< ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quiraing
The Quiraing ( gd, A' Chuith-Raing) is a landslip on the eastern face of , the northernmost summit of the Trotternish on the Isle of Skye, Scotland. The whole of the Trotternish Ridge escarpment was formed by a great series of landslips; the Quiraing is the only part of the slip still moving – the road at its base, near Flodigarry, requires repairs each year. Parts of the distinctive landscape have earned particular names. The Needle is a jagged landmark pinnacle, a remnant of landslipping. Northwest of it is The Table, a flat grassy area slipped down from the summit plateau, with vistas of the Torridon Hills and the mountains of Wester Ross. Southwest is the Prison, a pyramidal rocky peak which can look like a medieval keep when viewed from the right angle – the ascent of this is an airy scramble. The name Quiraing comes from Old Norse , which means 'Round Fold'. Within the fold is The Table, an elevated plateau hidden amongst the pillars. It is said that the fold was us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landforms Of The Inner Hebrides
A landform is a natural or anthropogenic land feature on the solid surface of the Earth or other planetary body. Landforms together make up a given terrain, and their arrangement in the landscape is known as topography. Landforms include hills, mountains, canyons, and valleys, as well as shoreline features such as bays, peninsulas, and seas, including submerged features such as mid-ocean ridges, volcanoes, and the great ocean basins. Physical characteristics Landforms are categorized by characteristic physical attributes such as elevation, slope, orientation, Stratum, stratification, rock exposure and soil type. Gross physical features or landforms include intuitive elements such as berms, mounds, hills, ridges, cliffs, valleys, rivers, peninsulas, volcanoes, and numerous other structural and size-scaled (e.g. ponds vs. lakes, hills vs. mountain A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sounds Of Scotland
This is a list of the Sounds of Scotland. These straits vary in size from substantial sea channels to the tiny Clachan Sound, which is only {{convert, 21.3, m, ft wide and spanned by the Clachan Bridge.Murray (1977) p. 121. There are numerous other stretches of open water around the Scottish coasts that could be classified as straits, but which are called by names other than "Sound". Shetland *Balta Sound on the island of Unst *Bluemull Sound between Unst and Yell * Colgrave Sound between Fetlar and Yell *Easter Sound between Vaila and Whitesness on the West Mainland *Sound of Papa between Papa Stour and West Mainland * Uyea Sound between Uyea and Unst *Vaila Sound separating Vaila from Linga and the bays of Walls *Wester Sound between Vaila and Burrastow on the West Mainland * Yell Sound between Yell and Mainland Shetland Orkney *Auskerry Sound between Stronsay and Auskerry *Burra Sound between Hoy and Graemsay *Clestrain Sound between Mainland Orkney and Graemsay *Eynhallow So ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |







.jpg)