|
Sonderkommando Rote Kapelle
Sonderkommando Rote Kapelle was a German special commission that was created by German High Command in November 1942, in response to the capture of two leading members of a Soviet espionage group that operated in Europe, that was called the Red Orchestra (German:Rote Kapelle) by the '' Abwehr''. The Sonderkommando Rote Kapelle was an internal counter-intelligence operation run by the ''Abwehr'' and the Gestapo. Consisting of a small independent Gestapo unit and led by SS-Obersturmbannführer Friedrich Panzinger and investigated by Karl Giering, its remit was to discover and arrest members of the Red Orchestra in Germany, Belgium, France, Netherlands, Switzerland and Italy during World War II. Archival history While some documents on the "Rote Kapelle Special Commission Commission" are available, others for example, from the Military Historical Archives in Prague and Moscow have not been examined. At the same time, none of the former Gestapo or Abwehr personnel made reports after ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Orchestra (espionage)
The Red Orchestra (german: Die Rote Kapelle, ), as it was known in Germany, was the name given by the Abwehr Section III.F to German resistance to Nazism, anti-Nazi resistance workers in August 1941. It primarily referred to a loose network of resistance groups, connected through personal contacts, uniting hundreds of opponents of the Nazi Germany, Nazi regime. These included groups of friends who held discussions that were centred on Harro Schulze-Boysen, Adam Kuckhoff and Arvid Harnack in Berlin, alongside many others. They printed and distributed prohibited leaflets, posters, and stickers, hoping to incite civil disobedience. They aided Jews and resistance to escape the regime, documented the atrocities of the Nazis, and transmitted military intelligence to the Allies. Contrary to legend, the Red Orchestra was neither directed by Soviet Union, Soviet communists nor under a single leadership. It was a network of groups and individuals, often operating independently. To date, ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walter Schellenberg
Walter Friedrich Schellenberg (16 January 1910 – 31 March 1952) was a German SS functionary during the Nazi era. He rose through the ranks of the SS, becoming one of the highest ranking men in the ''Sicherheitsdienst'' (SD) and eventually assumed the position as head of foreign intelligence for Nazi Germany following the abolition of the ''Abwehr'' in 1944. Career Schellenberg, born in Saarbrücken, Germany, was his parents' seventh child; his father was a piano manufacturer. Schellenberg moved with his family to Luxembourg when the French occupied (1920) the Saar Basin after the First World War and the Weimar Republic experienced an economic crisis in the early 1920s. Like many young intellectuals who later joined the ''Sicherheitsdienst'' (SD), Schellenberg was deeply affected by the economic woes which befell Germany in the wake of the First World War. Schellenberg returned to Germany to attend university, first at the University of Marburg and then, from 1929, at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
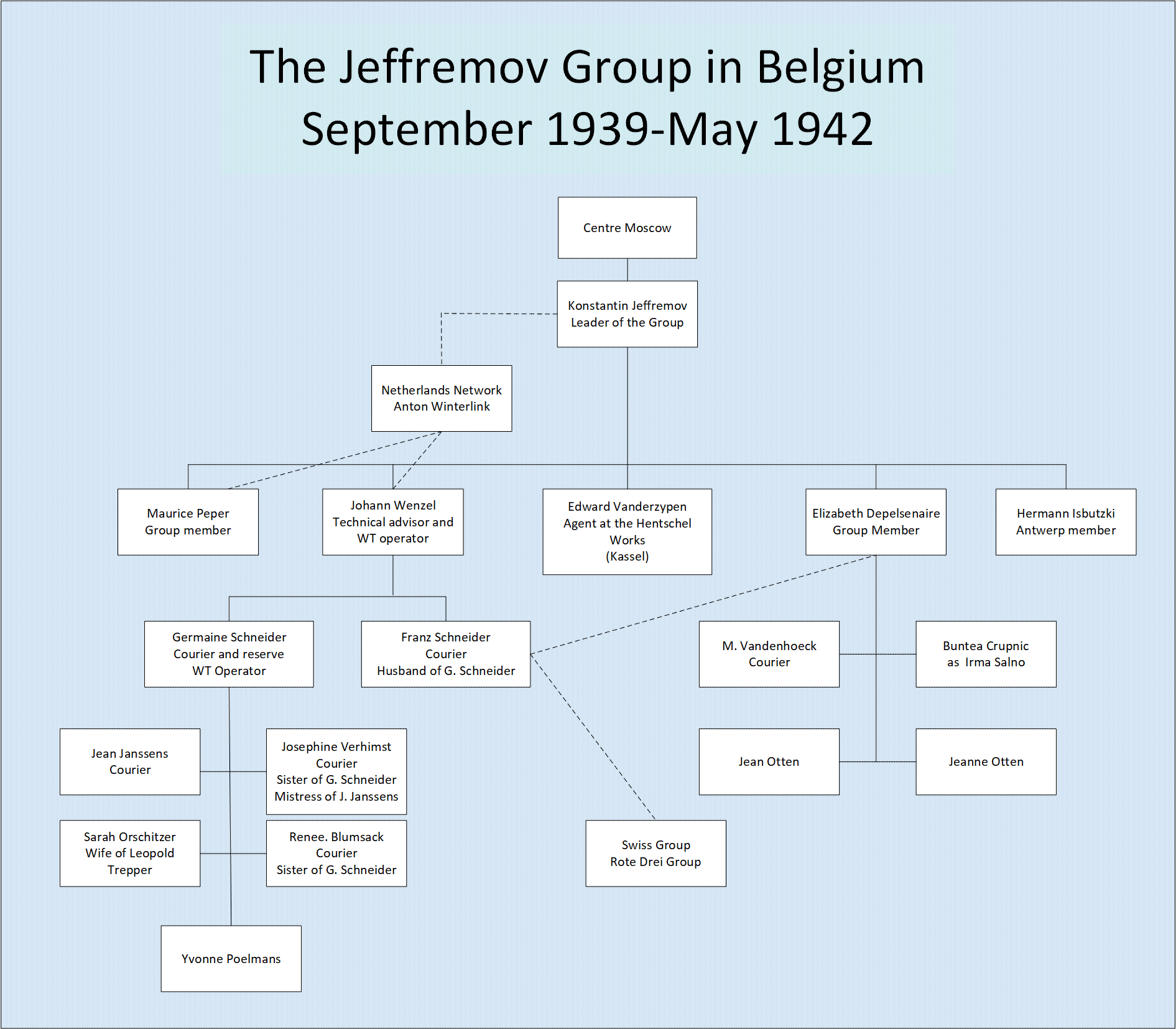
Germaine Schneider
Germaine Schneider (17 March 1903 - 12 November 1945) was a Belgian communist and Communist International (Comintern) agent. During the latter half of the 1920s, Schneider worked predominantly for the Communist Party of Belgium. During the interwar period and early World War II, Schneider was a core member of a Soviet espionage group. She worked as a principal courier for the groups that were associated with the Comintern agent, Henry Robinson in the late 1930s in France and later the Soviet GRU officer, Konstantin Jeffremov in Belgium and the Low Countries, in the early 1940s. These groups were later identified by the Abwehr under the moniker the Red Orchestra. Schneider used the aliases ''Clais'', ''Pauline'', ''Odette'', ''Papillon'' and ''Butterfly'' (''Schmetterling'') to disguise her identity. Life Schneider had been living and working in Brussels since 1920. In January 1925, Germaine Schneider ( Clais) married Swiss national Franz Schneider. The couple had a long ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Funkspiel
''Funkspiel'' (german: radio game) was a German term describing a technique of transmission of controlled information over a captured agent's radio so that the agent's parent service had no knowledge that the agent had turned and decided to work for the enemy. It was a standard technique in radio counterintelligence and was used throughout the world. Definition The German term ''Funkspiel'', ''Playbacks'', the British term or the American term, ''G-V Game'', was the transmission of controlled information over a captured agent's radio so that the agent's parent service had no knowledge that the agent had been turned and decided to work for the enemy. France Captured radio operators in France were forced to send false messages to British intelligence. That allowed Nazi intelligence to intercept Allied military information, convey disinformation to the enemy and actively fight resistance movements. By doing so, Nazi intelligence made the pretense of being the French resistance with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Konstantin Jeffremov
Konstantin Lukitsch Jeffremov (born 15 May 1910), also known as Konstantin Yeffremov, was a Soviet GRU intelligence officer, known as a ''scout'' in Soviet intelligence parlance, with the rank of captain. Jeffremov, an anti-Semite. was an expert in chemical warfare. Jeffremov used the aliases Pascal and Eric Jernstroem to disguise his identity in messages He had been working for Soviet intelligence since 1936. and the alias Bordo. He was the organizer of a Soviet espionage network in the Netherlands and the Low Countries In 1942, Jeffremov took over the running of a number of networks in Belgium and the Netherlands, that had been damaged in the months prior, after several members were arrested by the Abwehr. These networks was later given the moniker, the Red Orchestra ("Rote Kapelle") by the Abwehr. Jeffremov was arrested in July 1942 and agreed to work for the Abwehr in a ''Funkspiel'' operation, after being tortured. Life After completing seven years of schooling including ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abraham Rajchmann
Abraham Rajchmann (born 24 September 1902 in Dziurków, Poland) was a Jewish Polish career criminal and revolutionary militant, expert forger and engraver who worked for Soviet intelligence from 1934. Through his contact with Comintern official Léon Grossvogel, he was recruited into a Soviet espionage group initially in Belgium that was being run by Leopold Trepper, that would later be called the Red Orchestra ("Rote Kapelle") by the Abwehr, during the Nazi period. Rajchmann used a number of aliases to disguise his identity, including Adam Blanssi, Arthur Roussel, Katenmann, Fabrikant and Max. Communist Rajchmann was a member of the Communist International (Comintern) '' Pass-Apparat'', an industrial scale identity document forging operation, that was started in Berlin in 1919–1920 and eventually had offices all over Europe. For much of the 1930s, Rajchmann worked as an agent for Comintern. In 1937, Rajchmann was contacted by Léon Grossvogel, to request he obtain several ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Breendonk
Fort Breendonk ( nl, Fort van Breendonk, french: Fort de Breendonk) is a former military installation at Breendonk, near Mechelen, in Belgium which served as a Nazi prison camp (''Auffanglager'') during the German occupation of Belgium during World War II. Originally constructed between 1906 and 1913 as part of the second ring of the National Redoubt defending Antwerp, Fort Breendonk was used by the Belgian Army and was covered by a five-metre thick layer of soil for defense against artillery fire, a water-filled moat and measured . It was used in both World War I and World War II by which time it had become militarily obsolete. Fort Breendonk was requisitioned by the Schutzstaffel (SS) shortly after the Belgian surrender on 28 May 1940 and used as a prison camp for the detention of political prisoners, resistance members, and Jews. Although technically a prison rather than a concentration camp, it became infamous for the poor living conditions in which the prisoners were hou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horst Kopkow
Horst Kopkow (29 November 1910, Ortelsburg, East Prussia, Germany (now Szczytno, Poland) – 13 October 1996, Gelsenkirchen, Germany) was a Nazi German SS major who worked for German Security police and, after the war, was concealed by British intelligence to use his knowledge during the Cold War. Life During World War II, Kopkow served in German National Security Headquarters (Reichssicherheitshauptamt) in Berlin. He was responsible for counter-sabotage and counterespionage. In May 1942 SS general Reinhard Heydrich extended his responsibilities to include the capture of Soviet parachute agents in Czechoslovakia and Poland. After Heydrich's death following a British-directed Czech resistance attack, Kopkow's responsibilities were extended to include all allied parachute agents in the German Reich. During the war, Kopkow's agents captured several hundred Soviet and British agents. Kopkow was informed and consulted over every capture, although he never left his headquarters i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leopold Trepper
Leopold Zakharovich Trepper (23 February 1904 – 10 January 1982) was a Polish Communist and career Soviet agent of the Red Army Intelligence. With the code name Otto'','' Trepper had worked with the Red Army since 1930. He was also a resistance fighter and journalist. Trepper and Richard Sorge, a Soviet military intelligence officer, were the two main Soviet agents in Europe and were employed as ''roving agents'' to set up espionage networks throughout Europe and in Japan. While Sorge was a penetration agent, Trepper ran a series of clandestine cells for organising agents in Europe. Trepper used the latest technology at the time—small wireless radios—to communicate with Soviet intelligence. Although the Funkabwehr's monitoring of the radios transmission eventually led to the destruction of Treppers organisation, this sophisticated use of the technology-enabled the espionage organisation to behave as a network with the ability to achieve tactical surprise and deliver high- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sicherheitsdienst
' (, ''Security Service''), full title ' (Security Service of the ''Reichsführer-SS''), or SD, was the intelligence agency of the SS and the Nazi Party in Nazi Germany. Established in 1931, the SD was the first Nazi intelligence organization and the Gestapo (formed in 1933) was considered its sister organization through the integration of SS members and operational procedures. The SD was administered as an independent SS office between 1933 and 1939. That year, the SD was transferred over to the Reich Security Main Office (''Reichssicherheitshauptamt''; RSHA), as one of its seven departments. Its first director, Reinhard Heydrich, intended for the SD to bring every single individual within the Third Reich's reach under "continuous supervision". Following Germany's defeat in World War II, the tribunal at the Nuremberg trials officially declared that the SD was a criminal organisation, along with the rest of Heydrich's RSHA (including the Gestapo) both individually and as branch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilhelm Vauck
Wilhelm Vauck (born 8 October 1896 in Neustadt, Dresden; died 8 December 1968 in Bautzen) was a German mathematician, physicist and university lecturer in physics and electrical engineering. During World War II, Vauck was the director of the agents Referat within the Funkabwehr, the German Armies radio counter-intelligence organisation. As an anti-nazi, Vauck's work on the discovery of the Rote Kapelle anti-fascist resistance group during World War II, burdened him deeply until the end of his life. Life After World War I finished, Vauck undertook study of mathematics and physics at the Technical University of Dresden. In 1922, he passed the exam for a higher education office, and two years later, under supervision of Gerhard Kowalewski, Vauck was promoted to Dr. phil with a thesis titled ''A generalisation of Bolzano's continuous but non-differentiable function'' (german: Versuch einer Verallgemeinerung der stetigen nirgends differenzierbaren Funktion Bolzanos) which is within ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |